New Genetics, Food and Agriculture: Scientific ... - ArgenBio
New Genetics, Food and Agriculture: Scientific ... - ArgenBio
New Genetics, Food and Agriculture: Scientific ... - ArgenBio
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
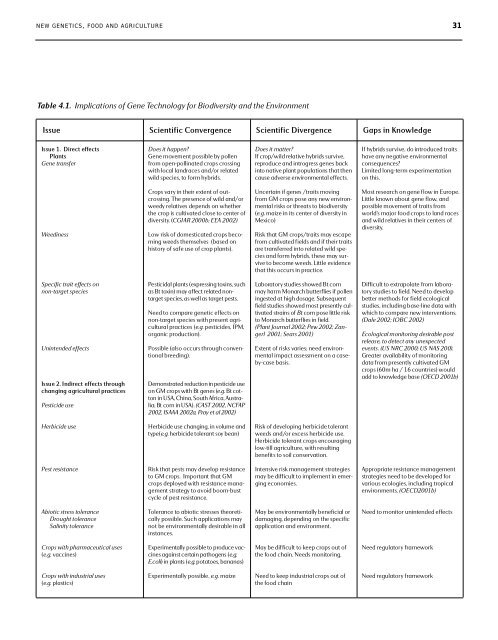
N E W G E N E T I C S, F O O D A N D A G R I C U LT U R E 31Table 4.1. Implications of Gene Technology for Biodiversity <strong>and</strong> the EnvironmentIssue <strong>Scientific</strong> Convergence <strong>Scientific</strong> Divergence Gaps in KnowledgeIssue 1. Direct effectsPl an t sGene tran s fe rD oes it happe n?Gene movement po s s i ble by pol l e nfrom ope n - pol l i n ated crops cro s s i n gw i th local lan d ra ces an d /or re l ate dwild spe c i es, to form hybrids.D oes it matte r?If cro p/wild re l ative hybrids surv ive ,re p rodu ce <strong>and</strong> introgress genes ba c ki n to native pl ant po p u l ations th at th e nca use adve rse env i ro n m e n tal effects.If hybrids surv ive, do introdu ced trai t sh ave any negative env i ro n m e n ta lco n s e q u e n ces?Li m i ted long-term expe r i m e n tationon this.Weed i n es sCrops vary in their extent of out -c rossing. The pres e n ce of wild an d /o rwe e dy re l atives depends on wh e th e rthe crop is cu l tivated close to ce n ter ofd ive rs i ty. (CGIAR 2000b; EEA 2002)Low risk of domes ti cated crops be comingweeds th e m s e l ves (based onh i s to ry of safe use of crop pl ants).Un ce r tain if genes /traits mov i n gfrom GM crops pose any new env i ro n-m e n tal risks or th re ats to biod ive rs i ty(e .g . m ai ze in its ce n ter of dive rs i ty inMe x i co )R i sk th at GM cro p s / traits may es ca pefrom cu l tivated fields <strong>and</strong> if their trai t sare tran s fe r red into re l ated wild speci es <strong>and</strong> form hyb r i d s, th ese may survive to be come weeds. Li ttle ev i d e n ceth at this occurs in pra c ti ce.Most res e arch on gene fl ow in Euro pe .Li ttle known abo ut gene fl ow, an dpo s s i ble movement of traits fro mwo r l d ’s major food crops to l<strong>and</strong> ra ces<strong>and</strong> wild re l atives in their ce n te rs ofd ive rs i ty.Spec i fic trait effects onn o n - target spec i esUn i n te n d ed effec t sIssue 2. Indirect effects th roughc h anging agr i cu l tural pra c ti cesPes ticide us ePes ticidal pl ants (expressing tox i n s, suchas Bt toxin) may affect re l ated nontargetspe c i es, as well as target pests.Need to co m pare genetic effects onn o n - target spe c i es with present agr i-cu l tural pra c ti ces (e .g .pes ti c i d es, IPM ,o rg anic produ c tion).Po s s i ble (also occurs th rough co nve n-tional breeding).D e m o n s trated re du c tion in pes ticide us eon GM crops with Bt genes (e .g .Bt co t-ton in USA, Ch i n a, So uth Afr i ca, Aus trali a; Bt corn in USA). ( CAST 2002, NCFA P2002, ISAAA 2002a, Pray et al 2002)La bo rato ry stu d i es sh owed Bt co r nm ay harm Mo n arch butte r fl i es if pol l e ni n g es ted at high dosage. Subsequentfield stu d i es sh owed most pres e n tly cu l-tivated strains of B t corn pose little riskto Mo n arch butte r fl i es in field.( Pl ant Jo urnal 2002; Pew 2002; Zangerl2001; Sears 2001)Ex tent of risks var i es; need env i ro n-m e n tal impact as s essment on a cas e -by - case basis.D i ffi cult to extra pol ate from labo ratory stu d i es to field. Need to deve l o pbe tter meth ods for field ecol og i ca ls tu d i es, including base-line data withwhich to co m pare new inte rve n tions.(Dale 2002; IOBC 2002)Ecol og i cal monitoring des i ra ble po s trel ease, to detect any un e x pec tedevents. (US NRC 2000; US NAS 200).Gre ater avai l a b i l i ty of monito r i n gd ata from pres e n tly cu l tivated GMc rops (60m ha / 16 co un tr i es) wo u l dadd to knowledge base ( O ECD 2001b )Herbicide us eHerbicide use chan g i n g, in vol ume an dtype (e .g .herbicide tol e rant soy be an )R i sk of developing herbicide tol e ran tweeds an d /or excess herbicide us e .Herbicide tol e rant crops enco ura g i n gl ow - till agr i cu l ture, with res u l ti n gbe n e fits to soil co n s e rvati o n .Pest res i s tan ceR i sk th at pests may develop res i s tan ceto GM crops. Impo r tant th at GMc rops depl oyed with res i s tan ce man a-gement strate gy to avoid boo m - b us tcycle of pest res i s tan ce .I n te n s ive risk management strate g i esm ay be diffi cult to implement in emergingeco n o m i es.A p p ro p r i ate res i s tan ce man a g e m e n ts trate g i es need to be deve l o ped fo rvar i o us ecol og i es, including tro p i ca le nv i ronments. ( O ECD2 0 0 1b )Ab i o tic stress tol e ran ceD rought tol e ran ceSa l i n i ty tol e ran ceTol e ran ce to abiotic stres s es th e o re ticallypo s s i ble. Such appl i cations maynot be env i ro n m e n tally des i ra ble in alli n s tan ces.May be env i ro n m e n tally be n e ficial ord am a g i n g, depending on the spe c i fi ca p pl i cation <strong>and</strong> env i ro n m e n t .Need to monitor un i n tended effe c t sCrops with ph ar m a ce uti cal us es(e .g . va cc i n es )Ex pe r i m e n tally po s s i ble to produ ce va c-c i n es against ce r tain path ogens (e .g .E .col i) in pl ants (e .g .po tatoes, ban an as)May be diffi cult to keep crops out ofthe food chain. Needs monito r i n g .Need re g u l ato ry fram eworkCrops with indus trial us es(e .g .pl as ti cs )Ex pe r i m e n tally po s s i ble, e .g . m ai zeNeed to keep indus trial crops out ofthe food chai nNeed re g u l ato ry fram ewo r k