You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
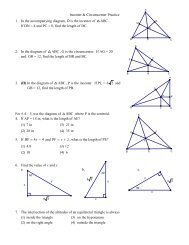
G~o~leIFy NAME: ...........................................................NOTES: <strong>Circles</strong> -Arcs & CentralAngles PERIOD: DATE:A circle has a total of 360°...Arcs & Central Angles of <strong>Circles</strong>To understand angle relationships related to circles, the_[bllowing terms are required:~e_.~ffr~AnN]e An angle with its vertex at the center of the circle.ArcAn unbroken part of a circle...any two points on a circle are the endpoints of thearc between them.Like an angle, arc’s have a corresponding degree measure.An arc measuring less than 180°.Minor arcs are named usm~ the arc s e adpomts w~th an arched hat ... ex: ABThe measure of a minor arc is equal to the measure of its central angle. (mAB)An arc measuring more than 180°, but less than 360°.Major arcs are named for the endpoints and a point between them.., ex: ACBThe measure of a major arc is equal to 360° minus the measure of its minor arc.An arc whose endpoints are on a diameter of the circle.A semicircle also uses three letter notation.A semicircle measures 180°.ddjacentArcs Two arcs in the same circle with exactly one point in common (an endpoint).Intercepted Are The arc formed by intersecting an angle with a circle (the arc "cut off" by an angle)Use Circle Q to complete the folhm~ing.1) Name two (2) central angles.2) Name four (4) minor arcs.3) Name four (4) major arcs.4) Name two (2) semicircles.5) Name two (2) minor arcs adjacent to AB.6) Name one (1) major arc adjacent to AB. (Why isAl)l~ NO’r an answer?)7) Name the arc intercepted by/_DQC.8) Ifm/_AQD = 60°, then mAD =9) IfmDBC = 220°, then mDC =and mABD =and mLDQC =