The Hessian Matrix - CEDAR
The Hessian Matrix - CEDAR
The Hessian Matrix - CEDAR
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
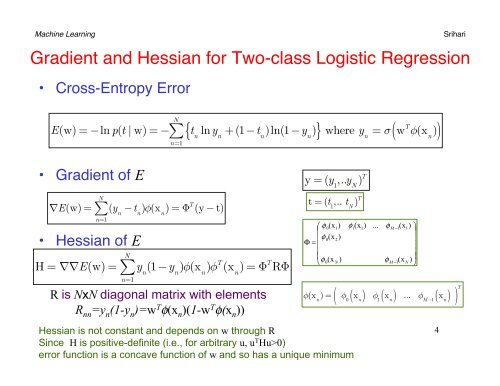
Machine Learning SrihariGradient and <strong>Hessian</strong> for Two-class Logistic Regression• Cross-Entropy ErrorNE(w) = −ln p(t | w) = −∑ t nlny n+(1−t n)ln(1−y n) where y n= σ w T φ(x n)n=1{ }( )• Gradient of E• <strong>Hessian</strong> of EN∑∇E(w) = (y n−t n)φ(x n) = Φ T (y − t)n=1H = ∇∇E(w) =N∑n=1y n(1−y n)φ(x n)φ T (x n) = Φ T RΦR is NxN diagonal matrix with elementsR nn =y n (1-y n )=w T φ(x n )(1-w T φ(x n ))y = (y 1,..y N) Tt = (t 1,.. t N) T⎛ φ0(x1)⎜⎜ φ0(x2)Φ = ⎜⎜⎝φ0(xN)φ (x )φ(x n) = φ 0x n11...φM −1(x1)⎞⎟⎟⎟⎟φM −1(xN) ⎠( ( ) φ 1 ( x n ) ... φ M−1 ( x n ) ) T<strong>Hessian</strong> is not constant and depends on w through RSince H is positive-definite (i.e., for arbitrary u, u T Hu>0)error function is a concave function of w and so has a unique minimum4