B TECH MECHANICAL SYLLABUS SEM I-VI.pdf - Ganpat University
B TECH MECHANICAL SYLLABUS SEM I-VI.pdf - Ganpat University
B TECH MECHANICAL SYLLABUS SEM I-VI.pdf - Ganpat University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Teaching Scheme (Hrs.)LectHrsTuHrsPrec.HrsGANPAT UNIVERSITY<strong>SEM</strong>ESTER – I/II (IT/CE/EC/BM&I/MC/ME/Civil)2HS 103: Language & Communication SkillsCreditTotal Theory Pr/TW Total Int.AssessExamination Scheme ( Marks)TheorySem. TW/PracticalHrsEnd02 02 00 04 02 01 03 30 70 3 25 125TotalUnitNo.TopicsLectures(Hour)1 Basics of Technical Communication: 4Introduction to English language and communication, Principles, process and formsof communication, Role of Language in communication, Barriers to communication,Difference between general and technical communication2 Listening & Reading Skills: 4Listening Skill: Definition and process of listening skill, Types of listening, Modes oflistening, Active listening and reflective response.Reading Skill: Reading as a communicative process, Types and strategies of readinglike reading for facts, guessing meanings from context, paraphrasing, scanning,skimming, inferring meaning, critical reading, Reading at various speeds (slow, fast,very fast); reading different kinds of texts for varied purposes; reading between lines,Reading of technical text3 Oral Communication: 6Presentation and Public Speaking: Nature of presentation, How to preparepresentation, Presentation tools along with guidelines of effective presentation,Boredom Factors in presentation and how to overcome them, Interactivepresentation. Nature of public speaking, Tips for public speaking, Difference betweenpresentation and public speakingJob Interviews and Group Discussion: The interview process, Objectives of jobinterview, Types of interview, Characteristics of job interview, Pre-interviewpreparation techniques, Interview questions and answering techniques, Nature ofgroup discussion, Characteristics of group discussion, Organizational groupdiscussion, Group discussion as a part of selection process, group discussionstrategies, Techniques for individual contribution in group discussion4 Business Writing: 5Business letter writing: Essentials of effective letter writing, Need, Functions andTypes of business letters. Structure and Layout of a business letter, Drafting ofbusiness letters like inquiry, reply, purchase order, complaint and adjustment letter,sales promotionAdvertisements: Basics of advertisement, Nature and purpose of advertisement,Types of an advertisement, Media for advertisement, preparing of an advertisementdraft1/2
101112phase, Star – Delta, Voltage ,Current & Power relationship in balanced 3-Phase Circuits, Measurement of power in 3-phase circuit and Effect ofpower factor on Wattmeter readings.Economic Aspects :Load curve and related factors, Tariff & its types, Causes and effects of low 03power factor, Methods of improving power factor.Measuring Instrument :Operating system of Indicating instrument, Constructional and working of03PMMC, Moving Iron, Dynamometer instruments, shunts and multiplier,multimeter and megger.Safety & Protection :Safety, electric shock, first aid for electric shock other hazards of electrical02laboratories & safety rules, circuit protection devices, fuses, MCB, ELCB &relaysTotal 48Laboratory workAt least 10 Practicals to be performed based on above syllabus.TutorialsAt least 10 Assignments and Tutorials to be solved.Reference Books:(1) Electrical Technology Volume-I by B.L.Thereja, Pub. By S.Chand(2) Elements of Electrical & Electronics Engineering by U.A.Patel , Pub. By Atul Prakashan(3) Basic Electrical Engineering by V.N.Mittal Pub. By Tata Mc Grawhill, New Delhi(4) Electrical Wiring ,Estimating and Costing by S.L.Uppal, By Khanna Publication(5) Principles of Power Systems by V.K.Mehta Pub. By S.Chand2/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2ME 101: Elements of Mechanical EngineeringExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Pract. TotalInt.TotalTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.4 2 6 4 1 5 30 70 3 100 25 125UnitNo.12345678910TopicsIntroduction: Prime movers, Sources of energy, Types of prime movers,Force and mass, Pressure, Work, Power, Energy, Heat, Temperature,Units of heat, Specific heat capacity, Interchange of heat, Change of state,Mechanical equivalent of heat, Internal energy, Enthalpy, Entropy,Efficiency, Statements of Zeroth Law, First law and Second Law ofThermodynamics.Fuels and Combustion: Introduction, Classification, Solid fuels, LiquidFuels, Gaseous fuels, LPG,CNG and biofuels ,Calorific values.Properties of gases : Gas laws, Boyle's law, Charle's law, Combined gaslaw, Gas constant, Internal energy, Relation between Cp and Cv,Enthalpy, Non flow process, Constant volume process, Constant pressureprocess, Isothermal process, Poly-tropic process, Adiabatic process.Properties of Steam : Introduction, Steam formation, Types of Steam,Enthalpy, Specific volume of steam and dryness fraction of steam ,Internal energy, Steam tables, Non-flow process. Measurement of drynessfraction, Throttling calorimeter, Separating calorimeter, Combinedcalorimeter.Heat Engines: Thermal prime movers, Elementary heat engines, Sourcesof heat, Working substances, Converting machines, Classification of heatengines.Steam Boilers : Introduction, Classification, Simple vertical boiler,Vertical multitubular boiler, Cochran type, Lancashire boiler, Locomotiveboiler, Babcock and Wilcox boiler, Boiler details, Boiler performance.Functioning of different mountings and accessories.Internal Combustion Engines : Introduction, Classification, Enginedetails, otto four-stroke cycle, Diesel-four-stroke cycle, Differencebetween otto cycle and Diesel cycle, Two-stroke cycle, Differencebetween two-stroke and four-stroke cycle, indicated power (ip), BrakePower (bp), Efficiencies.Speed Control: Introduction, Governors, I.C. Engine governing, Flywheel.Pumps: Introduction, Reciprocating pump, types and operation, AirChamber, Centrifugal pumps, Priming, Positive displacement pumps.Air Compressors: Introduction, Uses of Compressed air, Reciprocatingcompressors, Operation of a compressor, Work for compression, Powerrequired, Reciprocating compressor efficiency, Multistage reciprocatingcompressors, Rotary compressors.Lectures(Hours)040205050305060204031/2
111213Refrigeration & Air Conditioning: Introduction, Refrigerant, Types ofrefrigerators, Vapour compression refrigerating system, Window and split 03air conditioners.Couplings, Clutches and Brakes: Introduction, Couplings, Clutches,03Brakes, Types of brakes. Difference between a brake and a clutch.Transmission of Motion and Power: Introduction, Methods of drive,Power transmission elements, shaft and axle, Belt-drive, Pulleys, Power 03transmitted by a belt, Chain drive, Friction drive, Gear drive.Total 48Reference Books:1. Thermal Science and Engineering by Dr. D.S. Kumar, S.K. Kataria & sons Publication New Delhi2. Fundamental of Mechanical Engineering by G.S. Sawhney, Prentice Hall of India PublicationNew Delhi3. Thermal Engineering by R.K. Rajput ,S.Chand Publication New Delhi2/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2CI 102: Mechanics of SolidsExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Tu Pract. TotalInt.TotalTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) Hrs (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 02 06 04 01 05 30 70 03 100 25 125UnitNo.Topics1 Introduction:-Scalar and vector quantities, absolute and derived units, the science ofmechanics, fundamental principles, SI units.2 Forces & Force Systems:-Force and force systems, composition and resolution of forces, moment ofa force, law of parallelogram, resultant of different force systems,Varignon’s principle..3 Equilibrium:Equilibrium of a particle, resultant and equilibrant, free body and freebody diagram, Lami’s theorem, equilibrium of human body joints.4 Centre of gravity and Moment of Inertia:-Center of gravity of curves, plane areas and bodies, Pappus Guldinustheorem I & II, method of integration, Area moment of inertia, massmoment of inertia, M.I. of flywheel, different methods of M.I., law ofparallel axis, law of perpendicular axis.5 Friction:-Theory of friction, Types of friction, inclined plane friction, ladderfriction, wedge friction, belt and rope friction.6 Simple Lifting Machines:-Velocity ratio, mechanical advantage, efficiency, reversibility, law ofmachines, simple wheel & axle, differential wheel & axle, single purchasecrab winch, differential wheel & axle, pulley & pulley block.7 Dynamics of Particles:-De-Alembert's principle, motion of connected bodies, motion alonginclined planes, impulse and momentum, Single degree free vibration8 Physical and Mechanical properties of materials:Properties related to axial, bending and torsional and shear loading,Toughness, hardness ,proof stress, factor of safety, working stress, loadfactor.9 Stresses & Strains:-Elastic, homogeneous, isotropic materials, limit of elasticity andproportionality, yield limit, ultimate strength, strain hardening, section ofcomposite materials, prismatic and non prismatic sections.Strains: Linear, shear,lateral,thermal and volumetric, Poisson’s ratio.Stresses: Normal stresses, axial- tensile and compressive, shear andcomplementry shear, thermal and hoop. Applications to compositematerial stepped and tapered bars.Lectures(Hours)1638334371/2
10 Beams:-Types of supports, Types of beams, Types of loads, determinateandindeterminate beams. .Bending moments and Shear force , Bendingmoment and shear force diagrams for statically determinate beamssubjected to couples, connected forces, uniformly distributed loadings,relation between bending moment, shear force and rate of loading, pointof contra flexture.10Total 48Reference Books:(1) Engineering Mechanics by Beer & Johnston(2) Applied Mechanics by S.B.Junarkar & H. J. Shah(3) Mechanics of Structure Vol. I by S.B.Junarkar & H. J. Shah(4) Engineering Mechanics by M.N.Patel(5) Engineering Mechanics by P.J.Shah(6) Engineering Mechanics by A. K. Tayal(7) Engineering Mechanics by S. Ramamrutham(8) Engineering Mechanics by Kumar(9) Strength of Materials by Timo Shenko(10) Strength of Materials by S. Ramamrutham2/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2CI 103: Environment Study & Disaster ManagementExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Pract. TotalInt.TotalTuTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 00 04 04 00 04 30 70 03 100 00 100UnitNo.12345TopicsIntroduction to Environment:Definition, Inter-relationships amongst and between them, Components ofEnvironment, Relationship between different components, Man-Environment relationshipImpact of Technology on the environment, Environmental Degradation.Ecology & Ecosystems:Introduction: Ecology- Objectives and Classification, Concepts of anecosystem- structure & function of ecosystem, Components of ecosystem-Producers, Consumers, Decomposers, Bio-Geo- Chemical Cycles-Hydrological Cycle, carbon cycle, Oxygen Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle, SulfurCycle, Energy Flow in Ecosystem, Food Chains: Grazing, Detritus, &Food webs, Ecological Pyramids, Major Ecosystems: Forest Ecosystem,Grassland Ecosystem, Desert Ecosystem, Aquatic ecosystem, EstuarineEcosystem.Environmental Pollution:Air Pollution: Composition of air , Structure of atmosphere, Ambient AirQuality Standards, Classification of air pollutants, Sources of common airpollutants like SPM, SO2, NOX – Natural & Anthropogenic Sources,Effects of common air pollutants, Carbon credit.Noise Pollution: Introduction- Sources of Noise Pollution, Ambient noiselevels, Effects of noise pollution on human being and wild life, Noisepollution controls, Noise standards.Water Pollution: Introduction – Water Quality Standards, Sources ofWater Pollution,Classification of water pollutants, Effects of water pollutants,Eutrophication.Current Environmental Global Issues: Global Warming & GreenHouses Effects, Acid Rain, Depletion of Ozone Layer.Energy Resources:Renewable & Nonrenewable Resources: Renewable Resources,Nonrenewable Resources, Destruction versus Conservation.Energy Resources: Energy Resources - Indian Scenario , ConventionalEnergy Sources & its problems, non-conventional energy sources-Advantages & its limitations , Problems due to Overexploitation ofEnergy Resources.Natural Disasters:Introduction, Floods, Earthquakes and Landslides, Cyclones andThunderstorms, Tsunami, Drought, Heat wave and Sandstorms1/2Lectures(Hours)48848
