- Page 1 and 2:
AMSCO’SGEOMETRYAnn Xavier Gantert
- Page 3 and 4:
PREFACE✔✔✔✔✔✔Geometry i
- Page 5:
CONTENTSChapter 1ESSENTIALS OF GEOM
- Page 8 and 9:
viiiCONTENTSReview Exercises 323Cum
- Page 10 and 11:
xCONTENTS14-3 Five Fundamental Loci
- Page 12 and 13:
2 Essentials of Geometry1-1 UNDEFIN
- Page 14 and 15:
4 Essentials of GeometryThe number
- Page 16 and 17:
6 Essentials of GeometryEXAMPLE 1In
- Page 18 and 19:
8 Essentials of GeometryRecall that
- Page 20 and 21:
10 Essentials of GeometryEXAMPLE 1O
- Page 22 and 23:
12 Essentials of GeometryOn the num
- Page 24 and 25:
14 Essentials of Geometry7. A, B, C
- Page 26 and 27:
16 Essentials of Geometry1. By a ca
- Page 28 and 29:
18 Essentials of GeometrySolutiona.
- Page 30 and 31:
20 Essentials of GeometryBisector o
- Page 32 and 33:
22 Essentials of GeometryIn 11-13,
- Page 34 and 35:
24 Essentials of GeometryIncluded S
- Page 36 and 37:
26 Essentials of GeometryRight Tria
- Page 38 and 39:
28 Essentials of GeometryIn 5 and 6
- Page 40 and 41:
30 Essentials of GeometryPR S TProp
- Page 42 and 43:
32 Essentials of Geometry12. In iso
- Page 44 and 45:
CHAPTER2CHAPTERTABLE OF CONTENTS2-1
- Page 46 and 47:
36 LogicSome sentences are true for
- Page 48 and 49:
38 LogicNegationsIn the study of lo
- Page 50 and 51:
40 Logic2. a. Give an example of a
- Page 52 and 53:
42 Logic2-2 CONJUNCTIONSWe have ide
- Page 54 and 55:
44 LogicA compound sentence may con
- Page 56 and 57:
46 LogicEXAMPLE 4Three sentences ar
- Page 58 and 59:
48 Logic31. I have the hiccups and
- Page 60 and 61:
50 LogicAnswers(1) k ∨ q a. Every
- Page 62 and 63:
52 Logic8. A gram is a measure of l
- Page 64 and 65:
54 LogicParts of a ConditionalThe p
- Page 66 and 67:
56 Logic2. “In order to succeed,
- Page 68 and 69:
58 LogicExercisesWriting About Math
- Page 70 and 71:
60 Logic42. The conditional p → q
- Page 72 and 73:
62 Logicp: Angle A and B are congru
- Page 74 and 75:
64 LogicOn Friday, p is true and q
- Page 76 and 77:
66 LogicConditional If Jessica like
- Page 78 and 79:
68 LogicIn 7-10: a. Write the inver
- Page 80 and 81:
70 LogicRecall that a conjunction i
- Page 82 and 83:
72 LogicEXAMPLE 2The statement “I
- Page 84 and 85:
74 LogicApplying Skills17. Let p re
- Page 86 and 87:
76 LogicThe Law of Disjunctive Infe
- Page 88 and 89:
78 Logic(1) Eliminate the second ro
- Page 90 and 91:
80 Logic17. If 2b 6 14, then 2b
- Page 92 and 93:
82 Logicglass” is also true. Appl
- Page 94 and 95:
84 Logic7. When p → q and p ∧ q
- Page 96 and 97:
86 Logic•A hypothesis, also calle
- Page 98 and 99:
88 Logic8. July is a winter month i
- Page 100 and 101:
90 LogicExploration1. A tautology i
- Page 102 and 103:
92 Logic11. The first two sentences
- Page 104 and 105:
94 Proving Statements in Geometry3-
- Page 106 and 107:
96 Proving Statements in GeometryDe
- Page 108 and 109:
98 Proving Statements in GeometryBe
- Page 110 and 111:
100 Proving Statements in Geometry1
- Page 112 and 113:
102 Proving Statements in GeometryE
- Page 114 and 115:
104 Proving Statements in GeometryA
- Page 116 and 117:
106 Proving Statements in GeometryA
- Page 118 and 119:
108 Proving Statements in GeometryC
- Page 120 and 121:
110 Proving Statements in GeometryS
- Page 122 and 123:
112 Proving Statements in GeometryE
- Page 124 and 125:
114 Proving Statements in GeometryA
- Page 126 and 127:
116 Proving Statements in GeometryF
- Page 128 and 129:
118 Proving Statements in Geometry3
- Page 130 and 131:
120 Proving Statements in GeometryJ
- Page 132 and 133:
122 Proving Statements in GeometryE
- Page 134 and 135:
124 Proving Statements in Geometry3
- Page 136 and 137:
126 Proving Statements in GeometryE
- Page 138 and 139:
128 Proving Statements in GeometryC
- Page 140 and 141:
