STUDENT WORKSHEET The Incredible Edible Cell - QUT
STUDENT WORKSHEET The Incredible Edible Cell - QUT
STUDENT WORKSHEET The Incredible Edible Cell - QUT
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
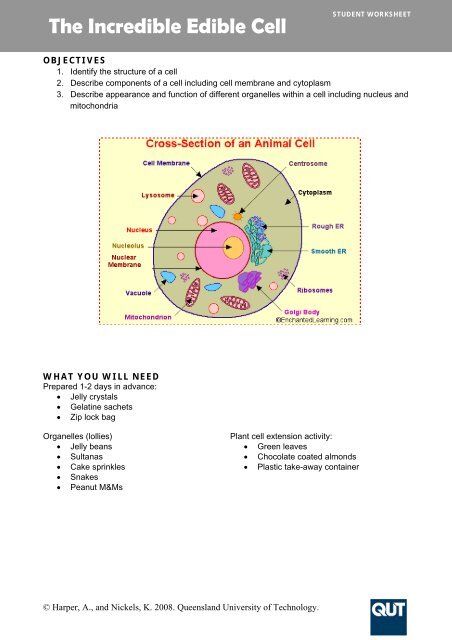
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Incredible</strong> <strong>Edible</strong> <strong>Cell</strong><strong>STUDENT</strong> <strong>WORKSHEET</strong>OBJECTIVES1. Identify the structure of a cell2. Describe components of a cell including cell membrane and cytoplasm3. Describe appearance and function of different organelles within a cell including nucleus andmitochondriaWHAT YOU WILL NEEDPrepared 1-2 days in advance:• Jelly crystals• Gelatine sachets• Zip lock bagOrganelles (lollies)• Jelly beans• Sultanas• Cake sprinkles• Snakes• Peanut M&MsPlant cell extension activity:• Green leaves• Chocolate coated almonds• Plastic take-away container© Harper, A., and Nickels, K. 2008. Queensland University of Technology.
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Incredible</strong> <strong>Edible</strong> <strong>Cell</strong><strong>STUDENT</strong> <strong>WORKSHEET</strong>WHAT TO DOYou have been provided with a cell membrane (zip lock bag) and cytoplasm (jelly), you need tomake your cell with the organelles (lollies) listed in the table below. Use the diagram and Table 1 tohelp.Once you have made your cell fill in Table 2: My <strong>Cell</strong>: structure and function. Use the Table 1 towork out what each organelle does. Write down which lollies you used to represent each organelleand how it relates to the structure/function of a cell.Table 2: My <strong>Cell</strong>: structure and function<strong>Cell</strong> part Function Material/lollies used How does this relate tostructure &/or function ofa cell?Plasma membrane <strong>Cell</strong> barrier Zip lock bag Serves as an external semipermeablecell barrier.Cytoplasm Jelly Holds organelles within thecellCytoplasmicorganelles<strong>The</strong> cell nucleusMitochondriaRibosomesEndoplasmicreticulumGolgi apparatusLysosomesVacuolesQUESTIONS1. What are the three differences between an animal and plant cell?2. Why are these differences necessary?3. How would you represent these differences?4. What is the purpose of the nucleus envelope?© Harper, A., and Nickels, K. 2008. Queensland University of Technology.
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Incredible</strong> <strong>Edible</strong> <strong>Cell</strong><strong>STUDENT</strong> <strong>WORKSHEET</strong>Table 1: <strong>Cell</strong> parts: structure and function<strong>Cell</strong> part Structure FunctionPlasma membrane(cell barrier)Cytoplasm(scaffolding)Cytoplasmic organelles(the metabolic machinery ofthe cell)<strong>The</strong> cell nucleus( the information centre)Mitochondria(the power generators)Ribosomes(protein production centres)Endoplasmic reticulum(macromolecule managers)Golgi apparatus(macromolecule managers)Lysosomes(cell destroyer)Membrane made of a double layer oflipids (phospholipids, cholesterol, etc).<strong>Cell</strong>ular region between the nuclear andplasma membranes; consists of fluidcytosol, containing dissolved solutesand organelles<strong>The</strong> cell nucleus is the largest organellefound in the cell. <strong>The</strong> nucleus isspherical in shape and separated fromthe cytoplasm by a double membranecalled the nuclear envelope. <strong>The</strong>nuclear envelope isolates and protects acell's DNA from various molecules thatcould accidentally damage its structureor interfere with its processing.Rodlike, double-membrane structures;inner membrane folded into projectionscalled cristae.Dense particles consisting of twosubunits, each composed of ribosomalRNA and protein; free or attached torough ERMembranous system of sacs andtubules.A stack of smooth membrane sacs andassociated vesicles close to thenucleus.Membranous sacs containing acidhydrolases.Serves as an external cell barrier; actsin transport of substances into or out ofthe cell.Holds organelles within the cell.It houses the cell's chromosomes, andis the place where almost all DNAreplication and RNA synthesis occur.Site of ATP synthesis; powerhouse ofthe cell<strong>The</strong> sites of protein synthesisTransport network for moleculestargeted for certain modifications andspecific destinations, as compared tomolecules that will float freely in thecytoplasm.Packages, modifies, and segregatesproteins for secretion from the cell,inclusion in lysosomes, andincorporation into the plasmamembrane.Sites of intracellular digestion.Vacuoles(food and waste storage)A vacuole is a membrane-bound sac. Inanimal cells, vacuoles are generallysmall.Vacuoles tend to be large in plant cells.<strong>The</strong> vacuole plays a role in intracellulardigestion and the release of cellularwaste products.In plant cells vacuoles play a roleturgor pressure. When a plant is wellwatered,water collects in cell vacuolesproducing rigidity in the plant. Withoutsufficient water, pressure in thevacuole is reduced and the plant wilts.© Harper, A., and Nickels, K. 2008. Queensland University of Technology.