678Man made Disasters:War and Terrorism, Riots and Demonstrations, Residential and Industrial 7Fires, Transportation Accidents, Nuclear Power Accidents, HazardousMaterials and Toxic Emission, Utility Failure.Problems regarding victims and its awareness:Saving Victims – First Twenty-Four Hours, Conducting Medical Relief 6Operations, Managing Relief Operations, Psychological Issues, CarryingOut Rehabilitation WorkPlanning for disaster management:Local Disaster Management Cell, How to Prepare a Business Recovery 3Plan?, Government Response in Disaster.Total 48NOTE: It is necessary to include mock drill, field visit and expert lectures in the portion of DisasterManagement. The format of the question paper in the portion of Disaster Management should beobjective with short answer questions, multiple choice questions etc.REFERENCE BOOKS:1. Citizen’s guide to disaster management by Satish Modh Publisher:-Macmillan Publishers India,2. Environment Engineering Vol-I & II, by Dr.S.K.Garg,3. Introduction to Air Pollution, by R.K.Trivedi & P.K.Goel.-BS Publications,4. Environmental Pollution Control Engineering, by C.S.Rao,5. Vol-I- Air Pollution, Vol-II- Water Pollution, Vol-V- Noise Pollution – By S.K.Agarwal –A.P.H.Publishing Corporation,6. Environmental Studies: R. Rajagopalan,Oxford <strong>University</strong> Press7. Environmental Pollution: Causes, Effects & Control by K.C Agrawal8. Environmental Science by Richard T Wright & Bernard J Nebel9. Environmental Science by Daniel B Botkin & Edward A Keller10. Environmental Engineering & Management by Suresh K Dameja11. Environmental Management by Dr. Swapan C Deb12. Environment & Ecology by Dr Gourkrishna Dasmohapatra13. Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Science by Master Gilbert M.2/2
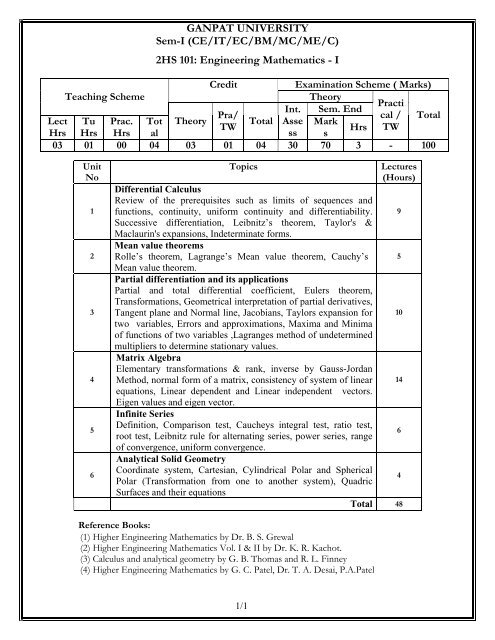
GANPAT UNIVERSITYSem-II (CE/IT/EC/BM/MC/ME/C)2HS 102: Engineering Mathematics – IICreditExamination Scheme ( Marks)Teaching SchemeTheoryPractiInt. Sem. EndPra/cal / TotalLect Tu Prac. Tot TheoryTW Total Asse MarkHrs TWHrs Hrs Hrs alss s03 01 00 04 03 01 04 30 70 3 - 100UnitNo123456TopicsIntegral CalculusBeta & Gamma, Error functions, Elliptic functions.Application of integration-- Length of a curve, Area of abounded region, Volume & surface area of a solid ofrevolution for Cartesian, parametric & polar form.Reduction FormulaeReduction formulae of the type ∫ sin n x dx, ∫ cos n x dx,∫ sin m xcos n xdx, ∫ cot n xdx, and ∫ tan n xdx.Multiple integralsDouble integral, change of order of integration,transformation of variables by Jacobian only for doubleintegration, change to polar co-ordinates in doubleintegrals,Triple integral, Application of multiple integrationto find areas, volumes, C.G., M.I. and mean values.Complex NumbersDeMoivres theorem & its applications, functions of complexvariables Exponential ,hyperbolic & inverse hyperbolic,trigonometric & logarithmic.Differential Equations & ModellingModelling of Engineering systems (leading to ODE of firstorder, first degree, including orthogonal trajectories), Exactdifferential equations and integrating factors, unifiedapproach to solve first order equations, linear, reducible tolinear and higher degree differential equations (Clairut’sequation only).Curves TracingTracing of Curves: Cartesian, polar and parametric forms.Lectures(Hours)841210104Total 48Reference Books:(1) Higher Engineering Mathematics by Dr. B. S. Grewal(2) Higher Engineering Mathematics Vol. I & II by Dr. K. R. Kachot.(3) Advanced Engineering Mathematics (Fifth Edition), Erwin Kreyszig.(4) Applied Mathematics for Engineering by Dr. R. C. Shah.1/1
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2EC 101: Engineering ScienceExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Pract. TotalInt.TotalTuTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 00 04 04 00 04 30 70 03 100 00 100UnitNo.12345678TopicsThermal PhysicsIntroduction, Joule-Thomson Effect, Thermometry, Conduction,Convection, Radiation, Thermal Conductivity of material, Concept of heatand work, Laws related to thermodynamic radiation, EntropyOpticsIntroduction, Different theories based on the properties of light, Reflection,Refraction, Dispersion, Absorption, Lasers and Fiber Optics- Introductionand applications, Photoelectric Effects and its applicationsAcousticsIntroduction, Parameters associated with sound wave, Doppler effects,Introduction to Ultrasonic and its applicationsMagneticsIntroduction, Magnetic dipole moment, Magnetic field, Classification ofmagnetic materials, Ferromagnetism, Diamagnetism, Application ofmagnetic materialsModern PhysicsIntroduction, Nucleus, Introduction to cosmic rays, Introduction to X- raysand Its applications, Introduction to Nano-technology and Nano-materials,Its properties and application,Introduction andApplications of Plasma Physics, Superconducting materialSemiconductors and Diode TheoryConductors, Semiconductors, silicon crystals, intrinsic semiconductors,doping, types of semiconductors, biasing, Breakdown, energy levels andhill, barrier potential, biasing of diode, diode approximations, troubleshooting, up down circuit Analysis, reading a data sheet, resistances ofdiodeDiode CircuitsHalf wave rectifier, transformer, full wave rectifier, bridge rectifier, chokeinput filter, capacitor input filter, Peak inverse voltage and surge, otherpower supply topics, trouble shooting, clippers and limiters, Clampers,voltage multipliersBipolar TransistorsTransistor construction, transistor operation, unbiased transistor, biasedtransistor, transistor currents, CE configuration, base curve and collectorcurves, transistor approximation, reading data sheets, Trouble shooting,transistor testing1/2Lectures(Hours)554551095
Reference Books:Total 48(1) Modern Engineering Physics by A.S.Vasudeva Pub: S. Chand(2) Fundamentals of Physics by Halliday, Resnik, Walker Pub: Willey(3) A Text book of Engineering Physics by M.N. Avadhanuly, P.G.Kshirsagar Pub: S.Chand(4) Modern Physics by G. Aruldhas, P.Rajagopal Pub: PHI Pub.(5) <strong>University</strong> Physics by Harris Benson Pub: Willey Pub.(6) Electronics Principles by A.P. Malvino (TMG)(7)Modern Physics by G. Aruldhas & P. Rajagopal (PHI)2/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2CI 101: Elements of Civil EngineeringExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Pract. TotalInt.TotalTuTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 02 06 04 01 05 30 70 03 100 25 125UnitNo.Topics1 Introduction :Impact of Infrastructural Development on the Economy of a Country, Roleof Civil Engineers, Importance of Planning, Scheduling and Constructionmanagement.2 Water Resources and Hydraulics:Importance of Hydrology, Classification of Water resources & Requirementof water for various uses, Water Management Strategies, Water ResourcesDevelopment in India. Introduction of Dams, Introduction of water supplyand Drainage System3 Surveying:Chain Survey: Linear measurements, Errors in chaining, problems onobstacleDirections and Bearings: Types of Bearings and Meridians, Whole CircleBearing and Quarter Circle Bearings, Compunctions of Angles frombearings and bearings from angle, Magnetic Declination, Local Attraction,Various ProblemsElevation Measurements: Introduction of Level Machine, Methods ofleveling, Recording and Reducing of levels, Contour Survey.Area and volume: measurement by PlanimeterModern Tools of Surveying and Mapping: Introduction to Theodolite,ElectronicDistance Measurement Instruments, Total Station, Global PositioningSystem, Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System4 Construction Materials:Introduction, Masonry Materials: Stones, Bricks, Blocks, Tiles; BindingMaterials: Lime & Cement; Aggregates, Mortar & Concrete, Timber,Specification of all Building Materials as per IS Standards, Method ofDrawing Plan, Elevation and Section of BuildingLectures(Hours)020816125 Transportation Engineering:08Role of Transportation in National development, Transportation Ways,Surface Transportation and Aviation, Elements of Highway materialsproperties and highway Construction, BOT Projects for Highways, Elementsof Traffic Engineering and Traffic ControlTotal 481/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2ME 102: Engineering GraphicsExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Pract. TotalInt.TotalTuTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 02 00 06 04 01 05 30 70 03 100 25 125UnitNo.1234567TopicsLectures(Hours)Introduction: Importance of Engineering Drawing, Engineering DrawingInstruments and uses, B.I.S and I.S.O. Conventions for drawings, Use of 01plane scales and Representative FractionLoci of Point: Path of the points moving on simple arrangements andsimple Mechanism, Slider Crank Mechanism, Four bar Chain Mechanism 03etc.Engineering Curves: Classification of Engineering Curves,Construction of Conics curves with different methods, Construction of 04Cycloidal Curves, Involute and Spiral.Projection of Points and Straight Lines: Introduction to principal planesof projections, Notation System- Points in First, Second, Third and Fourthquadrants, Projections of line Parallel to Two and Perpendicular to one ofthe principal planes, Line parallel to one and inclined to two principal06planes, Line inclined to all the three principal planes, True length of theline and its inclination with the reference planes.Projection of Planes: Concept of different planes, Projections of planeswith its inclination to one principal plane and with two principal planes. 04Concept of auxiliary plane method for projections of the plane.Projection of Solids and Sections of Solids: Classifications of Solids,Projections of right and regular solids with their axis Parallel to Two andPerpendicular to one of the principal planes, axis parallel to one and 06inclined to two principal planes, axis inclined to all the three principalplanes. Section of such a solids and the true shape of the section.Development of surfaces: Methods of development of lateral surface ofright solids, Parallel line development, Radial line development. 048910Interpenetration of Solid: Interpenetration of Right Regular Solids –Intersection of Cylinder Vs Cylinder, Cylinder Vs Prism, Cylinder VsCone.Orthographic Projections & Sectional Orthographic Projections:Principle of projection, Principal planes of projection, Projections fromthe pictorial view of the object on the principal planes for View fromFront, View from Top and View from Side using first angle projectionmethod and third angle projection method, Full Sectional View.Isometric Projections and Isometric View or Drawing: IsometricScale, Conversion of orthographic views into isometric projection,isometric view or drawing.1/2040806
