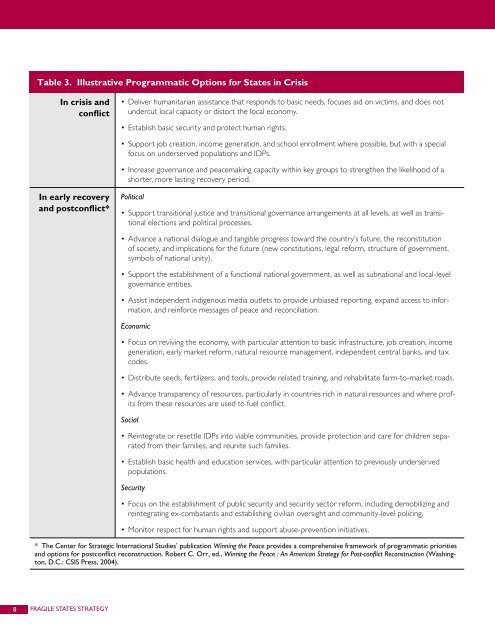
Table 3. Illustrative Programmatic Options for <strong>States</strong> in CrisisIn crisis andconflict• Deliver humanitarian assistance that responds to basic needs, focuses aid on victims, and does notundercut local capacity or distort the local economy.• Establish basic security and protect human rights.• Support job creation, income generation, and school enrollment where possible, but with a specialfocus on underserved populations and IDPs.• Increase governance and peacemaking capacity within key groups to strengthen the likelihood of ashorter, more lasting recovery period.In early recoveryand postconflict*Political• Support transitional justice and transitional governance arrangements at all levels, as well as transitionalelections and political processes.• Advance a national dialogue and tangible progress toward the country’s future, the reconstitutionof society, and implications for the future (new constitutions, legal reform, structure of government,symbols of national unity).• Support the establishment of a functional national government, as well as subnational and local-levelgovernance entities.• Assist independent indigenous media outlets to provide unbiased reporting, expand access to information,and reinforce messages of peace and reconciliation.Economic• Focus on reviving the economy, with particular attention to basic infrastructure, job creation, incomegeneration, early market reform, natural resource management, independent central banks, and taxcodes.• Distribute seeds, fertilizers, and tools, provide related training, and rehabilitate farm-to-market roads.• Advance transparency of resources, particularly in countries rich in natural resources and where profitsfrom these resources are used to fuel conflict.Social• Reintegrate or resettle IDPs into viable communities, provide protection and care for children separatedfrom their families, and reunite such families.• Establish basic health and education services, with particular attention to previously underservedpopulations.Security• Focus on the establishment of public security and security sector reform, including demobilizing andreintegrating ex-combatants and establishing civilian oversight and community-level policing.• Monitor respect for human rights and support abuse-prevention initiatives.* <strong>The</strong> Center for Strategic International Studies’ publication Winning the Peace provides a comprehensive framework of programmatic prioritiesand options for postconflict reconstruction. Robert C. Orr, ed., Winning the Peace : An American <strong>Strategy</strong> for Post-conflict Reconstruction (Washington,D.C.: CSIS Press, 2004).8 FRAGILE STATES STRATEGY
For lasting recovery to take hold, a number of keyfactors must be in place, which, in turn, have importantimplications for how to sequence assistance.unfair control of natural resources areoften an exacerbating factor.• In postconflict situations, the natureof the settlement is pivotal, forexample, whether there is a victor,stalemate, or formal peace accord.• <strong>The</strong> influence of neighboring countriesand other international actors(e.g., the level of international commitmentto speed recovery).• Potentially volatile recovery issues(e.g., treatment of past crimes andabuses and access to natural resourcewealth and commodities).For lasting recovery to take hold, anumber of key factors must be in place,which, in turn, have important implicationsfor how to sequence assistance.<strong>The</strong> central factor is physical securitythat allows for movement of people andcommerce. A sufficiently acceptableform of national government must alsobe in place, one that includes a workingrelationship between civilian andmilitary leadership. <strong>The</strong>re must also beagreement on a process that will resultin the formulation and ratification ofa basic law or constitution. A certainlevel of economic predictability is alsoimportant, including a central bankingauthority, government agencies ableto collect and distribute revenue, andmacroeconomic stability. Clear rightsto property, including land and othernatural resources, are integral to economicrecovery.A <strong>Fragile</strong> <strong>States</strong> BusinessModel: From Vision toActionTo bring this vision to reality andachieve greater strategic coherence andprecision in <strong>USAID</strong>’s response willrequire important operational changes.While <strong>USAID</strong> has substantial experiencein complex emergencies and postconflictresponse that will inform thesechanges, the Agency will need to expandits capabilities to engage with fragilestates and with other U.S. Governmentagencies and the donor community.At the core of this strategy is a newAgency business model for fragilestates response, which will be furtherelaborated in subsequent guidance. Itsmain features include better integratingand sharpening <strong>USAID</strong>’s response instrategic planning, reporting, budgeting,operational response, and administrativeprocedures; as well as exercising greaterleadership within the U.S. Governmentand broader donor community. A fewelements of the strategy are already underway.Ultimately, the business modelwill ensure that all Agency functions areappropriate to the realities and challengesof operating in fragile states.Integrate and Sharpen <strong>USAID</strong>ResponsesResponding effectively to fragile stateswill require concerted, coordinated,and sustained efforts by all parts ofthe Agency. This will necessitate integratinganalysis, strategy development,and implementation perspectives; andensuring that the broadest range offlexible instruments is made availableto <strong>USAID</strong> staff implementing programsin fragile states.As an important first step, the Agencyhas created a <strong>Fragile</strong> <strong>States</strong> Council,chaired by the Agency counselor andcomposed of senior managers from allbureaus. <strong>The</strong> council will play a facilitativerole, reviewing and monitoringthe strategic tracking system, providingrecommendations on the Agency’sresponse in fragile states, identifyingresources, and ensuring that implementationis timely and well coordinated.<strong>The</strong> council will also provide a criticalcoordination link to broader interagencyefforts on fragile states.For strategic planning, reporting, andbudgeting, some of the key steps requiredto increase flexibility include thefollowing:• Adopting strategic priorities consistentwith the situation in crisiscountries.• Encouraging shorter planninghorizons and adapting programs tochanging environments and targets ofopportunity. 77 While current <strong>USAID</strong> interim strategic guidancedoes not require specific planning timeframes,there remains a tendency to adopt longer-termtraditional development planning horizons.FRAGILE STATES STRATEGY 9