PCA9533 4-bit I C LED dimmer - E-LAB Computers
PCA9533 4-bit I C LED dimmer - E-LAB Computers
PCA9533 4-bit I C LED dimmer - E-LAB Computers
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
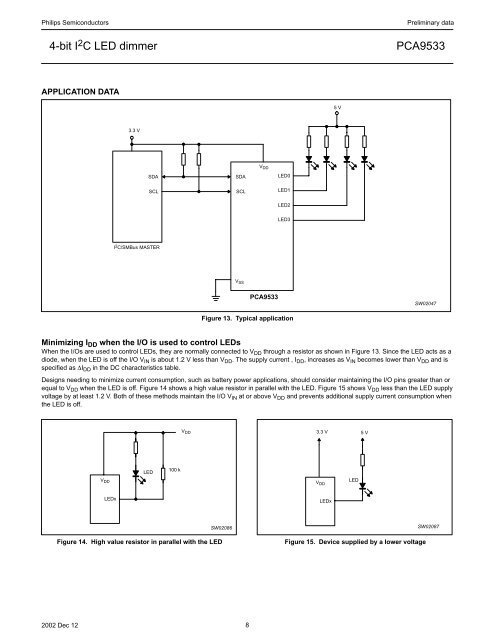
Philips Semiconductors4-<strong>bit</strong> I 2 C <strong>LED</strong> <strong>dimmer</strong>Preliminary data<strong>PCA9533</strong>APPLICATION DATA5 V3.3 VV DDSDASCLSDASCL<strong>LED</strong>0<strong>LED</strong>1<strong>LED</strong>2<strong>LED</strong>3I 2 C/SMBus MASTERV SS<strong>PCA9533</strong>SW02047Figure 13. Typical applicationMinimizing I DD when the I/O is used to control <strong>LED</strong>sWhen the I/Os are used to control <strong>LED</strong>s, they are normally connected to V DD through a resistor as shown in Figure 13. Since the <strong>LED</strong> acts as adiode, when the <strong>LED</strong> is off the I/O V IN is about 1.2 V less than V DD . The supply current , I DD , increases as V IN becomes lower than V DD and isspecified as ∆I DD in the DC characteristics table.Designs needing to minimize current consumption, such as battery power applications, should consider maintaining the I/O pins greater than orequal to V DD when the <strong>LED</strong> is off. Figure 14 shows a high value resistor in parallel with the <strong>LED</strong>. Figure 15 shows V DD less than the <strong>LED</strong> supplyvoltage by at least 1.2 V. Both of these methods maintain the I/O V IN at or above V DD and prevents additional supply current consumption whenthe <strong>LED</strong> is off.V DD3.3 V5 VV DD<strong>LED</strong>100 kV DD<strong>LED</strong><strong>LED</strong>x<strong>LED</strong>xSW02086Figure 14. High value resistor in parallel with the <strong>LED</strong>Figure 15. Device supplied by a lower voltageSW020872002 Dec 12 8