Botany Lab Exam Review Worksheet KEY 1. What phylum do ...
Botany Lab Exam Review Worksheet KEY 1. What phylum do ...
Botany Lab Exam Review Worksheet KEY 1. What phylum do ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
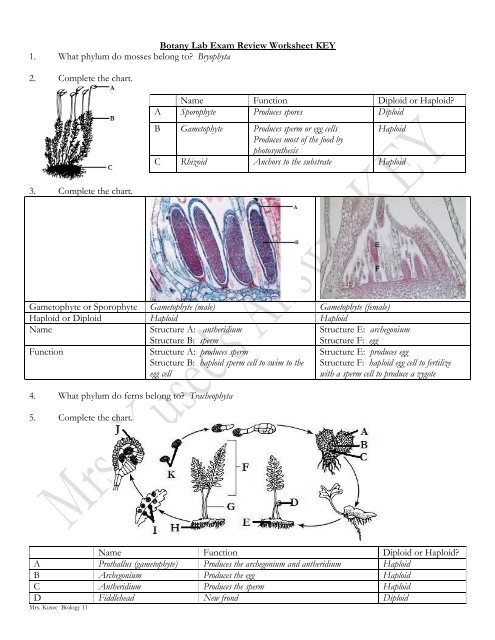
<strong>Botany</strong> <strong>Lab</strong> <strong>Exam</strong> <strong>Review</strong> <strong>Worksheet</strong> <strong>KEY</strong><strong>1.</strong> <strong>What</strong> <strong>phylum</strong> <strong>do</strong> mosses belong to? Bryophyta2. Complete the chart.Name Function Diploid or Haploid?A Sporophyte Produces spores DiploidB Gametophyte Produces sperm or egg cells HaploidProduces most of the food byphotosynthesisC Rhizoid Anchors to the substrate Haploid3. Complete the chart.Gametophyte or Sporophyte Gametophyte (male) Gametophyte (female)Haploid or Diploid Haploid HaploidNameStructure A: antheridiumStructure B: spermStructure E: archegoniumStructure F: eggFunctionStructure A: produces spermStructure B: haploid sperm cell to swim to theegg cellStructure E: produces eggStructure F: haploid egg cell to fertilizewith a sperm cell to produce a zygote4. <strong>What</strong> <strong>phylum</strong> <strong>do</strong> ferns belong to? Tracheophyta5. Complete the chart.Name Function Diploid or Haploid?A Prothallus (gametophyte) Produces the archegonium and antheridium HaploidB Archegonium Produces the egg HaploidC Antheridium Produces the sperm HaploidD Fiddlehead New frond DiploidMrs. Kusec Biology 11
E Rhizome Underground stem that gives rise to the frond DiploidF Frond Provides food through photosynthesis DiploidG Stipe The stalk that attaches the fern frond to the rhizome DiploidH Roots Anchor the fern in place and absorb water from the DiploidsoilI Sori Contains many sporganium DiploidJ Sporangium Undergoes meiosis to produce spores DiploidK Spore Will grown into a new prothallus Haploid6. Complete the chart.7. Complete the chart.NameFunctionA Cutin Protects the leaf from drying outB Upper epidermis Produces the cutinForms the upper layer of the leafC Palisade parenchyma PhotosynthesiscellD Spongy parenchyma cell PhotosynthesisE Air space Provides air for photosynthesisF Lower epidermis Produces the cutinForms the lower layer of the leafG Guard cell Controls the opening of the stomataH Stomata Opening to the air spaceNameFunctionA Stamen Contains the male gametophyteB Anther Produces pollenC Filament To support the antherD Stigma Location for the pollen to landE Style To support the stigmaF Ovary Produces the eggG Egg Female gametophyte to fertilizewith a sperm to produce a zygoteH Pistil Contains the female gametophyteI Petal Attracts pollinatorsJ Sepal Protects the flower duringdevelopment of the flowerK Peduncle Supports the flowerL Corolla Attracts pollinatorsM Calyx Protects the flower duringdevelopment of the flower8. <strong>What</strong> <strong>phylum</strong> <strong>do</strong> conifers belong to? <strong>What</strong> class <strong>do</strong> conifers belong to? Tracheophyta, Gymonospermata9. <strong>What</strong> <strong>phylum</strong> <strong>do</strong> flowering plants belong to? <strong>What</strong> class <strong>do</strong> flowering plants belong to? Tracheophyta,AngiospermataMrs. Kusec Biology 11
10. List 3 differences between monocots and dicots.1<strong>1.</strong> List 3 ways that seeds can be dispersed. Water, wind, animalsMrs. Kusec Biology 11