130 Proving Statements in Geometry1
- Page 142 and 143:
132 Proving Statements in Geometry8
- Page 144 and 145:
CHAPTER1344CHAPTERTABLE OF CONTENTS
- Page 146 and 147:
136 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 148 and 149:
138 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 150 and 151:
140 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 152 and 153:
142 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 154 and 155:
144 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 156 and 157:
146 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 158 and 159:
148 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 160 and 161:
150 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 162 and 163:
152 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 164 and 165:
154 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 166 and 167:
156 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 168 and 169:
158 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 170 and 171:
160 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 172 and 173:
162 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 174 and 175:
164 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 176 and 177:
166 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 178 and 179:
168 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 180 and 181:
170 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 182 and 183:
172 Congruence of Line Segments,Ang
- Page 184 and 185:
CHAPTER1745CHAPTERTABLE OF CONTENTS
- Page 186 and 187:
176 Congruence Based on TrianglesAC
- Page 188 and 189:
178 Congruence Based on Triangles6.
- Page 190 and 191:
180 Congruence Based on TrianglesDe
- Page 192 and 193:
182 Congruence Based on TrianglesTh
- Page 194 and 195:
184 Congruence Based on Triangles(C
- Page 196 and 197:
186 Congruence Based on Triangles5-
- Page 198 and 199:
188 Congruence Based on Triangles7.
- Page 200 and 201:
190 Congruence Based on Triangles2.
- Page 202 and 203:
192 Congruence Based on TrianglesTh
- Page 204 and 205:
194 Congruence Based on TrianglesTh
- Page 206 and 207:
196 Congruence Based on TrianglesAp
- Page 208 and 209:
198 Congruence Based on TrianglesCo
- Page 210 and 211:
200 Congruence Based on TrianglesCo
- Page 212 and 213:
202 Congruence Based on TrianglesEX
- Page 214 and 215:
204 Congruence Based on TrianglesCH
- Page 216 and 217:
206 Congruence Based on TrianglesCU
- Page 218 and 219:
208 Congruence Based on Triangles13
- Page 220 and 221:
210 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 222 and 223:
212 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 224 and 225:
214 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 226 and 227:
216 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 228 and 229:
218 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 230 and 231:
220 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 232 and 233:
222 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 234 and 235:
224 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 236 and 237:
226 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 238 and 239:
228 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 240 and 241:
230 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 242 and 243:
232 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 244 and 245:
234 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 246 and 247:
236 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 248 and 249:
238 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 250 and 251:
240 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 252 and 253:
242 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 254 and 255:
