Wampole C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE 11-2011.pmd - TechLab
Wampole C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE 11-2011.pmd - TechLab
Wampole C. DIFF QUIK CHEK COMPLETE 11-2011.pmd - TechLab
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
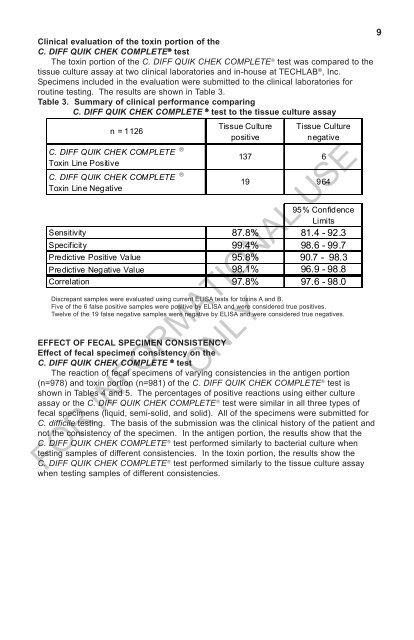
9Clinical evaluation of the toxin portion of theC. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® testThe toxin portion of the C. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® test was compared to thetissue culture assay at two clinical laboratories and in-house at TECHLAB ® , Inc.Specimens included in the evaluation were submitted to the clinical laboratories forroutine testing. The results are shown in Table 3.Table 3. Summary of clinical performance comparingC. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® test to the tissue culture assayn = <strong>11</strong>26C. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> Toxin Line PositiveC. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> Toxin Line NegativeTissue CulturepositiveTissue Culturenegative137 619 96495% ConfidenceLimitsSensitivity 87.8% 81.4 - 92.3Specificity 99.4% 98.6 - 99.7Predictive Positive Value 95.8% 90.7 - 98.3Predictive Negative Value 98.1% 96.9 - 98.8Correlation 97.8% 97.6 - 98.0Discrepant samples were evaluated using current ELISA tests for toxins A and B.Five of the 6 false positive samples were positive by ELISA and were considered true positives.Twelve of the 19 false negative samples were negative by ELISA and were considered true negatives.EFFECT OF FECAL SPECIMEN CONSISTENCYEffect of fecal specimen consistency on theC. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® testThe reaction of fecal specimens of varying consistencies in the antigen portion(n=978) and toxin portion (n=981) of the C. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® test isshown in Tables 4 and 5. The percentages of positive reactions using either cultureassay or the C. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® test were similar in all three types offecal specimens (liquid, semi-solid, and solid). All of the specimens were submitted forC. difficile testing. The basis of the submission was the clinical history of the patient andnot the consistency of the specimen. In the antigen portion, the results show that theC. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® test performed similarly to bacterial culture whentesting samples of different consistencies. In the toxin portion, the results show theC. <strong>DIFF</strong> <strong>QUIK</strong> <strong>CHEK</strong> <strong>COMPLETE</strong> ® test performed similarly to the tissue culture assaywhen testing samples of different consistencies.FOR INFORMATIONAL USEONLY