Introduction to Carboxylic Acids
Introduction to Carboxylic Acids
Introduction to Carboxylic Acids
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
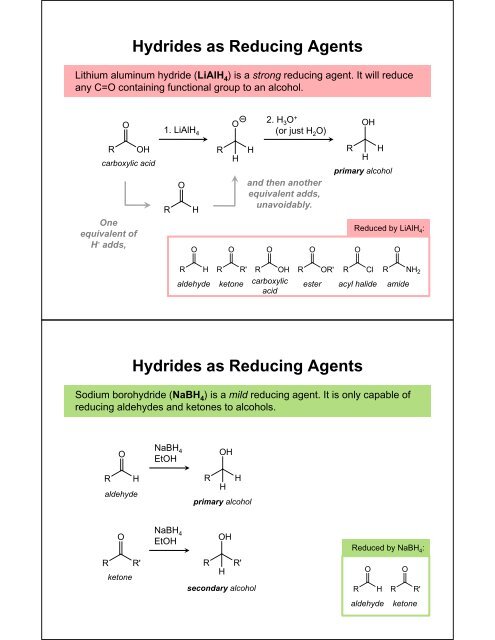
Hydrides as Reducing AgentsLithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH 4 ) is a strong reducing agent. It will reduceany C=O containing functional group <strong>to</strong> an alcohol.2. H 3 O +(or just H 2 O)1. LiAlH 4primary alcoholcarboxylic acidand then anotherequivalent adds,unavoidably.Oneequivalent ofH - adds,Reduced by LiAlH 4 :aldehydeke<strong>to</strong>necarboxylicacidesteracyl halideamideHydrides as Reducing AgentsSodium borohydride (NaBH 4 ) is a mild reducing agent. It is only capable ofreducing aldehydes and ke<strong>to</strong>nes <strong>to</strong> alcohols.NaBH 4EtOHaldehydeprimary alcoholNaBH 4EtOHReduced by NaBH 4 :ke<strong>to</strong>nesecondary alcoholaldehydeke<strong>to</strong>ne
Biological Cofac<strong>to</strong>rs as Redox AgentsCofac<strong>to</strong>r: A small-molecule “helper” that is required by an enzyme <strong>to</strong> catalyze areaction. Many vitamins are cofac<strong>to</strong>rs.NADH reduces byacting as an H - donorenzymeNADH(derived from niacin,vitamin B 3 )NAD + oxidizes byacting as an H - accep<strong>to</strong>rNAD +Hindered Reducing Agents S<strong>to</strong>p At Aldehyde(Chapter 21)OAlHH AlOROR'ester“DIBAL-H”R HaldehydeOROHcarboxylic acidLiHOAlOOOO(Chapter 21)RClacyl halideLiAlH(OtBu) 3R Haldehyde