11Fastening and Connecting Methods: Screw threads, Bolts, Nut, Stud,locking devices, Riveted joint, Coupling, Foundation bolts,02Total 48Term Work.Based on above syllabus, each candidate shall submit a set of the following graphics sheets and sketchbook certified by the principal of the college that they have been executed in a satisfactory manner in thegraphics halls of the college.Text Books:1. A Text Book of Engineering Graphics By P.J.Shah S.Chand & Company Ltd., New Delhi2. A Text Book of Machine Drawing By P.J.Shah S.Chand & Company Ltd., New Delhi3. Elementary Engineering Drawing By N.D.Bhatt Charotar Publishing House, AnandReference Books:1. Engineering Graphics – I and II By Arunoday Kumar Tech – Max Publication, Pune2. Engineering Drawing & Graphics using Auto CAD 2000 By T. JeyapoovanVikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi3. A text book of Engineering Drawing By R.K.Dhawan S.Chand & Company Ltd., New Delhi4. A text book of Engineering Drawing By P.S.Gill S.K.Kataria & sons, Delhi5. Engineering Drawing with an Introduction to AutoCAD By D.A.Jolhe Tata McGraw-Hill PublishingCo. Ltd., New Delhi6. Computer Aided Engineering Drawing, S. Trymbaka Murthy I.K.International Publishing House Pvt.Ltd., New Delhi7. Engineering Drawing and Graphics, Venugopal2/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech I/II (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2CE 101: Computer ProgrammingExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandPract./ TWLect. Pract. TotalInt.TotalTuTheory Pr/TW Total Marks Hrs. Total Assessment(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.02 00 04 06 02 02 04 30 70 03 100 25 125UnitNo.010203040506070809TopicsIntroduction to Programming & CIntroduction to programming and programming language, ProblemSolving Methods: Algorithms and Flowcharts, Introduction to C, Basicstructure of C programs, Sample C programs, Process of compiling andrunning a C ProgramConstants, Variables and data Types:Character Set, C tokens, Keywords and Identifiers, Constants, Variables,Data types, Declaration of Variables, Assigning values to variables,typedef, Defining symbolic constants. Printf & scanf function.Operators and Expression:Introduction, Arithmetic Operators, Relational Operators, LogicalOperators, Assignment Operators, Increment and Decrement Operators,Conditional Operators, Special Operators, Evaluation of expressions,Precedence of arithmetic operators, Type conversions in expressions,Operator precedence and associativity.Management Input and Output Operators:Introduction, reading a character, writing a character, formatted input,formatted output.Decision Making branching:Introduction, Decision making with IF statement, the IF.. ELSE statement,nesting of IF … ELSE statements, The ELSE IF ladder, The switchstatement, and the turnery (?:) Operator, the GOTO statementDecision Making Looping:Introduction, the WHILE statement, the DO statement, FOR statement,Break and Continue.Array:Introduction, One-dimensional, arrays, Two-dimensional arrays, arrays, Conceptof Multidimensional arrays.Handling of Character strings:Introduction, Declaring and initializing string variables, Reading stringfrom terminal, Writing string to screen, String, atoi(), Operations: StringCopy, String Compare, String Concatenation And String Length(usingpredefined functions & without using them), Table of strings.User-Defined Functions:Introduction, Need for user-defined functions, The form of C function,elements of UDf, Return values and their types, Calling a function,category of functions, Nesting of functions.Lectures(Hours)2342444451/2
1011124Structures and Unions:Introduction, Structure definition, declaring and initializing Structurevariables ,accessing Structure members, Copying & Comparison of5structures, Arrays of structures, Arrays within structures, Structureswithin Structures, Structures and functions, Unions.User –Defined Functions –IIRecursion , Functions with arrays, The scope and Lifetime of variables in 2functions, multifile program.Pointers:Introduction, Understanding pointers, Accessing the address of variable,Declaring and initializing pointers, Accessing a variable through itspointer, chain of Pointers, Pointer expressions, Pointer increments and 6scale factor, Pointers and arrays, Pointers & character strings, Pointers &Functions, Function returning multiple values(9.14),Pointers andstructures.File Management in C:Introduction, Defining files and its Operations, Error handling during I/O 3operations, Random access files, Command line arguments.Total 48Reference Books:(1) Programming in ANSI-C By E. Balaguruswami, TMH Publication(2) Let us C By Yashwant Kanetkar, BPB Publication(3) C Programming language By Kernighan, Brian, W, Retchie, Dennis PHI Publication2/2
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.Tech FIRST YEAR (CE/IT/EC/BM & I/MC/ME/C)2ME 103: WorkShop PracticeTeaching Scheme (Hrs.)CreditTheoryExamination SchemePracticalT P TotalInt. Sem. EndPractical/oralTheory Pr/TW TotalTotal(Hrs) (Hrs) (Hrs)Asses.Marks HrsAssessment00 00 04 04 00 02 02 0 0 0 0 50 50L(Hrs)GrandTotalObjectives:To make the students familiar with various operations and processes like joining, machining anduse of different tools of common use. This will develop various hand skills and impart workingknowledge of various Machines, devices, tools, instruments etc. and safe practices, and to makethem familiar with different machines of common use and domestic appliances.(A) <strong>MECHANICAL</strong>UNIT-1 INSTRUCTION AND DEMONSTRATIONInstruction should be given for each of following shops which include importance of the shopin engineering, new materials available, use of each tool / equipment, methods of processingany special machines, power required etc.UNIT-2UNIT-3Carpentry Shop:Study of tools & operations and carpentry joints, Simple exercise using jack plane, Simpleexercise on woodworking lathe.Fitting Shop:Study of tools & operations, Simple exercises involving fitting work, Make perfect malefemalejoint, Simple exercises involving drilling/tapping/dieing.UNIT-4 Smithy Shop:Study of tools & operations, Simple exercises base on smithy operations such as upsetting,drawing down, punching, bending, fullering & swaging.UNIT-5 Plumbing Shop:Study of Tools and Operations, Simple exercises of piping.UNIT-6 Welding Shop:Study of tools & operations of Gas welding & Arc welding, Simple butt and Lap welded joints,Oxy-acetylene flame cutting.UNIT-7 Sheet-metal Shop:Study of tools & operations, making sheet metal component using ‘soldering’. Ex: Funnel,tool-box, tray, electric panel box etc.UNIT-8 Machine Shop:Study of machine tools and operations, Demonstrations of basic machine tools like Lathe,1/3
Shaper, drilling machine with basic operations etc.UNIT-9 Foundry Shop:Study of tools & operations like Pattern making, Mould making with the use of a core. VariousCasting processes.(B) ELECTRICAL/ ELECTRONICS.UNIT- 1. Identification of electrical and electronics components.Resistors, Capacitors, Inductors, Diodes, Transistors, ThyristorsUNIT- 2. Soldering.Different electrical and electronics components on PCBUNIT- 3. Domestic and Industrial Electrical wiring.Types of wiring, domestic wiring installation, sub circuits in domestic wiring, simplecontrol circuit in domestic installation, industrial electrification.UNIT- 4. Fault finding of following domestic devices.UNIT- 5. Earthing.1. Mixer Grinder2. Washing Machine3. Domestic Floor Mill4. Electric Iron5. Oven Toaster Griller6. GeyserMeasurement of Earth resistance, Earthing methods and insulation resistancemeasurement by Meager.UNIT- 6. ICs and Data Sheet.Identification of ICs and data sheet reading.UNIT- 7. Operation of Passive Devicesa. Relays.b. Optoectronic devices.c. Switches.d. Conductors.UNIT- 8. Bell Circuits and IndicatorsTypes of bell, Alarm circuits without relay, Types of diagram, The use of relay inalarming circuits, Bell circuits using supplies, T.D.R. (Time Delay Relay) circuits, Useof indicators in various circuits.UNIT- 9. Electrical Energy meter1Φ & 3Φ Energy meter, Energy calculation2/3
Term WorkTerm Work will be based on above syllabus. Students will be given creative mini project underfun module.Reference Books:1. Elements of Mechanical Engineering by Hajra Chaudhary2. Elements of Mechanical Engineering by Mathur & Mehta3. Work shop technology by Hajra Chaudhary4. Work shop technology by Chapmen5. Electronics principle by A. Malvino6. Electrical wiring, estimating and costing by S.L.Uppal, Khanna Publication.3/3
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. III (Mechanical Engineering)2ME301 - ENGINEERING ECONOMICS & INDUSTRIAL ORGANISATIONExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 00 03 03 00 03 30 70 03 100 00 1001. Nature and scope of economics; its relation with other sciences, Micro andMacro economics, national income, Gross Domestic Product, Per Capita Income2. Value, Price, Wealth, Wants; origin of Wants, characteristics of Wants, classification of Wants, Capital,Money, income and sources of income, Margin, Utility, Marginal Utility, total Utility, law of diminishingUtility.3. Market Demand, law of Demand, factors affecting Demand, elasticity of Demand, demand forecasting,theory of supply, the law of substitution, equilibrium and price determination, monopoly, purecompetition and monopolistic competition.4. International Trade; balance of payment, customs duty, World trade organization, free trade.5. Rent, Profit, Banks and Banking , types of Banks, Commercial Banks, the State bank of India, Exchangebanks, Central Banks, the Reserved bank of India, Stock Exchange, Income tax, Foreign exchange6. Organization and Organizational structure; Bureaucratic approach, principle of organization, span ofmanagement and level of authority, line staff relations, line and staff concept and role, types of line andstaff relationships,7. Delegation , base of Delegation, process of Delegation, nature of Delegation of authority, objective andadvantages of Delegation, principles and obstacles to effective Delegation, Decentralization, principle ofDecentralization, advantages of Decentralization.8. Motivation, needs, theories of Motivation, the Need Hierachy theory, two factor theory, comparison ofMaslow’s Herzberg's theory, achievement Motivation theory, Path-Goal theory, Models of motivation,money and Motivation Definition of Morale, Morale and productivity, building morale, measuringmorale.9. Concept and nature of Coordination need of Coordination, types of Coordination, methods ofCoordination.10. Meaning of leadership, the principal tasks of leadership, approach to leadership.11. Plant location: - Introduction, factors governing plant location, merit and demerit of urban, sub urbanand ruler area, quantitative method for evolution of plant location.Plant layout: - Introduction, objective and principle, types of layout, workStation, factory building.12. Cost and depreciation: - Introduction, element of cost, overhead, component of the cost, break evenanalysis, depreciation.
Reference Books:Organization and Management By R.D. AgrwalIndustrial Engineering and Operations Management By S.K. Sharma and Savita sharmeIndustrial Engineering and Management By O.P. KhannaPrinciples of economics By Prof. B.M. Muley and Prof Anjali GokhruEconomics By Samuelson Nordhaus
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. III (Mechanical Engineering)2ME302- Strength of MaterialExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 02 06 04 01 05 30 70 03 100 50 1501. Bending Stresses in BeamsIntroduction, simple bending, theory of simple bending, moment of resistance, modulus of section, beam ofuniform section, composite section.2. Shearing Stresses in BeamsIntroduction, shear stress distribution for beam of rectangular, circular, triangle and I- section.3. Principal Stresses and strainsPrincipal planes, principle stresses, Analytical method for principal stress, Mohr's circle of stress and strain,Theories of failure.4. Deflection of beamsStrain curvature and moment, curvature relations, differential equations for deflection of elastics beams,different methods for determining slope and deflections.5. Columns and strutsShort column subjected axial forces and bending moments, engineering problems, long columns, stability andequilibrium, ranking formula, Indian standard formula, criteria for design of columns.6. Structured connectionsRiveted and welded connections, methods of failure of connections, eccentric riveted and welded connections,design requirements.7. Torsion:Basic assumption, Torsion formula, Design of circular sections, Angle of twist, Shearing stress, Deformation,Closed coiled helical springs, Helical Springs, power transmitted by shaft, keys & coupling8. Thick and thin cylinderIntroduction, Thin cylinder and thin spherical vessels under pressure, Applications of thin cylinder, Hoop andradial Stresses in cylinders, longitudinal stresses in thick cylinder, Application of thick cylinder, Maxcircumferential and Radial stresses in thick cylinders9. Direct and bending stressesMembers subjected to eccentric loads, middle third rule, and kernel of section, chimney subjected to windpressure, retaining walls and dams subjected to hydraulic pressure.Practical work: -The practical work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on the topics mentioned above and willbe defended by the candidates.REFERENCE BOOKS :1. Mechanics of structure vol I - By S. B. Junnarkar and H.J. ShahCharotar publishing house, Anand2. Strength of materials - By S. RamamruthamDhanpat rai & Sons.3. Strength of materials - By R. S. KhurmiS. Chand & Co. New Delhi.4. Strength of materials - By M. ChakrabortiS. K. Kataria & Sons.5. Strength of materials - By Timo ShenkoCBS Publisher, New Delhi.