244 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 256 and 257:
246 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 258 and 259:
248 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 260 and 261:
250 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 262 and 263:
252 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 264 and 265:
254 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 266 and 267:
256 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 268 and 269:
258 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 270 and 271:
260 Transformations and the Coordin
- Page 272 and 273:
CHAPTER7CHAPTERTABLE OF CONTENTS7-1
- Page 274 and 275:
264 Geometric InequalitiesThis corr
- Page 276 and 277:
266 Geometric InequalitiesExercises
- Page 278 and 279:
268 Geometric InequalitiesSubtracti
- Page 280 and 281:
270 Geometric Inequalities7-3 INEQU
- Page 282 and 283:
272 Geometric InequalitiesExercises
- Page 284 and 285:
274 Geometric InequalitiesEXAMPLE 2
- Page 286 and 287:
276 Geometric InequalitiesHands-On
- Page 288 and 289:
278 Geometric InequalitiesABMCProof
- Page 290 and 291:
280 Geometric InequalitiesExercises
- Page 292 and 293:
282 Geometric InequalitiesGivenTo p
- Page 294 and 295:
284 Geometric InequalitiesCIf the m
- Page 296 and 297:
286 Geometric Inequalities7.3 If th
- Page 298 and 299:
288 Geometric InequalitiesCUMULATIV
- Page 300 and 301:
CHAPTER2908CHAPTERTABLE OF CONTENTS
- Page 302:
292 Slopes and Equations of LinesAl
- Page 305 and 306:
Developing SkillsIn 3-11, in each c
- Page 307 and 308:
y 2 bx 2 a 5 m The Equation of a Li
- Page 309 and 310:
5 ? 3 2(2) 1 1 5 ? 2(0) 1 7 5 ? 2
- Page 311 and 312:
zontal line, they all have the same
- Page 313 and 314:
Midpoint of a Line Segment 303Proof
- Page 315 and 316:
Midpoint of a Line Segment 305EXAMP
- Page 317 and 318:
The Slopes of Perpendicular Lines 3
- Page 319 and 320:
The Slopes of Perpendicular Lines 3
- Page 321 and 322:
Developing SkillsIn 3-12: a. Find t
- Page 323 and 324:
Coordinate Proof 3138-5 COORDINATE
- Page 325 and 326:
Coordinate Proof 315ProofThis is a
- Page 327 and 328:
Concurrence of the Altitudes of a T
- Page 329 and 330:
Concurrence of the Altitudes of a T
- Page 331 and 332:
Concurrence of the Altitudes of a T
- Page 333 and 334:
VOCABULARY8-1 Slope • x • y8-2
- Page 335 and 336:
Cumulative Review 325CUMULATIVE REV
- Page 337 and 338:
Cumulative Review 327Part IVAnswer
- Page 339 and 340:
Proving Lines Parallel 3299-1 PROVI
- Page 341 and 342:
Proving Lines Parallel 331In the di
- Page 343 and 344:
Proving Lines Parallel 333The proof
- Page 345 and 346:
Properties of Parallel Lines 3359-2
- Page 347 and 348:
Properties of Parallel Lines 337The
- Page 349 and 350:
gEJ. Therefore, AB g CD gbecause i
- Page 351 and 352:
c. Is the measure of an exterior an
- Page 353 and 354:
Parallel Lines in the Coordinate Pl
- Page 355 and 356:
Parallel Lines in the Coordinate Pl
- Page 357 and 358:
. Find the midpoints of two sides o
- Page 359 and 360:
The Sum of the Measures of the Angl
- Page 361 and 362:
The Sum of the Measures of the Angl
- Page 363 and 364:
Proving Triangles Congruent by Angl
- Page 365 and 366:
Proving Triangles Congruent by Angl
- Page 367 and 368:
The Converse of the Isosceles Trian
- Page 369 and 370:
The Converse of the Isosceles Trian
- Page 371 and 372:
In 3-6, in each case the degree mea
- Page 373 and 374:
(1) Since any line segment may beex
- Page 375 and 376:
Proving Right Triangles Congruent b
- Page 377 and 378:
Interior and Exterior Angles of Pol
- Page 379 and 380:
Interior and Exterior Angles of Pol
- Page 381 and 382:
Interior and Exterior Angles of Pol
- Page 383 and 384:
Chapter Summary 373CHAPTER SUMMARYD
- Page 385 and 386:
