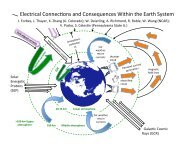
Solar Semidiurnal Tide in the Dusty Atmosphere of Mars
Solar Semidiurnal Tide in the Dusty Atmosphere of Mars
Solar Semidiurnal Tide in the Dusty Atmosphere of Mars
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
JULY 2006 FORBES AND MIYAHARA 1817<strong>in</strong>g tides <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmosphere <strong>of</strong> <strong>Mars</strong>. J. Geophys. Res., 107,5113, doi:10.1029/2001JE001582.——, X. Zhang, E. R. Talaat, and W. Ward, 2003: Nonmigrat<strong>in</strong>gdiurnal tides <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 108,1033, doi:10.1029/2002JA009262.Forget, F., and Coauthors, 1999: Improved general circulationmodels <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere from <strong>the</strong> surface to above80 km. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 24 155–24 176.Hamilton, K., 1982: The effect <strong>of</strong> solar tides on <strong>the</strong> general circulation<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 39, 481–485.Hunten, D. M., 1973: The escape <strong>of</strong> light gases from planetaryatmospheres. J. Atmos. Sci., 30, 1481–1494.——, 1974: Vertical transport <strong>in</strong> atmospheres. <strong>Atmosphere</strong>s <strong>of</strong>Earth and <strong>the</strong> Planets: Proceed<strong>in</strong>gs <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Summer AdvancedStudy Institute Held at <strong>the</strong> University <strong>of</strong> Liège, Belgium, July29–August 9, 1974, B. M. McCormac, Ed., Reidel, 59–72.Jakosky, B. M., and T. Z. Mart<strong>in</strong>, 1987: <strong>Mars</strong>: North-polar atmosphericwarm<strong>in</strong>g dur<strong>in</strong>g dust storms. Icarus, 72, 528–534.Joshi, M. M., B. N. Lawrence, and S. R. Lewis, 1995: Gravity wavedrag <strong>in</strong> three-dimensional atmospheric models <strong>of</strong> <strong>Mars</strong>. J.Geophys. Res., 100, 21 235–21 245.Keat<strong>in</strong>g, G. M., and Coauthors, 1998: The structure <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> upperatmosphere <strong>of</strong> <strong>Mars</strong>: In situ accelerometer measurementsfrom <strong>Mars</strong> Global Surveyor. Science, 279, 1672–1675.Krasitskii, O. P., 1978: A model for <strong>the</strong> diurnal variation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> composition<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere. Cosmic Res., 16, 350–356.Krasnopolsky, V. A., 1993: <strong>Solar</strong> cycle variations <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> hydrogenescape rate and <strong>the</strong> CO mix<strong>in</strong>g ratio on <strong>Mars</strong>. Icarus, 101,33–41.Leovy, C. B., 1982: Control <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> homopause level. Icarus, 50,311–321.——, and R. W. Zurek, 1979: Thermal tides and Martian duststorms: Direct evidence for coupl<strong>in</strong>g. J. Geophys. Res., 84,2956–2968.Lewis, S. R., and P. L. Read, 2003: Equatorial jets <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> dustyMartian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 5034, doi:10.1029/2002JE001933.L<strong>in</strong>dzen, R. S., 1970: Internal gravity waves <strong>in</strong> atmospheres withrealistic dissipation and temperature Part I. Ma<strong>the</strong>maticaldevelopment and propagation <strong>of</strong> waves <strong>in</strong>to <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmosphere.Geophys. Fluid Dyn., 1, 303–355.——, 1971: Internal gravity waves <strong>in</strong> atmospheres with realisticdissipation and temperature Part III. Daily variations <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong><strong>the</strong>rmosphere. Geophys. Fluid Dyn., 2, 89–121.——, 1981: Turbulence and stress ow<strong>in</strong>g to gravity wave and tidalbreakdown. J. Geophys. Res., 86, 9707–9714.——, and D. Blake, 1971: Internal gravity waves <strong>in</strong> atmosphereswith realistic dissipation and temperature Part II. Thermaltides excited below <strong>the</strong> mesopause. Geophys. Fluid Dyn., 2,31–61.——, and S.-S. Hong, 1974: Effects <strong>of</strong> mean w<strong>in</strong>ds and horizontaltemperature gradients on solar and lunar semidiurnal tides <strong>in</strong><strong>the</strong> atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 31, 1421–1446.——, and J. M. Forbes, 1983: Turbulence orig<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g from convectivelystable <strong>in</strong>ternal waves. J. Geophys. Res., 88, 6549–6553.Liu, J., M. I. Richardson, and R. J. Wilson, 2003: An assessment <strong>of</strong><strong>the</strong> global, seasonal, and <strong>in</strong>terannual spacecraft record <strong>of</strong>Martian climate <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmal <strong>in</strong>frared. J. Geophys. Res.,108, 5089, doi:10.1029/2002JE001921.Mart<strong>in</strong>, T. Z., and H. H. Kieffer, 1979: Thermal <strong>in</strong>frared properties<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere. 2. The 15 m band measurements.J. Geophys. Res., 84, 2843–2852.