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. III (Mechanical Engineering)2ME303 - Electrical TechnologyExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 02 06 04 01 05 30 70 03 100 50 150UnitNo.1234567TopicsLectures(Hours)DC Machines:Principle of operation, types, construction, winding, EMF equation, characteristics of07dc generators, dc motor operation and types, back EMF, torque, characteristics ofmotor, speed control of series and shunt motors, dc shunt motor starter.Transformer:Principle of operation, construction, types, EMF equation, voltage and currenttransformation ratio, transformer on no load and on load, phasor diagram, equivalent 08circuit, losses and efficiency, regulation, testing, auto transformer, CT & PT, Threephase transformer.Induction Motor:Working principle, types, construction, Torque equation, Torque / slip characteristics,09power flow, losses and efficiency, starting of induction motor, Single phaseinduction motor principle, types and construction, stepper motor.Synchronous Machines:Basic operating principle, construction, EMF equation, winding factor, armature10reaction, synchronous impedance and equivalent circuit, synchronous motoroperation, phasor diagram, starting, synchronous condenser.Electrical Power:Concept of power generation, transmission and distribution of electric power, 05Equipment used in power system protection.Heating and Welding :Advantage and methods of electric heating , Resistance heating- resistanceoven , control equipments , radiant and slot bath heating, Induction heating , arc 05furnaces, Electric welding , Resistance welding , Arc welding , Weldingtransformer.Drives:Introduction, merits and demerits of electrical drives, Factors affecting selection of 04electrical drives, classification, DC Machine drives, AC Machine drives.Total 48REFERENCE BOOKS :(i) Electrical Technology – Vol – II - BY B. L. Theraja(ii) Theory & Performance of Electrical Machines – BY J. B. Gupta(iii) Electrical Drives- concept and application by Vedam Subramanyam(iv) Utilization of Electric Power & Electric Traction – J. B. Gupta(v) Electrical Power by S. L. Uppal.(vi) Electrical power system by V .K .Mehta
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. III (Mechanical Engineering)2ME304 - Kinematics of MachinesExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 02 05 03 01 04 30 70 03 100 50 1501. Links & Mechanisms: -Introduction to mechanisms, definition, kinematics links, type of links, kinematics pairs, machine & structure,type of constrained motions, kinematics chain, type of joints in a chains, mechanisms, degree of freedoms,kutzbach & grumbler’s criteria, single slider crank mechanisms, double slider crank mechanisms, four bar chinmechanisms, inversions.Introduction to lower pair mechanisms, pantograph, straight line mechanisms, exact straight line motionmechanisms made up of turning pairs (peaucellier, hart’s), Oldham’s coupling, Scott Russell’s mechanisms,approximate straight line motion mechanisms (watts, grasshopper, Roberts), steering gear mechanisms, Davissteering gear mechanisms, Ackerman steering gear mechanisms, Geneva Mechanism.2. Kinematic analysis of mechanisms: -Introduction, motion of link, rectilinear and rotational motion in a plane, compound pendulum, equivalentdynamic system, velocity & acceleration in machine parts, instantaneous center, Number of I centers, ArnoldKennedy theorem, centroid velocity and acceleration diagrams for mechanisms (vector and graphical approach).3. Friction: -Type of friction, inclined plane, condition for maximum efficiency, uniform pressure of uniform wear, frictioncircle, friction axis, friction of pivot & collar bearings, belt & rope drive effect of centrifugal stress on powertransmitted, slip & creep effect, jockey pulleys.4. Brakes & Dynamometer: -Type of brakes, shoe brakes, band brake, band & block brakes, internal expanding shoe brake, effect of braking,braking of vehicle, type of dynamometers, prony brake, rope brake, belt transmission, bevies Gibson torsiondynamometer, hydraulic dynamometer.5. Cams: -Introduction, type of cams, type of followers, motion of the followers, displacement, velocity & acceleration ofcam, construction of cam profile with knife edge, roller and flat faced reciprocating & oscillating followers.6. Gear Train: -Simple, compound, reverted and epicycles gear train analysis of epicycles, sun & planet gear, torques inepicycles trains, bevel epicycles gear, differential gear box.Practical work: -The practical work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on the topics mentioned above and willbe defended by the candidates.
REFERENCE BOOKS:1. Theory of machines - by S.S. Ratan2. Mechanisms & Machine Theory - by S.S. Rao, R,K. Dukkipatti3. Theory of Machine - by V.P. Singh4. Theory of Machine - by Sadhu Singh.5. Theory of Machine - by Belani
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. III (Mechanical Engineering)2ME305- Engineering ThermodynamicsExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 00 03 03 00 03 30 70 03 100 00 1001. IntroductionMacroscopic & Microscopic viewpoint, Thermodynamic system & control volume, Thermodynamic properties,Processes & cycle, Homogenous& Heterogenous Systems, Thermodynamic Equilibrium, Quasistatic Processes,Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics2. First Law of ThermodynamicsClosed System (Non Flow Process), Open System (Flow System), Control volume., application of first law ofthermodynamics.3. Second law of thermodynamicsKelvin plank and Clausius statement, corollary of second law, application of second law, reversibility andirreversibility.4. Entropy.Entropy, T-S plot, Clausius in equality, entropy transfer with heat transfer, entropy generation in close and opensystem, entropy and direction, entropy and disorder.5. AvailabilityAvailable energy, quality of energy, dead state, second law, irreversibility, exergy balance6.Properties of pure substancesP-V, T-S and P-T Diagram, h-s diagram7. Gas mixtureEquation of state, properties of mixture of gas, entropy of gas mixture, law of corresponding states8. Thermodynamic relations, equilibrium and stabilityMaxwell equation, difference and ratio of heat capacity, energy equation, Joule Kelvin effect, ClausiusClapeyron equation.9. Vapour power cyclesRankine cycle, modified rankine cycle, comparison of Rankine and Carnot, binary vapor cycle.10. Gas power cyclesCarnot cycle, Stirling cycle, Ericson cycle, Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, Dual cycle, Lenoir cycle, Atkinson cycle,Brayton cycle, Brayton-Rankine combined cycleREFERENCES BOOK :1) Thermal Engineering P.L.Ballany2) Thermodynamics P.K.Nag3) Thermodynamics & R.YadavHeat Engine Vol.I, II4) Thermodynamics Cengel.
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. III (Mechanical Engineering)2ME306- Fluid MechanicsExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 02 06 04 01 05 30 70 03 100 50 1501. Properties of fluid:Introduction: Fluid, liquids and gases, physical properties such as density, specific weight, viscosity,compressibility, capillarity, surface tension, vapor pressure, cavitations & its all effects and remedies, Thoma’scavitations factor.2. Fluid Statics :Pressure at a point, center of pressure, pressure measurement, with manometers, buoyant force, meta center &meta centric height – analytical and experimental determination.3. Kinematics of fluid flow :Steam line path line, streak line, stream tube, classification of flow steady and unsteady uniform and nonuniform.One type and three dimensional flow definition, Laminar & Turbulent flow, Reynold’s number and criticalvelocity.Continuity equation for three dimensional flow in Cartesian co-ordinates, Euler’s equation and its application,Bernoulli’s equation and its application, venturimeter, pilot tube, generalized energy equation.4. Viscous flow :Flow between two parallel fixed plates, Counter flow, viscous flow through pipes, Hagen – Poisuli’s equation,friction factor, moody diagram, Darcy weight back equation stockes law, measurement of viscosity, viscosityindex, petrof’s equation for journal bearings, power lost in over – coming friction, water hammer & its effectsand remedies, surge tanks.5. Turbulent Flow:Introduction, Reynolds Experiment, Frictional loss in pipe flow, expression for loss of head due to friction inpipes, co-efficient of friction, shear stress in turbulent flow, Reynold expression for turbulent shear stress,velocity distribution in turbulent flow in pipes,6. Compressible Fluid Flow :Thermodynamic concept, speed of a sound wave, Mach number, Mach cone, Mach cone and Mach angle, flowwith friction through pipes, adiabatic and isothermal flow, jet propulsion flow through variable area, flowthrough nozzle, Back pressure variation.7. Dimensional analysis :Fundamental dimension, dimensional homogeneity, Rayleigh’s method and Buckingham’s theorem fordimensional analysis, dimensionless force ratios, Hydraulic similitude model testing.8. Flow Measurement :Measurement of flow with venturimeter, orifice plate, notch, nozzles, bendmeter, flowmeter and rotameter.
Practical work: -The practical work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on the topics mentioned aboveand will be defended by the candidates.REFERENCE BOOKS :1. Fluid Mechanics – (R.K. BANSAL)2. Fluid Mechanics – (K. R. ARORA)3. Fluid Mech. & Fluid Power Engg. (D.S. Kumar)4. Fluid Mechanics – by K.L. Kumar5. Mech. Measurements – by R.K. Jain6. Fluid Mechanics – by A.K. Jain7. Fluid Mechanics – by R.S. Khurmi
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. IV (Mechanical Engineering)2HS401- Engineering Mathematics – IIIExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.04 00 00 04 04 00 04 30 70 03 100 00 1001. Theory of complex variables:Analytic functions, Cauchy – Rieman equation, harmonic functions, line integral, Cauchy’s theorem andCauchy’s integral, Simple form of conform transformation with application of the solution of twodimensional problems.2. Ordinary differential equation (higher order) :Ordinary differential equation with constant coefficient, variation of parameter methods, Cauchy – Eulerdifferential equations, simultaneous differential equations with constant coefficient, applications of ordinarydifferential equation.3. PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS:Formation of partial differential equations, Lagranges first order partial differential equations, directlyintegrable equations, method of separable of variables, application to wave equations, diffusion equationand Laplace equation.4. LAPLACE TRANSFORMS:Definition, Laplace transform of elementary functions, properties of Laplace transform, inverse Laplacetransform, transform of derivatives, transform of intergration, multiplication by t n , division by t,convolution theorem, unit step and heaviside’s unit function, direct-delta function, periodic functions,solution of ordinary linear differential equations, simultaneous equation with constant co-efficient applied toelectrical circuits.5. FOURIER SERIES:Definition of periodic function, Euler’s formula, functions having points of discontinuity, change ofintervals, odd and even functions, expansion of odd or even periodic functions, half range sine and cosineseries, elements of harmonic analysis.6. FOURIER TRANSFORMS:Definition, Fourier integral, Fourier sine and cosine intergration, complex form of Fourier integral, Fouriertransform, Fourier transforms, Fourier sine and cosine transform, inverse Fourier transforms.7. STATISTICS:Probability, Total probability, Independent events, theorem of compound probability, Bay’s theorem, randomvariable, discrete probability distribution, continuous probability distribution, expectation, momentgenerating function, repeated trials, Binominal, Poisson’s and normal distribution applications, calculationof error, probable error, standard error.REFERENCE BOOKS:1. APPLIED MATHEMATICS VOL. I & II BY P.N. WARTIKAR & J.N. WARTIKAR2. HIGH ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS BY B.S. GREWAL3. ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS BY SHRIVASTVA4. TEXT BOOK OF ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS BY A.B. MATHUR & V.P. JAGGI
PART A. MACHINE DESIGN:GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. IV (Mechanical Engineering)2ME402- FUNDAMENTALS OF MACHINE DESIGN & DRAFTINGExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 02 05 03 01 04 30 70 03 100 50 1501. Introduction to machine design:Meaning of Design, Mechanical Engineering design, Introduction to machine design,Phases in design,Requisites of design engineer, Preferred Numbers & Standards, Codes for materials Properties & application ofengineering materials and their selection.2. Design considerations:Direct stresses (Tensile and Compressive), stress-strain diagram, Bending stresses, Bearing stresses, Torsionalstresses, Eccentric loading, Principal stresses, Contact stresses, Castigliano’s theory for determining deflections.Factor of safety and factor influencing it, Theories of failures.3. Design of cotter and Knuckle joint:Design of simple cotter joint, Sleeve and Cotter joint, Cotter foundation bolt, Gib and cotter joint, Design ofknuckle joint, turn Buckle.4. Design of Shaft, Keys & Couplings:Design of shaft & axles on basis of bending, torsion & combined loading, Shaft design on the basis of rigidity,Effect of keyways, Design of Square key, Rectangular key, Kennedy key, Splines, Flexible Shaft, Design ofMuff or Sleeve coupling, Clamp coupling, Flange coupling, Pin-bushed coupling, Universal Joint.5. Design of bolt and riveted joints:Riveted joints: Types of riveted joints, Design of double and triple riveted butt joint with equal and unequalcover plates, Design of riveted joint as per IBR, Design of lap joint, Lozenge jointBolted joints: Definitions, Types of threads, screw fastenings, locking devices for nuts, washers, eye bolts,Efficiency of threads, Static stresses in screw fasteningsEccentric loading in riveted and bolted joints: a) Loading parallel to axis of bolts b) Loading perpendicular toaxis of bolts c) Eccentric loading on circular base6. Design of springs:Types of springs, Terminology related to springs, Types of end in helical springs, Design of helical spring,Wahl’s factor, Spring in combination: parallel and series, Concentric spring, Design of leaf spring, TorsionSpring.7. Design of levers:Types of levers, Design of hand lever, Design of foot lever, Design of cranked lever, Design of lever of a safetyvalve, Design of bell-crank lever, Design of rocker-arm lever.8. Struts and columns:Design of connecting rod, Design of push rod, Design of piston rod9. Power Screw:Types of threads, design of screw with different types of threads used in practice, design of nuts, design of Cclamp, screw jack, design of toggle jack, design of coupler.