AB g In 1-5, CD gand these lines a
- Page 387 and 388:
2. The statement “If two angles f
- Page 389 and 390:
CHAPTERQUADRILATERALSEuclid’s fif
- Page 391 and 392:
The Parallelogram 381ADBCQuadrilate
- Page 393 and 394:
The Parallelogram 383DEFINITIONThe
- Page 395 and 396:
Proving That a Quadrilateral Is a P
- Page 397 and 398:
Proving That a Quadrilateral Is a P
- Page 399 and 400:
The Rectangle 38910-4 THE RECTANGLE
- Page 401 and 402:
The Rectangle 391EXAMPLE 1Given: AB
- Page 403 and 404:
The Rhombus 39316. The coordinates
- Page 405 and 406:
The Rhombus 395Theorem 10.15If a qu
- Page 407 and 408:
2. Concepta said that if the length
- Page 409 and 410:
The Square 39910-6 THE SQUAREDEFINI
- Page 411 and 412:
The Square 401EXAMPLE 2In square PQ
- Page 413 and 414:
The Trapezoid 403The Isosceles Trap
- Page 415 and 416:
The Trapezoid 405Proof We will show
- Page 417 and 418:
The Trapezoid 407The slopes of BC a
- Page 419 and 420:
18. Prove Theorem 10.23, “The len
- Page 421 and 422:
Areas of Polygons 4115. Find the ar
- Page 423 and 424:
Chapter Summary 413PostulateTheorem
- Page 425 and 426:
Review Exercises 41511. The diagona
- Page 427 and 428:
Cumulative Review 417CUMULATIVE REV
- Page 429 and 430:
CHAPTERTHEGEOMETRYOF THREEDIMENSION
- Page 431 and 432:
Points, Lines, and Planes 421Theore
- Page 433 and 434:
Perpendicular Lines and Planes 4231
- Page 435 and 436:
Perpendicular Lines and Planes 425G
- Page 437 and 438:
Perpendicular Lines and Planes 427l
- Page 439 and 440:
Perpendicular Lines and Planes 429G
- Page 441 and 442:
gPlanes p and q intersect in AB. In
- Page 443 and 444:
16. Prove that if two points are ea
- Page 445 and 446:
Parallel Lines and Planes 435Theore
- Page 447 and 448:
BF intersecting q at . Since p and
- Page 449 and 450:
ProofTwo lines perpendicular to the
- Page 451 and 452:
Since the bases are parallel, the c
- Page 453 and 454:
Surface Area of a Prism 443EXAMPLE
- Page 455 and 456: 10. A prism has bases that are trap
- Page 457 and 458: Volume of a Prism 447The other pris
- Page 459 and 460: Pyramids 44911-6 PYRAMIDSA pyramid
- Page 461 and 462: Pyramids 451For example, consider a
- Page 463 and 464: Cylinders 45314. Let F be the verte
- Page 465 and 466: Express this result as a rational a
- Page 467 and 468: Cones 457We can make a model of a r
- Page 469 and 470: 7. The volume of a cone is 127 cubi
- Page 471 and 472: Spheres 461Proof Statements Reasons
- Page 473 and 474: Spheres 463When we round to the nea
- Page 475 and 476: Chapter Summary 465• Perpendicula
- Page 477 and 478: Vocabulary 46711.14 The intersectio
- Page 479 and 480: Review Exercises 46914. A prism and
- Page 481 and 482: Cumulative Review 471b. Using the s
- Page 483 and 484: Cumulative Review 47314. Line segme
- Page 485 and 486: Ratio and Proportion 47512-1 RATIO
- Page 487 and 488: Ratio and Proportion 477ProofWe can
- Page 489 and 490: Ratio and Proportion 479EXAMPLE 3Th
- Page 491 and 492: Given ABC, D is the midpoint of AC,
- Page 493 and 494: Proportions Involving Line Segments
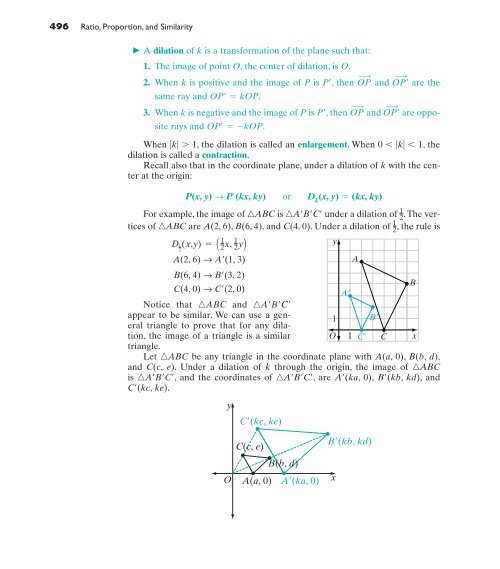
- Page 495 and 496: Proportions Involving Line Segments
- Page 497 and 498: If two polygons are similar, then t
- Page 499 and 500: Proving Triangles Similar 4899. Tri
- Page 501 and 502: Proving Triangles Similar 491We can
- Page 503 and 504: Proving Triangles Similar 493EXAMPL
- Page 505: Dilations 49511. If CA 48, DA 12,
- Page 509 and 510: EXAMPLE 2SolutionDilations 499Find
- Page 511 and 512: Dilations 50129. The vertices of oc
- Page 513 and 514: Proportional Relations Among Segmen
- Page 515 and 516: Proportional Relations Among Segmen
- Page 517 and 518: Concurrence of the Medians of a Tri
- Page 519 and 520: (2) Find the equation of AM g and t
