Combined Amino-Acid and Glucose Peritoneal Dialysis Solution for ...
Combined Amino-Acid and Glucose Peritoneal Dialysis Solution for ...
Combined Amino-Acid and Glucose Peritoneal Dialysis Solution for ...
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
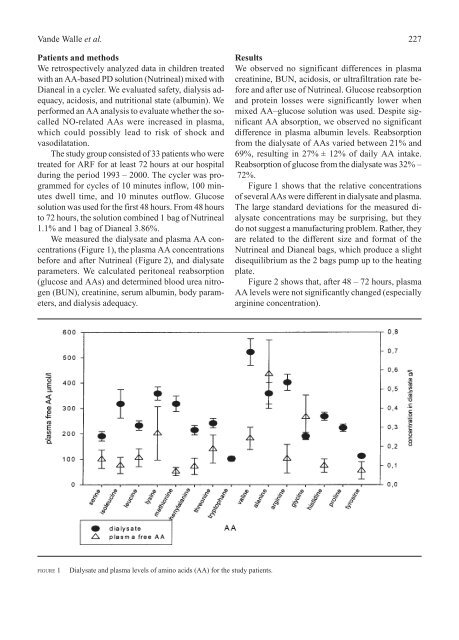
V<strong>and</strong>e Walle et al.Patients <strong>and</strong> methodsWe retrospectively analyzed data in children treatedwith an AA-based PD solution (Nutrineal) mixed withDianeal in a cycler. We evaluated safety, dialysis adequacy,acidosis, <strong>and</strong> nutritional state (albumin). Weper<strong>for</strong>med an AA analysis to evaluate whether the socalledNO-related AAs were increased in plasma,which could possibly lead to risk of shock <strong>and</strong>vasodilatation.The study group consisted of 33 patients who weretreated <strong>for</strong> ARF <strong>for</strong> at least 72 hours at our hospitalduring the period 1993 – 2000. The cycler was programmed<strong>for</strong> cycles of 10 minutes inflow, 100 minutesdwell time, <strong>and</strong> 10 minutes outflow. <strong>Glucose</strong>solution was used <strong>for</strong> the first 48 hours. From 48 hoursto 72 hours, the solution combined 1 bag of Nutrineal1.1% <strong>and</strong> 1 bag of Dianeal 3.86%.We measured the dialysate <strong>and</strong> plasma AA concentrations(Figure 1), the plasma AA concentrationsbe<strong>for</strong>e <strong>and</strong> after Nutrineal (Figure 2), <strong>and</strong> dialysateparameters. We calculated peritoneal reabsorption(glucose <strong>and</strong> AAs) <strong>and</strong> determined blood urea nitrogen(BUN), creatinine, serum albumin, body parameters,<strong>and</strong> dialysis adequacy.227ResultsWe observed no significant differences in plasmacreatinine, BUN, acidosis, or ultrafiltration rate be<strong>for</strong>e<strong>and</strong> after use of Nutrineal. <strong>Glucose</strong> reabsorption<strong>and</strong> protein losses were significantly lower whenmixed AA–glucose solution was used. Despite significantAA absorption, we observed no significantdifference in plasma albumin levels. Reabsorptionfrom the dialysate of AAs varied between 21% <strong>and</strong>69%, resulting in 27% ± 12% of daily AA intake.Reabsorption of glucose from the dialysate was 32% –72%.Figure 1 shows that the relative concentrationsof several AAs were different in dialysate <strong>and</strong> plasma.The large st<strong>and</strong>ard deviations <strong>for</strong> the measured dialysateconcentrations may be surprising, but theydo not suggest a manufacturing problem. Rather, theyare related to the different size <strong>and</strong> <strong>for</strong>mat of theNutrineal <strong>and</strong> Dianeal bags, which produce a slightdisequilibrium as the 2 bags pump up to the heatingplate.Figure 2 shows that, after 48 – 72 hours, plasmaAA levels were not significantly changed (especiallyarginine concentration).FIGURE 1Dialysate <strong>and</strong> plasma levels of amino acids (AA) <strong>for</strong> the study patients.