PART B and PART C are to be dealt in laboratory.1. INDUSTRIAL DRAFTING :Assembly Drawing, Standard drawing, Machine shop drawing, Pattern shop, Sheet metal drawing.2. Production Drawing :Element of production drawing, Information on Drawing, Tolerances, Manufacturing methods.3. Limits, Tolerances and Fits :Indicating geometrical tolerances on the drawing, Standard followed in industry.Surface Roughness :Roughness and machining symbols, Indication on drawings.PART C. DRAFTING AND MODELING PACKAGE1.Introduction to Computer Aided Drawing :Objectives, introduction to drawing using CAD, Advantages of using CAD. 2 & 3 dimensional modelling,application of CAD.2.Overview of solid modeling :Introduction, development, systems requirements, drawing by drafting package.3. Basics of solid modeling:Introduction of Main Menu, Starting new drawing, drawing editor, entering commands using mouse, pull downmenus, screen menu, getting help from drafting package, data entry, error correcting.4.Working with solid modeling package:Settings Limits, drawing lines, using zoom, erasing lines, drawing lines, saving the work.5. Drawing, Editing, Viewing, dimension and text commandsPlotting the DrawingBasics of Feature based, solid modeling, parametric modeling package. Extruding, Revolving, Sweeping usingmodeling package.PRACTICAL WORK :Part A MACHINE DESIGN :1. Design of machine elements and preparation of report:a) Design of screw, nut and other partsb) Design of leaversc) Design of couplingsd) Design of springe) Design of riveted jointf) Design of shaftg) Design of columnh) design consideration
Part B INDUSTRIAL DRAFTING2. Design & Assembly & detailed drawing of :a) Cotter / Knuckle joint/Connecting Rod (one sheet)b) Coupling (one sheet)The design calculations be included in Part A above. At least one drawing should be production drawing outof above. Drawing should be on A2 size ( both details and assembly.)Preparation of assembly and detail drawings of Machine components (production drawing)PART C Drafting and modeling package :Preparation of assembly & detail drawings of machine components, assembly using drafting package.NOTE : Part B/Part C be taught in laboratory & be tested only in oral examinationas under.REFERENCE BOOKS :(1) Machine Design, vol-1 - by Haideri(2) Machine Design - by V.B.Bhandr(3) Machine Design - by Pandya & Shah (1994 Edition)(4) Machine Design - by Sharma & Agrawal (6th Edit ion, 1997)(5) Mechanical engineering design - by J.E. Shigley(6) Machine Design - by R.B. Gupta(7) Machine Design Vol.-I - by R.C. Patel(8) Machine Design - by Sharma and purohit(9) Machine Design - by R.K. Jain(10) Machine Design – by R.B. Patil
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. IV (Mechanical Engineering)2ME403 - Industrial ElectronicsExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 02 05 03 01 04 30 70 03 100 50 1501. Thyristor and their application :Introduction, thyristor characteristic, two transistor model of thyristro, thyristor turn on/off, di/dt protection,dv/dt protection, thyristor types, series and paralle operation of thyristor, thyristor firing circuits, unijunctiontransistor, pulse transformer and power MOSFET, introduction of temperature control, illumination control,light activated turn-off circuit using DIAC-TRIAC and LDR, automatic water level indicator using SCR, flipflopcircuit using SCR.2. Inverter and ChoppersPrinciple, types, basic circuits, chopper, types, basic circuit, advantage and application.3. Solid state controls of a.c and d.c motorsIntroduction, speed controller of d.c and a.c. single and three phase motor, speed control of synchrony anduniverse motor, overload protection, over voltage protection of d.c. motor4. Basic of ConverterDiode with RC and RL loads, Diodes with LC and RLC loads, freewheeling diodes, single phase half wave andfull wave rectifier, single phase full wave rectifier with RL load, three phase bridge rectifier, three phase bridgerectifier with RL load, overview of cycloconverter5. Variable Frequency DrivePrinciple, components characteristic, limits of control, advantages, application6. A.C. & D.C. drivePerformance characteristic, stator voltage control, rotor voltage control, frequency control, voltage andfrequency control7. Overview of microprocessor and micro controllerFundamental concept, block diagram, overview of working and interfacing, programming8. PLCArchitecture, programming, benefits, application, Introduction to skada.Practical work: -The practical work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on the topics mentioned above and willbe defended by the candidates.REFERENCE BOOKS :(1) Power Electronics – by Muhammad H.Rashid(PHI)(2)Industrial Electronics and Control – by S.K.Bhattacharya, S.Chatterjee(3) Industrial Electronics – by G.K.Mittal(Khanna)(4) Microprocessor architecture programming and application with 8085by Ramesh S.Gonkar(5) Microcontroller 8051 – by Keneth J.Ayla(6) Introduction to programable logic controller – by Gary Dunning
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. IV (Mechanical Engineering)2ME404- DYNAMICS OF MACHINESExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 02 05 03 01 04 30 70 03 100 50 1501. Linkages: -Hook joint, double Hook joint, Oldham’s coupling, intermittent motion mechanism, fluid coupling.2. Static force analysis in Machine: -Basic concept of equilibrium, free body diagram, equilibrium of two force & three force member, Member withtwo forces & a torque, superposition, principle of virtual work.3. Dynamics of Rigid body: -D.A’ Lamberts principle, equivalent offset inertia force, dynamic analysis of four links mechanisms, dynamicanalysis of slider crank mechanisms velocity & acceleration of piston, inertia force in reciprocating engines(Klein’s construction), gyroscopic action, gyroscopic stabilization of ship and vehicle including aeroplane.4. Control force analysis: -Type of governor, watt governor, porter, Proell, Hartnell governor, spring controlled gravity governor, inertiagovernor, characteristics of governor - sensitiveness, hunting, isochronisms, stability, insensitiveness effort of agovernor, power of governor, controlling force of a governor.5. Theory of Gear: -Introduction, Law of gearing, Sliding velocity, Types of tooth profiles, length of path of contact, length of arc ofcontact, contact ratio, interference, min. number of teeth required to avoid interference in gear and pinion,geometry of helical, bevel worm gears.6. Introduction to Synthesis of Mechanisms: -Introduction of Synthesis and analysis, Types of synthesis, synthesis of a four bar chain, Freudenstein equationfor four bar mechanism, precision point for function generator (chebychev spacing method), Bloch method.Practical work: -The practical work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on the topics mentioned above and willbe defended by the candidates.Reference Book: -1. Theory of machine – By S.S. Ratan2. Theory of machine – By V.P. Singh3. Theory of machine – By J.S. Rao & R.V. Dukkipati4. Theory of machine – By Sadhu Singh
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. IV (Mechanical Engineering)2ME405 - NUMERICAL METHODS & COMPUTER PROGRAMMINGExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 02 05 03 01 04 30 70 03 100 50 150NUMERICAL ANALISYS1. Solving nonlinear equationsInterval Halving Revisited, Linear Interpolation Method, Newton’s Method, Muller’s Method, Newton’sMethod for polynomials, Bairstow’s method for quadratic factors2. Solving Sets of equationsMatrix notation, the elimination method, gauss & gauss-jordan methods, Iterative method, system of nonlinearequation3. Interpolation and curve fittingLagrangian polynomials, Divided difference, Least-Squares approximation4. Numerical differentiation and numerical integrationGetting derivatives and integrals numerically, Derivatives from difference table, higher order derivatives,extrapolation techniques, Newton-Cotes integration formulas, the trapezoidal rule, simpson’s rules5.Numerical solution of ordinary differential equationsThe Taylor-Series method, Euler and modified euler method, runge-kutta method, multistep method, milne’smethod, convergence criteria, error and error propagation, systems of equation and higher order equation,comparison of method/stiff equation6. Boundary-Value problems and characteristic-value problemThe Shooting method, solution through a set of equation, derivative boundary condition, rayleigh-ritz,collocation and galerkin method, the finite-element method, eigenvalues by iteration, eigenvalues by QRmethod, application of eigenvalues7. Numerical Solution of Partial Differential equationsRepresentation’s as a difference equation, Laplace’s equation on a rectangular region, interative methods forlaplace’s equation, the poisson equation, derivative boundary conditionsParabolic Partial-Differential Equations ,Hyperbolic Partial-Differential Equations,Approximation offunctions(Chebyshev Polynomials, Economized power series, approximation with rational function, fourierseries)
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING1. Principles of Object Oriented ProgrammingParadigm, Basic Concept, Benefits of OOP, Application of OOP, Structure of C++ program, scope resolutionoperator2. Function in C++The main function, call by reference, return by reference, inline function, default argument, const arguments,function overloading3. Class and ObjectIntroduction, specifying a class, defining member function, C++ program with class, making an outsidefunction inline, private member function, arrays within a class, static data member, static member function,array of objects, object as function arguments, friendly function, returning objects4.Constructors and DestructorsIntroduction, constructor, parameterized constructor, multiple constructor in a class, constructor with defaultarguments, dynamic initialization of objects, copy constructor, destructor5. Operator Overloading and Type ConversionIntroduction, defining operator overloading, overloading unary operator, overloading binary operator, typeconversion6. InheritanceIntroduction, defining derived class, single inheritance, multiple inheritance, multilevel inheritance, hierarchicalinheritance, hybrid inheritance, virtual base class, abstract class, constructor in derived class7. Pointers, Virtual Function and PolymorphismIntroduction, pointer to object, this pointer, pointers to derived class, virtual function, and pure virtual functionPractical work: -The practical work shall be based on and analytical work on the topics mentioned above and will bedefended by the candidates.Reference Books:1. Object Oriented Programming with C++ - E.Balagurusamy2. Teach Your Self C++ - Schmidt3. Object Oriented Programming in Turbo C++ - Lafore Robert4. Applied Numerical Analysis - Curtis F. Gerald, Patrick O.Wheatley5. C language and Numerical Method - C Xavier6. Numerical Method - E. Balagurusamy7. Computer Oriented Numerical Methods - V.Rajaraman
GANPAT UNIVERSITYU. V. Patel College of EngineeringB. Tech. Sem. IV (Mechanical Engineering)2ME406 - Manufacturing TechnologyExamination SchemeTeaching SchemeCreditTheoryPracticalSem. EndGrandLect. Pract. TotalInt.Pract. TotalTuTheory Pract. Total Marks Hrs. Total(Hrs.) (Hrs.) (Hrs.)Asses.03 00 02 05 03 01 04 30 70 03 100 50 1501 Foundry ProcessesClassification of manufacturing processes, advantages of casting processes over the other manufacturingprocesses.2 Sand CastingPatterns, types of patterns, advantages and limitations, pattern rational, pattern allowances, pattern colours,moulding sand, ingredients of moulding sand, sand making, additives of sand, moulding techniques, core andcoreprint, core making, defects arises due to sand casting.3 Principle of Gating and RiseringDifferent types of gates, gating design, advantages and limitations of gating system, riser, types of riser, riserdesign, locating of riser.4 Solidification of CastingNucleation, growth, and different types of solidification, progressive solidification, and directionalsolidification.5 Special Casting TechniquesMetallic moulding, shell moulding, Co 2 process, noback resin moulding, centrifugal casting, die casting,investment casting.6 Melting PracticeCrucible furnace, cupola furnace, induction furnace, and iron-fired furnace.7 Defects in Casting and their remedies.8 Basic Machine toolIntroduction to machining processes, machine tool classification, primary cutting motion and auxiliary motionin machine tool.9 Lathe machineWorking principle, classification, construction and arrangement of engine lathe, lathe specification, mechanism,accessories and attachment for extending processing capacity of engine lathe, turning and allied operations,capstan and turret lathe, estimation of machining time.10 Drilling machineWorking principle, classification, construction and arrangement of radial drilling machine, work holdingdevices, operations, estimation of machining time.
