Section 1: Self-evaluation grid
Section 1: Self-evaluation grid
Section 1: Self-evaluation grid
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
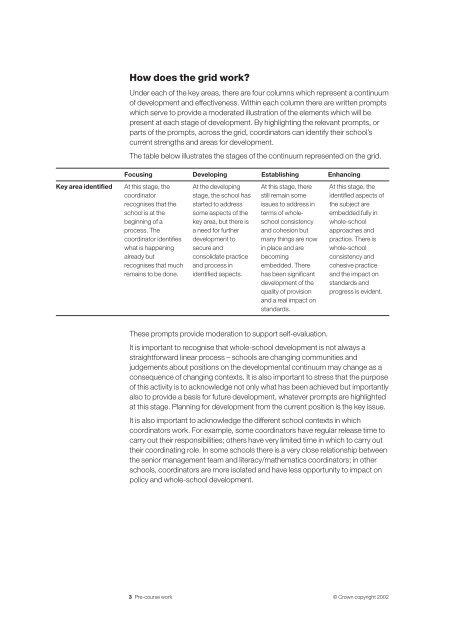
How does the <strong>grid</strong> work?Under each of the key areas, there are four columns which represent a continuumof development and effectiveness. Within each column there are written promptswhich serve to provide a moderated illustration of the elements which will bepresent at each stage of development. By highlighting the relevant prompts, orparts of the prompts, across the <strong>grid</strong>, coordinators can identify their school’scurrent strengths and areas for development.The table below illustrates the stages of the continuum represented on the <strong>grid</strong>.Focusing Developing Establishing EnhancingKey area identifiedAt this stage, thecoordinatorrecognises that theschool is at thebeginning of aprocess. Thecoordinator identifieswhat is happeningalready butrecognises that muchremains to be done.At the developingstage, the school hasstarted to addresssome aspects of thekey area, but there isa need for furtherdevelopment tosecure andconsolidate practiceand process inidentified aspects.At this stage, therestill remain someissues to address interms of wholeschoolconsistencyand cohesion butmany things are nowin place and arebecomingembedded. Therehas been significantdevelopment of thequality of provisionand a real impact onstandards.At this stage, theidentified aspects ofthe subject areembedded fully inwhole-schoolapproaches andpractice. There iswhole-schoolconsistency andcohesive practiceand the impact onstandards andprogress is evident.These prompts provide moderation to support self-<strong>evaluation</strong>.It is important to recognise that whole-school development is not always astraightforward linear process – schools are changing communities andjudgements about positions on the developmental continuum may change as aconsequence of changing contexts. It is also important to stress that the purposeof this activity is to acknowledge not only what has been achieved but importantlyalso to provide a basis for future development, whatever prompts are highlightedat this stage. Planning for development from the current position is the key issue.It is also important to acknowledge the different school contexts in whichcoordinators work. For example, some coordinators have regular release time tocarry out their responsibilities; others have very limited time in which to carry outtheir coordinating role. In some schools there is a very close relationship betweenthe senior management team and literacy/mathematics coordinators; in otherschools, coordinators are more isolated and have less opportunity to impact onpolicy and whole-school development.3 Pre-course work © Crown copyright 2002