5.74 Introductory Quantum Mechanics II - MIT OpenCourseWare
5.74 Introductory Quantum Mechanics II - MIT OpenCourseWare
5.74 Introductory Quantum Mechanics II - MIT OpenCourseWare
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
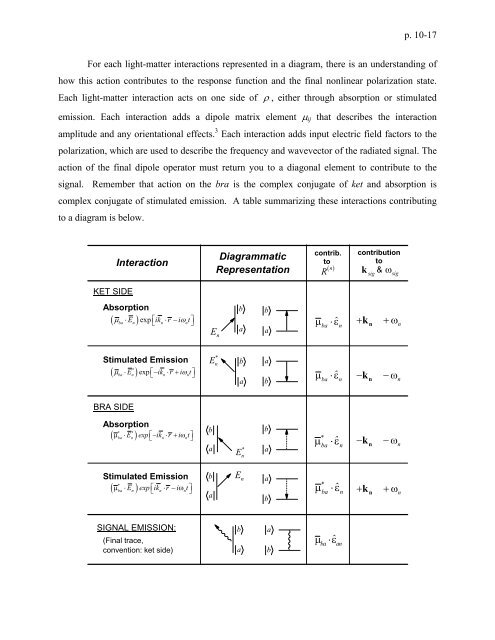
p. 10-17For each light-matter interactions represented in a diagram, there is an understanding ofhow this action contributes to the response function and the final nonlinear polarization state.Each light-matter interaction acts on one side of ρ , either through absorption or stimulatedemission. Each interaction adds a dipole matrix element μ ij that describes the interactionamplitude and any orientational effects. 3 Each interaction adds input electric field factors to thepolarization, which are used to describe the frequency and wavevector of the radiated signal. Theaction of the final dipole operator must return you to a diagonal element to contribute to thesignal. Remember that action on the bra is the complex conjugate of ket and absorption iscomplex conjugate of stimulated emission. A table summarizing these interactions contributingto a diagram is below.KET SIDEInteractioncontrib.DiagrammatictoRepresentation ( )R ncontributiontok sig&ωsigAbsorption( ) expμba⋅ En ⎣⎡ ikn⋅r− i ωnt⎤⎦Enbabaμ ⋅ε + kn+ ωnbaˆnStimulated Emission(* ) expμba⋅ En ⎣⎡ − ikn⋅ r + i ωnt⎦⎤*Enbaabbaˆnμ ⋅ε − kn− ωnBRA SIDEAbsorption* *( μba ⋅ En ) exp ⎣⎡ − ikn⋅ r + i ωnt⎦⎤ba*Enbaμ ⋅ε ˆ − kn− ωn*banStimulated Emission*( μba ⋅ En ) exp ⎣⎡ ikn⋅r −i ωnt⎦⎤baEnabˆ*μba⋅εn + kn+ ωnSIGNAL EMISSION:(Final trace,convention: ket side)baabbaˆanμ ⋅ε