Definition of cross sections 1 - Moodle
Definition of cross sections 1 - Moodle
Definition of cross sections 1 - Moodle
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
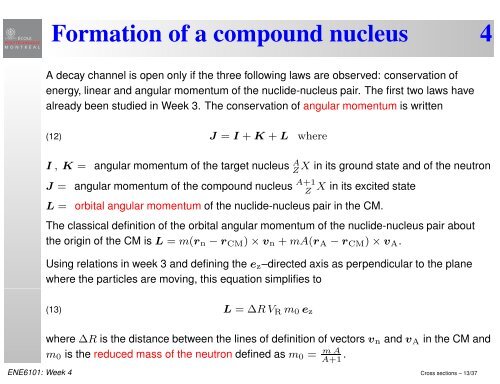
Formation <strong>of</strong> a compound nucleus 4A decay channel is open only if the three following laws are observed: conservation <strong>of</strong>energy, linear and angular momentum <strong>of</strong> the nuclide-nucleus pair. The first two laws havealready been studied in Week 3. The conservation <strong>of</strong> angular momentum is written(12)J = I +K +L whereI , K = angular momentum <strong>of</strong> the target nucleus A ZX in its ground state and <strong>of</strong> the neutronJ = angular momentum <strong>of</strong> the compound nucleus A+1ZX in its excited stateL = orbital angular momentum <strong>of</strong> the nuclide-nucleus pair in the CM.The classical definition <strong>of</strong> the orbital angular momentum <strong>of</strong> the nuclide-nucleus pair aboutthe origin <strong>of</strong> the CM is L = m(r n −r CM )×v n +mA(r A −r CM )×v A .Using relations in week 3 and defining the e z –directed axis as perpendicular to the planewhere the particles are moving, this equation simplifies to(13)L = ∆RV R m 0 e zwhere ∆R is the distance between the lines <strong>of</strong> definition <strong>of</strong> vectors v n and v A in the CM andm 0 is the reduced mass <strong>of</strong> the neutron defined as m 0 = mAA+1 .ENE6101: Week 4 Cross <strong>sections</strong> – 13/37