4-2 Translating Parabolas notes
4-2 Translating Parabolas notes
4-2 Translating Parabolas notes
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
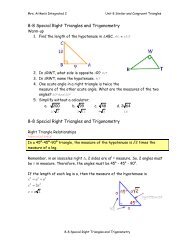
Integrated 24-2 <strong>Translating</strong> <strong>Parabolas</strong>Warm-up1. What is the coefficient of x 2 2in the function y = − 3x + 2x− 7 -32. The vertex of a parabola is at (2, -7). If the parabola is translated 5 units to the rightand 6 units down, what are the coordinates of the new vertex? (7, -13)3. Find the value of 2x 2 when x = -1. 24. Rewrite 2(x + 5) 2 + 6 as a sum of three terms. 2x 2 + 20x + 565. If y = 3( x− 1) + 1, find y when x= 0.y = -24-2 <strong>Translating</strong> <strong>Parabolas</strong>Width of a Parabola2The value of a in the function y = ax + bx+ c affects the width of the graph.*The greater the absolute value of a, the narrower the graph.Example 1Tell whether the graph of each function is wider than, narrower than, or the same shape asthe graph of y = x 2 .22A. y =−3x − 2x + 1B. y = 1 − x 22C. y = x + 4xSolutionA. The value of a is –3.Since |-3| > 1, the graph is narrower than the graph of y = x 2 .2B. In standard form, this function is y = − x + 1. The value of a is –1.Since |-1| = 1, this graph has the same shape as the graph y = x 2 .C. The value of a is 2/3.Since | 2/3 | < 1, this graph is wider than the graph of y = x 2 .Example 2Arrange these quadratic functions in order from the one with the narrowest graph to the onewith the widest graph.22A. y = 0.8x + 5 B. y=-0.2x -322C. y=-5x +4x D. y = 3x−16xSolutionA. a = 0.8 so 0.8 = 0.8 B. a = -0.2 so − 0.2 = 0.2C. a = -5 so − 5 = 5 D. a = -16 so − 16 = 163
Integrated 24-2 <strong>Translating</strong> <strong>Parabolas</strong>So, narrowest (largest a) to widest (smallest a):y x x22= 3 − 16 , y =− 5 x + 4x,y2= 0.8x+ 5 ,y = − −20.2 x 3Translations “slide”A translation changes only the position of a graph; it doesn’t change the size or shape of thegraph, or the direction that the graph opens.22Ex: The graph of y = 3( x −1) − 7 is a translation of the graph y = 3x.Translation of thegraph y = ax 2Equation of thetranslated graphh units right2y = a( x−h)h units left2y = a( x+h)k units up2y = ax + kk units down2y = ax − kSubtraction indicates a translation to the right.Addition indicates a translation to the left.Translations can also occur in two directions at the same time.*A graph can be translated to the right and up, to the right and down, to the leftand up, and to the left and down.Example 3Give the equation of the parabola that results when the graph ofdown and 3 units to the right.y4x2= is translated 5 unitsSolution2To translate the graph of y = 4x3 units to the right, replace x with (x-3).2y = 4( x − 3)22To translate the graph of y = 4( x − 3) down 5 units, subtract 5 from 4( x − 3) .2y = 4( x −3) − 52The equation of the parabola is y = 4( x −3) − 5Example 4Give the equation of the parabola that results when the graph ofto the left and 1 unit up.y4x2= is translated 7 unitsSolution:To translate the graph ofy = 4( x + 7 )To translate the graph ofy = + +24( x 7 ) 12yy2= 4x7 units to the left replace x with (x+7).2= 4( x + 7 ) up 1 unit, add 1 to24( x + 7 ) .
Integrated 24-2 <strong>Translating</strong> <strong>Parabolas</strong>Example 5Tell how to translate the graph ofA.B.C.D.2y =− 0.5( x+9)2y =− 0.5x+ 92y =−0.5( x− 2) + 12y =−0.5( x−12) − 3y0.5xSolution:A. Translate 9 units leftB. Translate 9 units upC. Translate 2 units right and 1 unit upD. Translate 12 units right and 3 units downExample 62=− in order to produce the graph of each function.1 ( 6) 2x 8Find the coordinates of the vertex of the graph of y =3+ +Solution2The graph of1y = ( x + 6) + 82is a translation of the graph y = x 6 units left and 833units up.2The vertex of the graph of y = 1 ( x + 6) + 8 is 6 units to the left and 8 units up from the31 2vertex of the graph of y = x , which is (0, 0).3(0 – 6, 0 + 8) (-6, 8)The coordinates of the vertex are (-6, 8)Side-note:To find the vertex: y = a(x – h) 2 + k is (h, K)y=a(x – h) 2 + k is called Vertex Form
Integrated 24-2 <strong>Translating</strong> <strong>Parabolas</strong>Table of Quadratic FormulasGeneral Quadratic functionStandard formVertex form, vertex (h, k)Vertex, in terms of a, b, and c2f ( x)= ax + bx+c2y = ax + bx+c2y = a( x− h)+ k2⎛ b b ⎞− , c −⎜2a4a⎟⎝⎠x-intercepts, in terms of a, b, and c⎛− ±⎜⎝−2a2b b 4ac⎞,0⎟⎠y-intercept ( 0,c )HomeworkRead pg. 193 - 196Pg. 196 #2-4, 6, 8, 9, 12-14, 16-19, 22-28 even