SNDT Women's University SNDT Women's University 1, Nathibai
SNDT Women's University SNDT Women's University 1, Nathibai
SNDT Women's University SNDT Women's University 1, Nathibai
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
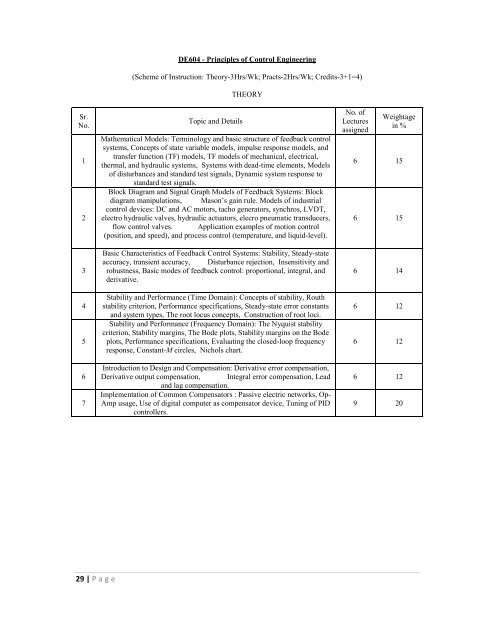
DE604 - Principles of Control Engineering(Scheme of Instruction: Theory-3Hrs/Wk; Practs-2Hrs/Wk; Credits-3+1=4)THEORYSr.No.1234567Topic and DetailsMathematical Models: Terminology and basic structure of feedback controlsystems, Concepts of state variable models, impulse response models, andtransfer function (TF) models, TF models of mechanical, electrical,thermal, and hydraulic systems, Systems with dead-time elements, Modelsof disturbances and standard test signals, Dynamic system response tostandard test signals.Block Diagram and Signal Graph Models of Feedback Systems: Blockdiagram manipulations, Mason’s gain rule. Models of industrialcontrol devices: DC and AC motors, tacho generators, synchros, LVDT,electro hydraulic valves, hydraulic actuators, elecro pneumatic transducers,flow control valves. Application examples of motion control(position, and speed), and process control (temperature, and liquid-level).Basic Characteristics of Feedback Control Systems: Stability, Steady-stateaccuracy, transient accuracy, Disturbance rejection, Insensitivity androbustness, Basic modes of feedback control: proportional, integral, andderivative.Stability and Performance (Time Domain): Concepts of stability, Routhstability criterion, Performance specifications, Steady-state error constantsand system types, The root locus concepts, Construction of root loci.Stability and Performance (Frequency Domain): The Nyquist stabilitycriterion, Stability margins, The Bode plots, Stability margins on the Bodeplots, Performance specifications, Evaluating the closed-loop frequencyresponse, Constant-M circles, Nichols chart.Introduction to Design and Compensation: Derivative error compensation,Derivative output compensation, Integral error compensation, Leadand lag compensation.Implementation of Common Compensators : Passive electric networks, Op-Amp usage, Use of digital computer as compensator device, Tuning of PIDcontrollers.No. ofLecturesassignedWeightagein %6 156 156 146 126 126 129 2029 | P a g e