HERE - Workplace Safety and Health Council
HERE - Workplace Safety and Health Council
HERE - Workplace Safety and Health Council
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
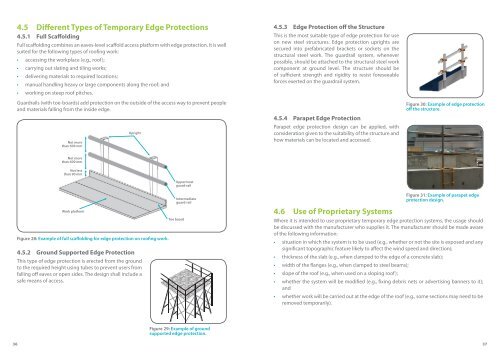
4.5 Different Types of Temporary Edge Protections4.5.1 Full ScaffoldingFull scaffolding combines an eaves-level scaffold access platform with edge protection. It is wellsuited for the following types of roofing work:• accessing the workplace (e.g., roof);• carrying out slating <strong>and</strong> tiling works;• delivering materials to required locations;• manual h<strong>and</strong>ling heavy or large components along the roof; <strong>and</strong>• working on steep roof pitches.Guardrails (with toe-boards) add protection on the outside of the access way to prevent people<strong>and</strong> materials falling from the inside edge.Not morethan 600 mmUpright4.5.3 Edge Protection off the StructureThis is the most suitable type of edge protection for useon new steel structures. Edge protection uprights aresecured into prefabricated brackets or sockets on thestructural steel work. The guardrail system, wheneverpossible, should be attached to the structural steel workcomponent at ground level. The structure should beof sufficient strength <strong>and</strong> rigidity to resist foreseeableforces exerted on the guardrail system.4.5.4 Parapet Edge ProtectionParapet edge protection design can be applied, withconsideration given to the suitability of the structure <strong>and</strong>how materials can be located <strong>and</strong> accessed.4-7Figure 30: Example of edge protectionoff the structure.Not morethan 600 mmNot lessthan 90 mmUppermostguard-railWork platformFigure 28: Example of full scaffolding for edge protection on roofing work.4.5.2 Ground Supported Edge ProtectionThis type of edge protection is erected from the groundto the required height using tubes to prevent users fromfalling off eaves or open sides. The design shall include asafe means of access.4-6Intermediateguard-railToe boardFigure 31: Example of parapet edgeprotection design.4.6 Use of Proprietary SystemsWhere it is intended to use proprietary temporary edge protection systems, the usage shouldbe discussed with the manufacturer who supplies it. The manufacturer should be made awareof the following information:• situation in which the system is to be used (e.g., whether or not the site is exposed <strong>and</strong> anysignificant topographic feature likely to affect the wind speed <strong>and</strong> direction);• thickness of the slab (e.g., when clamped to the edge of a concrete slab);• width of the flanges (e.g., when clamped to steel beams);• slope of the roof (e.g., when used on a sloping roof);• whether the system will be modified (e.g., fixing debris nets or advertising banners to it);<strong>and</strong>• whether work will be carried out at the edge of the roof (e.g., some sections may need to beremoved temporarily).Figure 29: Example of groundsupported edge protection.36 37