Symmetry Principles and Conservation Laws in Atomic and ...
Symmetry Principles and Conservation Laws in Atomic and ...
Symmetry Principles and Conservation Laws in Atomic and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
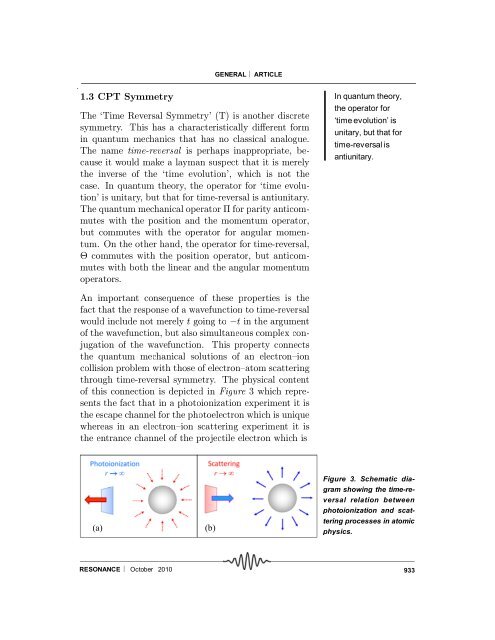
GENERAL ARTICLE1.3 CPT <strong>Symmetry</strong>The `Time Reversal <strong>Symmetry</strong>' (T) is another discretesymmetry. This has a characteristically di®erent form<strong>in</strong> quantum mechanics that has no classical analogue.The name time-reversal is perhaps <strong>in</strong>appropriate, becauseit would make a layman suspect that it is merelythe <strong>in</strong>verse of the `time evolution', which is not thecase. In quantum theory, the operator for `time evolution'is unitary, but that for time-reversal is antiunitary.The quantum mechanical operator ¦ for parity anticommuteswith the position <strong>and</strong> the momentum operator,but commutes with the operator for angular momentum.On the other h<strong>and</strong>, the operator for time-reversal,£ commutes with the position operator, but anticommuteswith both the l<strong>in</strong>ear <strong>and</strong> the angular momentumoperators.In quantum theory,the operator for‘time evolution’ isunitary, but that fortime-reversal isantiunitary.An important consequence of these properties is thefact that the response of a wavefunction to time-reversalwould <strong>in</strong>clude not merely t go<strong>in</strong>g to ¡t <strong>in</strong> the argumentof the wavefunction, but also simultaneous complex conjugationof the wavefunction. This property connectsthe quantum mechanical solutions of an electron{ioncollision problem with those of electron{atom scatter<strong>in</strong>gthrough time-reversal symmetry. The physical contentof this connection is depicted <strong>in</strong> Figure 3 which representsthe fact that <strong>in</strong> a photoionization experiment it isthe escape channel for the photoelectron which is uniquewhereas <strong>in</strong> an electron{ion scatter<strong>in</strong>g experiment it isthe entrance channel of the projectile electron which is(a)(b)Figure 3. Schematic diagramshow<strong>in</strong>g the time-reversalrelation betweenphotoionization <strong>and</strong> scatter<strong>in</strong>gprocesses <strong>in</strong> atomicphysics.RESONANCE October 2010933