- Page 521 and 522: Proportions in a Right Triangle 511
- Page 523 and 524: Proportions in a Right Triangle 513
- Page 525 and 526: Pythagorean Theorem 51512-9 PYTHAGO
- Page 527 and 528: Pythagorean Theorem 517EXAMPLE 2Whe
- Page 529 and 530: Pythagorean Theorem 519EXAMPLE 3In
- Page 531 and 532: The Distance Formula 52123. A young
- Page 533 and 534: The lengths of the sides of the qua
- Page 535 and 536: Developing SkillsIn 3-10, the coord
- Page 537 and 538: Chapter Summary 527CHAPTER SUMMARYD
- Page 539 and 540: Review Exercises 529FormulasIn the
- Page 541 and 542: 14. The length of a side of a rhomb
- Page 543 and 544: Cumulative Review 5334. The measure
- Page 545 and 546: CHAPTERGEOMETRYOF THECIRCLEEarly ge
- Page 547 and 548: Arcs and Angles 537In the diagram,
- Page 549 and 550: If (O > (Or and mCDX 5 mCrDr 60, t
- Page 551 and 552: Arcs and Angles 541b. mACX mAOC 75
- Page 553 and 554: Arcs and Chords 54313-2 ARCS AND CH
- Page 555 and 556: Arcs and Chords 545ProofFirst draw
- Page 557 and 558:
Arcs and Chords 547Since a diameter
- Page 559 and 560:
Arcs and Chords 549(5) Since AB CD
- Page 561 and 562:
Arcs and Chords 551EXAMPLE 3ProofPr
- Page 563 and 564:
Inscribed Angles and Their Measures
- Page 565 and 566:
. m/A 5 X 12 mBC c. m/C 5 180 2 (m/
- Page 567 and 568:
Inscribed Angles and Their Measures
- Page 569 and 570:
Tangents and Secants 559Theorem 13.
- Page 571 and 572:
ProofTangents and Secants 561We wil
- Page 573 and 574:
Tangents and Secants 563The proofs
- Page 575 and 576:
Developing SkillsIn 3 and 4, ABC is
- Page 577 and 578:
Hands-On ActivityConsider any regul
- Page 579 and 580:
Angles Formed by Tangents, Chords,
- Page 581 and 582:
Angles Formed by Tangents, Chords,
- Page 583 and 584:
Angles Formed by Tangents, Chords,
- Page 585 and 586:
Measures of Tangent Segments, Chord
- Page 587 and 588:
Measures of Tangent Segments, Chord
- Page 589 and 590:
Measures of Tangent Segments, Chord
- Page 591 and 592:
Circles in the Coordinate Plane 581
- Page 593 and 594:
T 3, 22lation :Circles in the Coord
- Page 595 and 596:
Developing SkillsIn 3-8, write an e
- Page 597 and 598:
Circles in the Coordinate Plane 587
- Page 599 and 600:
How to Proceed(1) Solve the pair of
- Page 601 and 602:
Tangents and Secants in the Coordin
- Page 603 and 604:
Chapter Summary 59321. a. Write an
- Page 605 and 606:
Chapter Summary 59513.12 The measur
- Page 607 and 608:
Vocabulary 597Formulas(Continued)Ty
- Page 609 and 610:
Review Exercises 59911. Two circles
- Page 611 and 612:
Cumulative Review 6012. The coordin
- Page 613 and 614:
Find the coordinatesR 90+ r y5x.Cum
- Page 615 and 616:
Constructing Parallel Lines 60514-1
- Page 617 and 618:
Constructing Parallel Lines 607Exer
- Page 619 and 620:
PL h b. Choose point N on . Constru
- Page 621 and 622:
The Meaning of Locus 611Note that i
- Page 623 and 624:
Five Fundamental Loci 613Applying S
- Page 625 and 626:
SolutionAnswerBCAB g CD g . The lo
- Page 627 and 628:
Points at a Fixed Distance in Coord
- Page 629 and 630:
Equidistant Lines in Coordinate Geo
- Page 631 and 632:
Equidistant Lines in Coordinate Geo
- Page 633 and 634:
Equidistant Lines in Coordinate Geo
- Page 635 and 636:
Points Equidistant from a Point and
- Page 637 and 638:
Points Equidistant from a Point and
- Page 639 and 640:
Points Equidistant from a Point and
- Page 641 and 642:
Review Exercises 631VOCABULARY14-2
- Page 643 and 644:
CUMULATIVE REVIEW Chapters 1-14Part
- Page 645 and 646:
Part IVAnswer all questions in this
- Page 647 and 648:
Index 637Biconditional(s), 69-73app
- Page 649 and 650:
Index 639multiplicative, 5Identity
- Page 651 and 652:
Index 641Projectionof point on a li
- Page 653:
Index 643Trichotomy postulate, 264-