——, and M. I. Richardson, 1993: Newdust opacity mapp<strong>in</strong>g fromVik<strong>in</strong>g Infrared Thermal Mapper data. J. Geophys. Res., 98,10 941–10 949.Miyahara, S., and D.-H. Wu, 1989: Effects <strong>of</strong> solar tides on <strong>the</strong>zonal mean circulation <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> lower <strong>the</strong>rmosphere: Solsticcondition. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys., 51, 635–648.Newman, M., and C. Leovy, 1992: Ma<strong>in</strong>tenance <strong>of</strong> strong rotationalw<strong>in</strong>ds <strong>in</strong> Venus’ middle atmosphere by <strong>the</strong>rmal tides.Science, 257, 647–650.Pollack, J. B., D. S. Colburn, F. M. Flasar, R. Kahn, C. E. Carlston,and D. Pidek, 1979: Properties and effects <strong>of</strong> dust particlessuspended <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res.,84, 2929–2945.Santee, M., and D. Crisp, 1993: Thermal structure and dust load<strong>in</strong>g<strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere dur<strong>in</strong>g late sou<strong>the</strong>rn summer:Mar<strong>in</strong>er 9 revisited. J. Geophys. Res., 98, 3261–3279.Sch<strong>of</strong>ield, J. T., and F. W. Taylor, 1983: Measurements <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>mean, solar-fixed temperature and cloud structure <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong>middle atmosphere <strong>of</strong> Venus. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc.,109, 57–80.Smith, M. D., 2003: TES limb-geometry observations <strong>of</strong> aerosols.Extended Abstracts, Sixth Int. Conf. on <strong>Mars</strong>, Pasadena, CA,NASA, Abstract 3174.——, J. C. Pearl, B. J. Conrath, and P. R. Christensen, 2001: ThermalEmission Spectrometer results: Atmospheric <strong>the</strong>rmalstructure and aerosol distribution. J. Geophys. Res., 106,23 929–23 945.——, ——, ——, and ——, 2002: Thermal Emission Spectrometerobservations <strong>of</strong> a planet-encircl<strong>in</strong>g dust storm. Icarus, 157,250–263.Stewart, A. I. F., 1987: Revised time dependent model <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>Martian atmosphere for use <strong>in</strong> orbit lifetime and sustenancestudies. LASP-JPL Rep. NQ-802429, 51 pp.Théodore, B., E. Lellouch, E. Chassefière, and A. Hauchecorne,1993: Solstitial temperature <strong>in</strong>versions <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian middleatmosphere: Observational clues and 2-D model<strong>in</strong>g. Icarus,105, 512–528.Wilson, R. J., 1997: A general circulation model simulation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>Martian polar warm<strong>in</strong>g. Geophys. Res. Lett., 24, 123–127.——, 2000: Evidence for diurnal period Kelv<strong>in</strong> waves <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martianatmosphere from <strong>Mars</strong> Global Surveyor TES data. Geophys.Res. Lett., 27, 3889–3892.——, 2002: Evidence for nonmigrat<strong>in</strong>g <strong>the</strong>rmal tides <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Mars</strong>upper atmosphere from <strong>the</strong> <strong>Mars</strong> Global Surveyor AccelerometerExperiment. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, 1120,doi:10.1029/2001GL013975.——, and K. Hamilton, 1996: Comprehensive simulation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmaltides <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martian atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 53, 1290–1326.——, and M. I. Richardson, 2000: The Martian atmosphere dur<strong>in</strong>g<strong>the</strong> Vik<strong>in</strong>g mission, 1: Infrared measurements <strong>of</strong> atmospherictemperatures revisited. Icarus, 145, 555–579.Wi<strong>the</strong>rs, P., S. W. Bougher, and G. M. Keat<strong>in</strong>g, 2003: The effects<strong>of</strong> topographically-controlled <strong>the</strong>rmal tides <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> Martianupper atmosphere as seen by <strong>the</strong> MGS accelerometer. Icarus,164, 14–32.Zurek, R. W., 1982: Martian great dust storms: An update. Icarus,50, 288–310.——, 1986: Atmospheric tidal forc<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> zonal mean circulation:The Martian dusty atmosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 43, 652–670.——, and C. B. Leovy, 1981: Thermal tides <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> dusty Martianatmosphere: A verification <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>ory. Science, 213, 437–439.——, and R. M. Haberle, 1988: Zonally symmetric response toatmospheric tidal forc<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> dusty Martian atmosphere. J.Atmos. Sci., 45, 2469–2485.