Maize-rice cropping systems in Bangladesh - Search CIMMYT ...
Maize-rice cropping systems in Bangladesh - Search CIMMYT ...
Maize-rice cropping systems in Bangladesh - Search CIMMYT ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
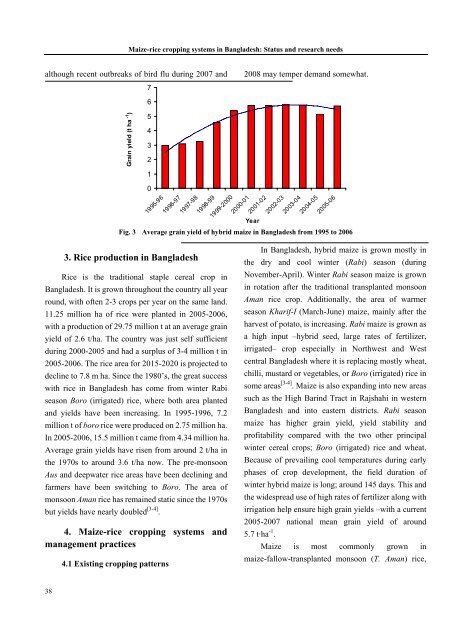
<strong>Maize</strong>-<strong>rice</strong> <strong>cropp<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>systems</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Bangladesh</strong>: Status and research needsalthough recent outbreaks of bird flu dur<strong>in</strong>g 2007 and2008 may temper demand somewhat.76Gra<strong>in</strong> yield (t ha -1 )5432101995-961996-971997-981998-991999-20002000-012001-02Year2002-032003-042004-052005-06Fig. 3 Average gra<strong>in</strong> yield of hybrid maize <strong>in</strong> <strong>Bangladesh</strong> from 1995 to 20063. Rice production <strong>in</strong> <strong>Bangladesh</strong>Rice is the traditional staple cereal crop <strong>in</strong><strong>Bangladesh</strong>. It is grown throughout the country all yearround, with often 2-3 crops per year on the same land.11.25 million ha of <strong>rice</strong> were planted <strong>in</strong> 2005-2006,with a production of 29.75 million t at an average gra<strong>in</strong>yield of 2.6 t/ha. The country was just self sufficientdur<strong>in</strong>g 2000-2005 and had a surplus of 3-4 million t <strong>in</strong>2005-2006. The <strong>rice</strong> area for 2015-2020 is projected todecl<strong>in</strong>e to 7.8 m ha. S<strong>in</strong>ce the 1980’s, the great successwith <strong>rice</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Bangladesh</strong> has come from w<strong>in</strong>ter Rabiseason Boro (irrigated) <strong>rice</strong>, where both area plantedand yields have been <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g. In 1995-1996, 7.2million t of boro <strong>rice</strong> were produced on 2.75 million ha.In 2005-2006, 15.5 million t came from 4.34 million ha.Average gra<strong>in</strong> yields have risen from around 2 t/ha <strong>in</strong>the 1970s to around 3.6 t/ha now. The pre-monsoonAus and deepwater <strong>rice</strong> areas have been decl<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g andfarmers have been switch<strong>in</strong>g to Boro. The area ofmonsoon Aman <strong>rice</strong> has rema<strong>in</strong>ed static s<strong>in</strong>ce the 1970sbut yields have nearly doubled [3-4] .4. <strong>Maize</strong>-<strong>rice</strong> <strong>cropp<strong>in</strong>g</strong> <strong>systems</strong> andmanagement practices4.1 Exist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>cropp<strong>in</strong>g</strong> patternsIn <strong>Bangladesh</strong>, hybrid maize is grown mostly <strong>in</strong>the dry and cool w<strong>in</strong>ter (Rabi) season (dur<strong>in</strong>gNovember-April). W<strong>in</strong>ter Rabi season maize is grown<strong>in</strong> rotation after the traditional transplanted monsoonAman <strong>rice</strong> crop. Additionally, the area of warmerseason Kharif-I (March-June) maize, ma<strong>in</strong>ly after theharvest of potato, is <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g. Rabi maize is grown asa high <strong>in</strong>put –hybrid seed, large rates of fertilizer,irrigated– crop especially <strong>in</strong> Northwest and Westcentral <strong>Bangladesh</strong> where it is replac<strong>in</strong>g mostly wheat,chilli, mustard or vegetables, or Boro (irrigated) <strong>rice</strong> <strong>in</strong>some areas [3-4] . <strong>Maize</strong> is also expand<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to new areassuch as the High Bar<strong>in</strong>d Tract <strong>in</strong> Rajshahi <strong>in</strong> western<strong>Bangladesh</strong> and <strong>in</strong>to eastern districts. Rabi seasonmaize has higher gra<strong>in</strong> yield, yield stability andprofitability compared with the two other pr<strong>in</strong>cipalw<strong>in</strong>ter cereal crops; Boro (irrigated) <strong>rice</strong> and wheat.Because of prevail<strong>in</strong>g cool temperatures dur<strong>in</strong>g earlyphases of crop development, the field duration ofw<strong>in</strong>ter hybrid maize is long; around 145 days. This andthe widespread use of high rates of fertilizer along withirrigation help ensure high gra<strong>in</strong> yields –with a current2005-2007 national mean gra<strong>in</strong> yield of around5.7 t·ha -1 .<strong>Maize</strong> is most commonly grown <strong>in</strong>maize-fallow-transplanted monsoon (T. Aman) <strong>rice</strong>,38