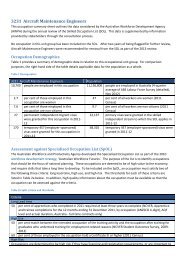
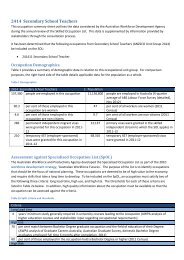
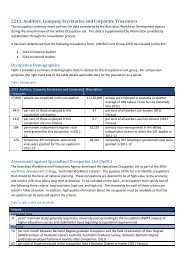
Human capital and productivity - AWPA
Human capital and productivity - AWPA
Human capital and productivity - AWPA
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
easoning is supported by Leuven, Lindahl, Oosterbeek <strong>and</strong> Webbink (2004) who present evidencethat early learning makes subsequent learning easier due to improved foundation skills. 38The importance of earlier education relative to later education is also supported by studies thatexamine learning subsequent to early childhood education. Psacharopoulous (1994), for example,found that primary education generally provided the highest return followed by secondary <strong>and</strong> tertiary.Likewise, Mason <strong>and</strong> van Ark (1994) considered that differences in the <strong>productivity</strong> of engineersbetween two countries were associated with the relative earlier availability of VET in schools.Other studies have found, however, that the relative returns from educational levels depend on aneconomy’s level of development. For example, Sianesi <strong>and</strong> Van Reenan (2003) <strong>and</strong> Matton (2006)suggest that tertiary education is most important for advanced economies. 39 The rational for this viewis the link between higher-level education <strong>and</strong> technology. The link between higher-level education<strong>and</strong> technology is discussed in further detail at Section 4. For present purposes, it is sufficient to notethat such findings appear supported by a significant body of literature that finds that the benefits oftechnological change may be biased towards higher skilled individuals.A summary of Sianesi <strong>and</strong> Van Reenan’s (2003) key findings on the importance of each educationallevel are set out in table 5 below.38 The study found that allowing disadvantaged children to start school one month earlier increases their LLNtest scores in grade 2 on average by about 0.06 of a st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation. No effect was found for nondisadvantagedstudents.39 Consistently, the study also suggests that primary <strong>and</strong> secondary skills appear related to growth in thepoorest <strong>and</strong> in intermediate developing countries, respectively.Australian Workforce <strong>and</strong> Productivity Agency | <strong>Human</strong> <strong>capital</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>productivity</strong> literature review 25