11 Milling machineWorking principle, classification, construction and arrangement of column and knee type milling machine,attachments, automatic feed mechanism, different cutter holding devices, types of milling cutters, elements ofplain milling cutter, peripheral milling, up milling, down milling, work holding devices, operations, gearindexing, estimation of machining time.12 Planer, Shaper and SlotterWorking principle, mechanism, work and tool holding devices, tools, operations and applications, estimation ofmachining time.13 Sawing and Broaching machineWorking principle, classification of sawing machine, types of broaching machines, attachment of broachingmachine, advantages and limitations of broaching machine.14 Grinding machineWorking principle, classification, types of abrasives, manufacturing of grinding wheel, grit, grade and structureof grinding wheel, I.S specification of wheel, Surface Grinding & Centre Less Grinding.15 Microfinishing ProcessesIntroduction, honing, lapping, polishing, buffing and superfinishing.Laboratory Works: -Each candidate shall submit the following work.Pattern making including wood turning.Casting of the above pattern.Plain, step and taper turning.Thread cutting.Machining plane surface on a shaper.Simple job on milling machine.REFERENCE BOOKS :(1) Work shop technology - by Hajara Choudhary Vol-I and Vol-II.(2) Manufacturing technology: metal cutting and machine - by P.N.Rao.(3) Manufacturing technology: foundry, forming and welding - by P.N.Rao.(4) Manufacturing technology - by John P. Lindback.(5) Principles of manufacturing materials and processes - by J.S.Campbell.(6) Processes and material of manufacturing - by Roy A. Lindberg.(7) Foundry technology - by O.P. Khana.
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. V – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME501- MATERIAL <strong>TECH</strong>NOLOGY (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs4 2 6 4 1 5 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Theory of Alloys:Systems, phases and phase rule, structural constituents, equilibrium diagram, cooling curves,lever – arm principle, eutectic reaction, eutectoid reaction, peritectic reaction, Iron carbondiagram, constitution, microstructures & properties of plain carbon steels.2. Heat treatment of steel:Study of heat treatment processes such as annealing, normalizing, spherodizing, hardening,tempering, carburizing, nitriding, cyaniding, induction hardening, flame hardening andhardenability of steel. Application of above processes to machine components & mechanicalequipments such as gears, shaft bearings, turbine blades, crank shafts, pistons etc.3. Steels :Effect of alloying elements such as manganese, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, vanadium,tungsten, cobalt and boron, law alloy steels, stainless steels, tool and die steels, high temperaturealloys, selection of steels for various machines components and mechanical equipments, codingof steels as per ASME and ISI.4. Cast Iron:Constitution, properties of gray, white, malleable and nodular cast irons, seasoning of cast iron,effect of silicon, manganese, sulphur, phosphorous and other elements on the properties of castiron, use of specific grades of cast iron in mechanical field.5. Non – ferrous Alloys:Constitution and properties of the alloys of copper, aluminum, lead, tin, zinc, magnesium etc.,Application of mechanical field.6. Powder Metallurgy:Application of powder metallurgy, advantages of powder metallurgy, manufacturing processes,production of powder ,compacting, sintering, products of powder metallurgy like filters,babbitted bearings for automobiles, cemented carbides, diamond impregnated tools.7 Corrosion of metal and alloys:Mechanism of corrosion, types of corrosion, corrosion prevention techniques.8. Development of Special Materials:Ceramic materials, Materials for nuclear reactors, High temperature alloys, cryogenic materials,Teflon, Araldite etc.,9. Refractory materials:Properties and classifications, selection of refractories for furnaces, boilers, cupola etc.10. Composite Materials: Classification, Characterization & application of composite materials.11. Nano Technology: Introduction to nano technology & nano science, field of application ofnano materials.
12. Polymer Materials: Introduction to polymer, classification and processing of polymermaterials.TERM WORK:The term work to be prepared by the candidates shall consists of technical report of about tenexperiments performed by the candidates out of which at least two experiments will be based oneach of the following topics listed under the headings ofa. Physical metallurgyb. Ferrous metallurgyc. Non-ferrous metallurgyTEXT BOOKS:1. O.P. Khanna, “Text Book of Materials Science & Metallurgy”, Dhanpat Rai and Sons2. Sidney H. Avner, “Introduction to Physical Metallurgy”, T.M.H. PublisherREFERENCE BOOKS:1. V. Raghavan, “Physical Metallurgy – Principles & Practice”, PHI Publisher2. Y.Lakhtin, “Engineering Physical Metallurgy & Heat-Treatment”, C.B.S. Publisher3. T.V.Rajan & C.P. Sharma, “Heat treatment”, PHI Publisher4. Fontanna M.G. & Green N.D, “Corrosion Engineering”, TaTa McGraw Hill5. Chawla Krishan K, “Composite Materials”, Spriger6. George E. Dieter, “Mechanical Metallurgy”, TaTa McGraw Hill7. Poole Charles P; Owens Frank J, “Introduction to Nano Technology”, Johan Wiley andSons. Ltd****************
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. V – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME502- ENERGY CONVERSION & UTILIZATION SYSTEM (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs4 2 6 4 1 5 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Fuel-air cycles: Variation of specific heats, Characteristics of fuel air mixtures, Dissociation orchemical equilibrium loss, Actual valve timing diagram for petrol and diesel engine.2. Fuels for I.C. Engines: Desirable properties of I.C. Engine fuels, Liquid and gaseous fuels,C.V. of fuels and their determination, Required qualities of fuels, Concept about alternate fuels,CNG, LPG, LNG, Biodiesel, H 2 fuels.3. Fuel supply systems:Petrol Engines: Properties of air-petrol mixture, Working of simple carburetor, Types ofcarburetors, Analysis of single jet carburetor with air fuel ratio, Diesel engines: Requirement ofdiesel injection system, Types of injection systems, Fuel pumps, Fuel injectors, Types of nozzles.4. Systems and Testing:Engine cooling system: Necessity of cooling, Air Cooling, Water Cooling,Lubrication systems: Objectives of lubrication, Types of lubricant, Requirement of an ideallubricant, Various engines losses and energy Balance, Measurement of friction power,Measurement of brake power. and Morse Tests.5. Air Cycle Refrigeration: Air refrigeration system working on Bell-Coleman air cycle, Types ofaircraft refrigeration systems, comparison of various air cooling systems used for aircraft.6. Vapor Compression and Absorption Refrigeration: Analysis of vapor compression cycle,Heat balance, Compound compression with intercooler, Cascading, Vapour absorption system,Thermodynamic analysis of absorption system, Non-conventional refrigeration systems, Lossesand efficiencies of components, Desirable properties of refrigerants and solvents. .7. Psychrometry and Psychometric Processes: Preparation of psychometric charts,Psychrometric process, Temperatures, Enthalpy deviation, Psychometric measurements, Mixingprocess, Bypass factor, Apparatus dew point, Sensible heat factor, Adiabatic humidification, Hotwater and Cold water humidification.8. Air Conditioning & Ventilation Systems: Classification of air conditioning system,Humidifiers, Air coolers, Dehumidifiers, Air cleaning, Impurities in air and air cleaners, Airwashers, Ducts, Pressure drop in ducts, Load calculation.
Term work:The term work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on topics mentioned above.Practical & Oral:The candidate shall be examined orally / practically on the base of above term work.BOOKS:1. M.L. Mathur and R.P. Sharma, “A Course in Internal Combustion Engines”, DhanpatRai and Sons Publications.2. C. P. Arora, “Refrigeration and Air conditioning”,Tata McGraw-Hill EducationREFERENCE BOOKS:1. V. Ganeshan, “Internal Combustion Engines”, McGraw Hill Company2. J.B. Heywood, “Internal Combustion Engines Fundamantal”, McGraw Hill3. P.S. Desai, “Advance in Refrigeration and Air conditioning”, Khanna publishers4. P.L.Ballaney, “Refrigeration and Air conditioning”, Khanna publishers5. R.K.Rajput, “Refrigeration and Air conditioning”. S.K. Kataria & Sons
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. V – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME503 - <strong>VI</strong>BRATION & BALANCING OF MACHINES (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs3 2 5 3 1 4 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Balancing: Introduction, Balancing of single revolving mass, Balancing of several massesrevolving in the same plane, Several masses revolving in different planes, Static & Dynamicbalancing, Balancing of reciprocating mass, Balancing of multi cylinder inline engine, Balancingof V-engine, Balancing of radial engine, Direct and reverse crank method of balancing,Balancing machine.2. Cam Dynamics: Graphical and analytical synthesis of cam profile for determination ofvelocity and accelerations, Jump phenomenon, Pressure angle, Polydyne cams, Cross-overshocks, Under cutting phenomenon of cam with roller follower, Polynomial curves, Dynamics ofhigh speed cam systems, Derivations of polynomial cams for displacement, velocity, accelerationand jurk (for 1 degree, 3 degree, 5 degree and 7 degree Polynomial cams).3. Vibration: Introduction, Types of vibrations, Harmonic motion, Beats phenomenon.Undamped free vibrations – Derivation of differential equation, Undamped torsional vibration,Equivalent stiffness of spring combinations.Damped free vibration, Types of damping, viscous damping, Logarithmic decrement, Forcedvibrations, Graphical representation of forces, Transmissibility, Support excitation, TransversevibrationVibration isolation, Critical speed of shafts, Vibration Measuring Instruments like FFT analyzer,stroboscope, accelerometer.Term work: -The term work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on topics mentioned above.Practical & Oral: -The candidate shall be examined orally / practically on the base of above term work.TEXT BOOKS1. S. S. Ratan, “Theory of machines”, Tata- Mcgraw-Hill publication2. G. K groover, “Mechanical vibrations”, Seventh Edition, Nem Chand & Bros., Roorkee.REFERENCE BOOKS:1. S. S. Rao, “ Mechanical Vibration”, 3 rd Edition, Pearson-Hall Edition, 2010.2. C. S. Sharma and Kamlesh Purohit, “Theory of Mechanisms and Machines”, FourthEdition, PHI Publication, 2011.3. Timo and Sinko, “Mechanical Vibrations”.4. V. P. Singh, “Theory of Machines”, Reprint, Dhanpat Rai & Co., 2010.
