Section 1.5 – Solve Quadratic Equations - McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Section 1.5 – Solve Quadratic Equations - McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Section 1.5 – Solve Quadratic Equations - McGraw-Hill Ryerson
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
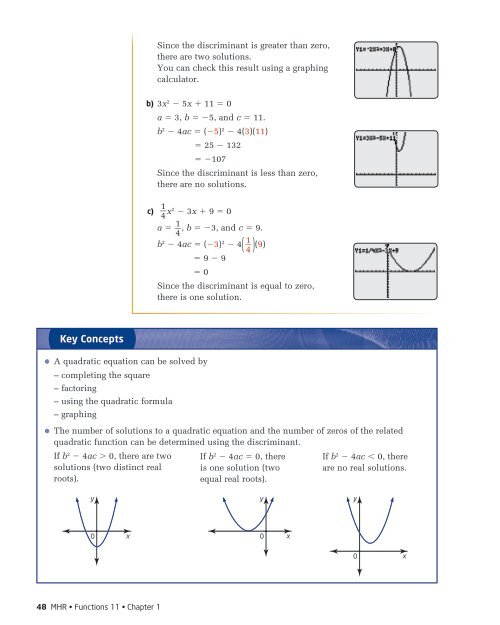
Since the discriminant is greater than zero,there are two solutions.You can check this result using a graphingcalculator.b) 3x 2 5x 11 5 0a 5 3, b 5 5, and c 5 11.b 2 4ac 5 (5) 2 4(3)(11)5 25 1325 107Since the discriminant is less than zero,there are no solutions.c) 1_4 x2 3x 9 5 0a 5 1_ , b 5 3, and c 5 9.4b 2 4ac 5 (3) 2 4 ( 1_4 ) (9)5 9 95 0Since the discriminant is equal to zero,there is one solution.Key ConceptsA quadratic equation can be solved by– completing the square– factoring– using the quadratic formula– graphingThe number of solutions to a quadratic equation and the number of zeros of the relatedquadratic function can be determined using the discriminant.If b 2 4ac 0, there are twosolutions (two distinct realroots).If b 2 4ac 5 0, thereis one solution (twoequal real roots).If b 2 4ac 0, thereare no real solutions.yyy0 x0 x0 x48 MHR • Functions 11 • Chapter 1