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. V – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME504 - FLUID POWER ENGINEERING (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs3 2 5 3 1 4 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Flow through pipes: Fluid friction, hydraulic gradient of pipe, losses of head due tofriction in pipe – siphon pipe- Equivalent size of a pipe - parallel flow through pipes, timeof emptying tank through a pipe, time of flow from one reservoir to another through longpipe, branched mains, Hydraulic Power Transmission through pipes2. Hydropower Station: Utilization of energy of water – development of hydraulic powerstations – selection of basic parameters for hydro station – types of hydraulic powerstations – layout of power station.3. Principle of working of Turbo – Machinery:Impact of jet on different types of flat and curved plates, fixed and moving, single andseries of plates, derivation of condition for maximum efficiency, hinged plate and pipebends.4. Hydraulic Turbines:Classification of turbines, Impulse and reaction, Radial, Axial, and mixed flow turbines,Major components of different turbines, Expressions for work done and efficiency ofPelton wheel, Bucket of Pelton wheel, Size and number of buckets, Single jet and multijet Pelton wheel, Francis turbine, Kaplan turbine and Propeller turbines.5. Performance of Turbines:Specific speed, Range of Specific speed for different turbines, performance curves ofturbine, Selection of turbines according to available head, discharge and load, Governingof turbines.6. Pumps, Compressors & Blowers:Rotodynamic pumps, Centrifugal turbine pumps, Submersible pumps, onstructionalfeatures and working theory, pressure rise through impeller, characteristic curves of C.F.pump, Priming, maximum suction limit – Minimum starting speed to deliver thedischarge, specific speed of pumps, suction specific speed. Centrifugal compressors andblowers, Drag and lift on aerofoil blade, pressure rise, Power input, Drag and lift coefficient.Calculation of pressure ratio, static and total Pressure static and totaltemperatures, work done, power input factor, and work Done Factor, pressure coefficient,slip factor, compressibility effect, pre-whirl, Compressor Performance curve, efficiencyand losses, surging and stalling.
7. Miscellaneous Hydraulic Machines :Construction & application of Hydraulic Press, Hydraulic Accumulator, HydraulicIntensifier, Hydraulic Crane, Hydraulic Jack, Hydraulic lift, Hydraulic Ram• Term work: -The term work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on topics mentionedabove• Practical & Oral: -The candidate shall be examined orally / practically on the base of above term work.• BOOKS1. R. K. Bansal, “Fluid mechanics and hydraulic machines”2. D.S. Kumar, “Fluid Power Engineering”• REFERENCE BOOKS:1. Jagdishlal, “Hydraulic and hydraulic machines”2. Vasandani, “Hydraulic Machines”3. Khajuria & Dubey, “Gas turbines & Jet propullision”4. R. K. Rajput, “Fluid mechanics and hydraulic machines”
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. V – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME 505 <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> MEASUREMENT AND METROLOGY (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs3 2 5 3 1 4 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 150METROLOGY1. Introduction to Metrology:Meaning, Necessity and Objectives of Metrology; Standards of Measurement;Elements of Measuring System; Methods of Measurement; Precision and Accuracy;Sources of Errors; Selection and Care of instruments; Standardizing organizations.2. Linear Measurements:Introduction & classification of Linear Measuring Instruments; Least count; workingprinciple, Sources of errors and precautions to be taken, Vernier Height Gauge;Vernier Depth Gauge, Micrometers ;slip gauges, Dial indicators: construction &working; comparators; calibration of various linear measuring instruments;Applications, Advantages & Limitations of commonly used linear measuringinstruments.3. Angular and Taper Measurements:Introduction; Working principle & construction of Angular Measuring instrumentslike Protractors, Sine bars, Applications, Advantages & limitations of commonly usedangular measuring instruments; Taper Measuring instruments: Measurement of tapershafts & holes.4. Limits, Fits and Tolerances:Limits, fits, and dimensional and geometrical or form tolerances, Gauges includingtheir design IS for plug & ring gauges, Interchangeable manufacturing.5. Screw Thread Measurements:Introduction & classification of Threads; Elements, Specification & forms of ScrewThreads; Various Methods for measuring elements of External & Internal ScrewThread; Screw Thread Gauges; errors in Threads.6. Gear Measurements:Introduction & Classification of gears; Forms of gear teeth; Gear tooth terminology;Measurement and testing of spur gear: Various methods of measuring tooth thickness,tooth profile & pitch; Gear Errors.7. Measurement of Surface Finish:Introduction; Surface Texture; Methods of Measuring Surface finish- ComparisonMethods & Direct Instrument Measurement; Sample Length; Numerical Evaluation ofSurface Texture; Indication of Surface roughness Symbols used; Adverse effects ofpoor surface finish.
<strong>MECHANICAL</strong> MEASUREMENT1. Motion Measurement:Measurement of displacement, velocity, acceleration and vibrations by potentiometer,strain gauges, seismic pickups, velocity pickups and acceleration pickups, calibrationof pickups.2. Force :Torque and shaft power measurement, Basic method of force measurements, elasticforce transducers, torque measurement on rotating shaft, shaft power measurement.3. Pressure measurement :Basic method of pressure measurement, dead weight gauges and manometers, elastictransducers and force balance transducer.4. Flow measurement :Gross flow rate measuring meters, constants area, variable pressure drop meters(obstruction meters) constant pressure drop variable arc meters (Rotameter), local flowvelocity magnitude and direction meters, pitot static tube and vawtube, Hotwireanemometer velometer.5. Temperature measurement :Measurement of temperature by liquid – in – glass thermometers, pressurethermometers, thermocouples, their calibration, resistance thermometer, bimetallicthermometer, thermistors, radiation and optical pyrometers.TERM WORK :The term work shall be based on the experimental work on the topic mentioned above.PRACTICAL/ORAL :The candidate shall be examined on the basis of continuous assessment of above teamwork.TEXT BOOKS :1. R.K. Jain, Khanna Publishers - A Text Book of Engineering Metrology2. M.Mahajan, Dhanpat Rai, New Delhi - A Text Book of Metrology3. D.S. Kumar, Metropolitan book Co. - Mechanical Measurement & Control4. R.K.Rajput, S.K.Kataria & Sons. - Mechanical measurement and instrumentationREFERENCE BOOKS :1. Dotson & Connie, Cengage Learning India Pvt. Ltd. - Dimensional Metrology2. By C.Elanchezhian, Eswar Press, Chennai - Engineering Metrology3. I.S. 919 Recommendation for limits and fits for engg.4. Galyer & Shotbolt (Elbs) - Metrology for Engineers5. K.J. Hume, Kalyani Publisher - Engineering Metrology6. Thomas G. Beckwith, Pearson Edu. - Mechanical Measurement7. S.P.Venkateshan, Ane Books India - Mechanical Measurement8. Nakra & Chaudary,Tata McGraw Hill - Instrumentation, Measurements and Control9. I.C. Gupta, Dhanpat Rai and Sons. - A Text Book of Engineering Metrology
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. V – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME506 - CAD SOFTWARE PACKAGES (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs- 3 3 - 2 2 - - - - 25 25 50 501. Introduction to CAD Software PackagesSolid works 2011, Nature of Solid works 2011, System requirements, important terms anddefinitions, file menu options, managing file, Function of mouse, various toolbars.2. SketcherConfiguring for sketcher, Setting sketching environment, Creating sketcher geometry, Modifyingsketcher geometry, Dimensioning sketcher geometry, Constraining geometry, To study ofDifferent entities : line, circle, rectangle, arc, ellipse, text, plane, point, fillet, polygon, straightslot, trim entity, convert entity, offset entity, mirror entity, linear sketch pattern, move entity,rapid sketch, quick sketch, repair sketch, Display delete relation.3. Part ModelingBasic (Parent child relationship), Base feature, Create datum’s features, Edit features,Engineering features, Advanced features, Creating drawing, Working model views,Dimensioning and detailing your models, Controlling drawing details with layers, Importing andexporting data, Features: extrude boss/base, revolved boss/base, swept boss, lofted boss,boundary boss, extrude cut, hole wizard, revolve cut, swept cut, lofted cut, boundary cut, fillet,pattern, rib, draft, dome, mirror, reference geometry, curves, instant 3D4. AssemblyReading top-down assemblies, creating bottom-up assemblies, Placement constraints, Assemblydatum planes, assembling the components, redefining the components of the assembly,reordering the components, modifying the components of the assembly, the bill of material,Mechanism & animations: Motor, Spring , Contact, Gravity, Animation wizard, Motion studyproperties, Save animation, Play back mode. Edit component, insert component, mate, smartfasteners, move component, show hidden component, assembly features, reference geometry,Linear component pattern, bill of materials, exploded view, Interference detection, clearanceverification, hole alignment, mass property, Section property, sensor, assembly visualization,symmetry check.5. DrawingView lay out, model view, projected view, auxiliary view, section view, detail view, broken outsection, break, crop view. Annotation : smart dimension, model items, spell checker, formatpainter, note, balloon, surface finish, weld symbol, hole callout, geometric tolerances, datumfeatures, datum target, area hatch/fill, blocks, centre mark, centre line, revision symbol, tables.
• Term work: -The term work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on topics mentionedabove• Practical & Oral:The candidate shall be examined orally / practically on the base of above term work.REFERENCE BOOKS:1. Sham Tikoo, “Solid works for engineers & designers”, Release – 2011TEXT BOOK:1. Bible, Matt Lombard, “Solid works 2010”, Wiley Publishing, Inc.Manual from the solid works web site
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. <strong>VI</strong> – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME601 - CONTROL SYSTEM ENGINEERING (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemesterGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract. TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs3 2 5 3 1 4 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501 Fundamentals of Modern Control SystemBasic Block Diagram of Closed Loop Control System, Control System Components ,Discrete and Automated Control of Industrial Process,2 Representation of Mechanical System in Control EngineeringBlock Diagram representation, Mathematical Modeling, transfer function of Hydraulic,Pneumatic and Thermal Systems and Components. Characteristic of hydraulic componentscontrol valves, sources of hydraulic power hydraulic meters, pitons and transmission,elements of circuit design, Accumulation control circuit such as position control and speedcontrol circuit.Pneumatic systems pneumatic power supply, Amplifiers with different controlling actions,Pneumatic valves and cylinders, theory of four way and pilot valves.3 Analysis of Control SystemTransient response of first order and second order systems to step, ramp and sinusoidalinput, steady state errors, Applications of Laplace transform methods, Reuth’sstability criteria and root locus methods improving system performance. Sinusoidalresponse of liner control system, Magnitude and phase curve, Bode plots, determinationof absolute and relative stability from Bode plot.4 Fuzzy LogicConcept of fuzzy logic, basic notions, Block diagram for typical fuzzy system , FuzzyControllers, Application of Fuzzy System5 Industrial ControllersPD, PI and PID Controllers and functions , Programmable logic Controllers (PLC)-functions , ladder Diagram , Control Logic and Industrial Process Control6 Case studiesDetail study and analysis of Control Systems for mechanical engineering systems, thermalpower plants, Rolling Mills, Boiler, refrigeration plants , central air-conditioning plantsand automobiles.TEXT BOOKS:1. Katsuhiko Ogata, “Modern Control Engineering”, Prentice – Hall of India.2. M. Gopal, “Control Systems - Principles and Design”, Prentice Hall of India3. S.R.Majumdar, “Oil Hydraulics”, Tata McGraw Hill4. S.R.Majumdar, “Pneumatics systems”, Tata McGraw HillREFERENCE BOOKS:1. Benjamin C Kao, “Automatic Control Systems - Seventh Edition”, Tata McGraw Hill2. Verma, “Automatic Control Systems”3. W. Bolton, “Industrial Control & Instrumentation” <strong>University</strong> Press (I) Ltd, Hyderabad.*****************
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. <strong>VI</strong> – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME602 - METAL FORMING & FABRICATION <strong>TECH</strong>NOLOGY (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemesterGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract. TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs4 2 6 4 1 5 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Fundamentals of metal forming:Classification of forming processes, mechanics of metal working, temperature in metal working,hot working, cold working, strain rate effects, metallurgical structure, workability, residualstresses.2. Primary metal working and processes:A. Forging: Classification of forging processes, forging equipment, forging defects.B. Rolling of metals: Classification of rolling processes, principle of metal rolling mills,simplified analysis of rolling load, rolling variables, defects in rolled products.C. Extrusion: Classification of extrusion process, extrusion equipments, hot extrusion,deformation, lubrication and defects in extrusion, cold extrusion, hydrostatic extrusion, extrusionof tubing, production of seamless pipe and tubing.D. Drawing of rods, wires and tubes: Sizing, coining and embossing.3. Cold forming (Sheet metal working):A. Deep drawing, squeezing, bending, blanking, piercing, notching etc. metal spinningoperations and applications.B. Press work: Types of press, drive mechanism for presses, terminology, press elements and dieclassification.4. Plastic Processing:Introduction, Plastic part manufacturing processes such as Compression moulding, Transfermoulding, Injection moulding, Extrusion moulding, Blow moulding etc..5. Fabrication process:A. Introduction to fabrication: mechanical, adhesive, weldingWelding: principle of welding, classification of welding and allied processes, weldingterminology, electrode coatings, flux, electrodesB. Oxy-Fuel welding: oxy-acetylene gas welding & cutting: Principle, equipment, applicationC. Arc Welding: Principle of arc, power source and characteristics, edge preparation, types ofjoints, equipment for AC & DC power source, coding and classification of electrodes, shieldedmetal arc welding, gas metal arc welding, gas tungsten arc welding, submerged arc welding,carbon arc welding, electro slag welding, electro gas welding, flux cored arc weldingD. Resistance welding: Principle of resistance welding, heat balance, spot welding, seamwelding, projection welding, upset butt welding, flash butt welding
E. Other welding process: electron beam welding, laser beam welding, Thermit welding, plasmaarc welding, and atomic hydrogen weldingF. Solid state welding process: friction welding, explosion welding, cold welding, diffusionwelding, forge welding, ultrasonic weldingG. Welding defects, causes and their remediesH. Soldering, Brazing and Braze welding: process, description and application.TEXT BOOKS:1. S. Kalpakajain, “Manufacturing Engg. And Technology” PHI/Pearson.2. P.N. Rao, “Manufacturing Technology (Foundry, Forming and Welding)”3. O.P. Khanna, “Text Book of Welding Technology”REFERENCE BOOKS:1. R.S Parmar, “Text Book of Welding Technology”2. Jain & Gupta, “ Production Technology”3. P.C. Sharma, “A Textbook of Production Engg.”4. Dieter, “Mechanical Metallurgy”5. Higgins, “Material Science Vol. I & II”6. Lindberg, “Manufacturing Process”7. B.E. Rosset, “Welding Engg.”8. Little, “Welding Engineering”
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.<strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. <strong>VI</strong> - <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME603 - HEAT & MASS TRANSFER (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalInt. SemesterGrandLect Pract Total Lect. Pract. TotalInt. SemAsses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs4 2 6 4 1 5 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Introduction: Modes of heat transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation.2. Conduction: Fourier’s law. General three-dimensional heat conduction equation inCartesian, cylindrical and spherical co-ordinates. One dimensional steady conductionthrough plane wall, cylinder and sphere, dependence of thermal conductivity of gases,liquids, metals, refractory material, Critical thickness of insulation, Temperaturedistribution and Heat flow in steady state through plane, cylindrical and spherical wallswith constant and variable thermal conductivity, Composite walls, Electrical analogy.Heat transfer from fins of uniform cross section.3. Convection: Principles of convection, Energy equation of the boundary layer on flatplate, The relation between fluid friction and heat transfer, Dimensional analysis,Empirical and practical relations for forced convection heat transfer, Free convection heattransfer on a vertical flat plate, Empirical relations for free convection, Free convectionform horizontal plates and inclined surfaces.4. Radiation: Physical mechanism, Radiation properties, Radiation shape factors, Basiclaws of radiation. black and grey surfaces, Heat transfer in presence of re-radiatingsurfaces. Effect of radiation shields.5. Heat Exchangers: Classifications of heat exchangers, Fouling factors, long meantemperature difference, Effectiveness-NTU, comparison and selection.6. Mass Transfer: Fick’s law of diffusion, Diffusion In gases, The mass transfercoefficient, Similarity between heat and mass transfer, heat and mass transfer inhumidification and dehumidification, Application to Engineering problems.• Term work: -The term work shall be based on experimental and analytical work onabovetopics mentioned• Practical & Oral: -The candidate shall be examined orally / practically on the base of above term work.
BOOKS:1. J.P. Holman, “Heat Transfer” McGraw Hill Book Co., (2011).2. R.K.Rajput S. Chand & Company Limited, “Heat & Mass Transfer”3. S.P. Sukhatme, “Heat Transfer” Universities Press Private Ltd.REFERENCE BOOKS:1. D.S. Kumar, “Heat and Mass Transfer”, Dhanpat Rai Publication.2. Mahesh M Rathore, “Engineering Heat and Mass Transfer” Laxmi Publications.3. Eckert and Drake, “Heat and Mass Transfer” McGraw Hill
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB.<strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. <strong>VI</strong> – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME604 - POWER PLANT ENGINEERING (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalPractInt. SemesterGrandLect Pract Total Lect.TotalInt. Sem.Asses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs3 2 5 3 1 4 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Modern Thermal Power Station:General layout of modern thermal power plant, Site selection, Presents status of powergeneration in India.2. High Pressure Boilers & Accessories:Unique features and advantages of high pressure boilers, LaMont, Benson, Loeffler, Schmidt-Hartmann, Velox, Supercritical, Supercharged and fluidized bed combustion boiler. Differenttypes of super-heaters, Re-heaters, Economizers, Air pre-heaters, Methods of superheat control,Corrosion in boilers and its prevention.3. Coal & Ash Handling:Fuels for thermal power plant, Out plant and In plant handling of coal, Preparation and transferof coal, Types of conveyors, Pulverized mills, Necessity of ash disposal, Mechanical, Hydraulic,Pneumatic and Steam jet ash handling system, Dust collection and its disposal, Mechanical dustcollector, Electrostatic precipitator.4. Fuel Feeding and Burning:Different types of liquid fuel burners such as Evaporation type, Rotating type, Re-circulatingtype, and Atomizing type, Pulverized fuel burners such as long flame, U – flame, Streamlined, Short flame, Turbulent tangential, Cyclone burners.5. Draught System:Natural draught- estimation of height of chimney, Maximum discharge, Forced, Induced andbalanced draught, Power requirement by fans.6. Condensers & Cooling Towers:Jet and Surface Condensers, Air leakages in condensers, Vacuum efficiency, Condenser watercooling systems, Various water cooling methods, Performance of condensers and cooling towers,Condensate pump.7. Feed Water treatment:Different types of impurities in water, Effects of impurities, Different methods of watertreatment, Internal boiler water treatment, External water treatment system, Sedimentation,Filtration, Removal of dissolved gases, Removal of solids.
8. Pollution and its control:Different pollutant and their effects, Control of particulates cyclone & precipitators, Control ofSo 2 , No x , Control of atmospheric pollution, Noise pollution and its control.9. Combined Cycle Co-generation Power Plant:Brayton cycle, Layout and Working principle of combined cycle and cogeneration power plants,Advantages over conventional gas turbine and steam turbine power plants, calculation ofefficiency.10. Nuclear Power Plant:Principles of Nuclear Energy, Types of reactors, Selection of materials for reactor components,Economics of nuclear power plants, Safety measures for nuclear power plants.Term work: -The term work shall be based on experimental and analytical work on topics mentionedabovePractical & Oral: -The candidate shall be examined orally / practically on the base of above term work.BOOKS:1. Domkundwar and Arora, “Power Plant Engineering” Dhanpat rai & Co.2. R.K.Rajput, “Power Plant Engineering” Laxmi publications ltd.REFERENCE BOOKS:1. Dr. P.C. Sharma, “Power Plant Engineering” S.K. Kataria & Sons, Delhi2. P.K. Nag, “Power Plant Engineering” Tata Mc-Grahill Co., Delhi3. Nagpal, “Power Plant Engineering”, Khanna Publishers, Delhi.
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. <strong>VI</strong> – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME605 - DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS(CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalPractInt. SemesterGrandLect Pract Total Lect.TotalInt. Sem.Asses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs4 2 6 4 1 5 30 70 3 100 25 25 50 1501. Manufacturing consideration in design:Design considerations for various manufacturing processes, Assembly, thermal, wear, ergonomicand aesthetic, Selection of materials for various components, Standardization.2. Design of welded joints:Weld design for fillet joints, lap joints and butt joints and eccentrically loaded welded joints.3. Fatigue loading:Completely reversed or cyclic stresses; stress v/s cycle (S-N) curves; fatigue and endurancelimit; effect of surface finish, size and loading on endurance strength; Finite and infinite life;design for finite and infinite life; stress concentration, notch sensitivity and fatigue stressconcentration factor; factor of safety for fatigue loading; Gerber, Goodman and Soderbergcriteria for design of parts subjected to variable loading; Combined variable normal and shearstresses; applications of fatigue loading for design of shafts, axles etc.4. Design of pressure vessels:Classification of pressure vessels; design of thin cylindrical and spherical shells subjected tointernal pressure, design of thick cylindrical shell subjected to internal and external pressure.Design of interference joints, press / shrink fitted assemblies, Design of cylinder covers, coverplates, pipes, pipe flanges for pipe joints, introduction to creep for pressure vessel design.5. Design of Belt Drive:Types of belt drives and its selection, materials for belt and their properties, velocity ratio, centerdistance and length of belt for various types of belt drives, power transmitted by flat and V beltsdrives, design of belt drives, selection of flat and V belts using manufacturers catalogues.6. Design of clutches and brakes:Positive clutches, friction clutches, single plate, multiple plate and centrifugal clutches, Designof band brake, external and internal shoe breaks internal expanding shoe brakes, design of discbrakes. Application of friction clutches and brakes in automotive and industrial machinery.
TERM WORK:1. Exercise on material selection of various machine elements2. Preparation of design report consisting of one of the following problems along withdrawing (parts and assembly). Such as,• Brakes – external shoe brake, internal expanding shoe brakes.• Clutches–cone, disc, single and multiple plate and centrifugal clutches.• Hydraulic press.• Power screw applications like fly press, screw press etc.3. Preparation of design report for at least ten minor problems and may be solved bycomputer programme.Practical / Oral: The candidate shall be examined on the basis of term-work.TEXT BOOKS :1. V. B. Bhandari, “Design of Machine Elements”, Second Edition, Tata McGraw HillPublication 2007.2. Farazdak Haideri, ”Design of Machine Elements”, Vol. II& III, Nirali Prakashan, PuneREFERENCE BOOK:1. Joseph Shiglay, ”Mechanical Engineering Design”, Second Edition, Mc-Graw HillPublication.2. Sharma & Agrawal, “Machine Design”, Eleventh Edition (Reprint 2008-09), S. K.Kataria & sons Publication.3. “P S G Design Data Book”, PSG College, Coimbatore.4. R. C. Patel, S. S. Sikh and A. D. Pandya, “Machine Design”, Twelth Edition, G.Jamnadas & Co., 1998.
GANPAT UNIVERSITYB. <strong>TECH</strong>. <strong>SEM</strong>. <strong>VI</strong> – <strong>MECHANICAL</strong> ENGINEERING2ME606 - <strong>SEM</strong>INAR (CBCS)Teaching Scheme Credit Exam. SchemeTheoryPracticalPractInt. SemesterGrandLect Pract Total Lect.TotalInt. Sem.Asses End TotalTotal TotalAsses EndMarks Hrs- 2 2 - 1 1 - - - - 25 25 50 50Students have to prepare brief report on Advance topics on any subject of MechanicalEngineering. They have to present highlights of seminar topic in the presents of students,students guide and examiners.