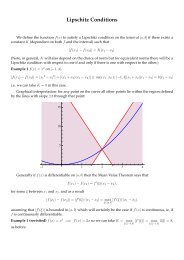
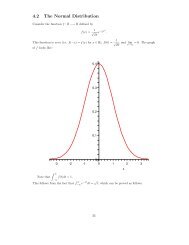
Tanja Lange
Tanja Lange
Tanja Lange
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 1
Elliptic strikes backD. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 2
To face the challenge, to take thecompetition to a completely new level. . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 3
. . . elliptic has to reconsider its form . . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 4
. . . has to abstract from its Weierstrass formD. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 5
. . . has to undergo severe isomorphictransformations . . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 6
. . . until it finds . . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 7
. . . its true . . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 8
. . . normal form!D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 9
Long, long ago . . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 10
Euler 1761“ Observationes de Comparatione Arcuum CurvarumIrrectificabilium”1y 2 = 1 − nx21 − x 2 ⇔ x2 + y 2 = 1 + nx 2 y 2 .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 11
Euler 1761Euler gives doubling and (special) addition for (a, A) ona 2 + A 2 = 1 − a 2 A 2 .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 12
Gauss, posthumouslyGauss gives general addition for arbitrary points on1 = s 2 + c 2 + s 2 c 2 .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 13
Ex uno pluraHarold M. Edwards, Bulletinof the AMS, 44, 393–422, 2007x 2 + y 2 = a 2 (1 + x 2 y 2 ), a 5 ≠ adescribes an elliptic curve overfield k of odd characteristic.Every elliptic curve can bewritten in this form – oversome extension field.Ur-elliptic curvex 2 + y 2 = 1 − x 2 y 2needs √ −1 ∈ k transform.Edwards gives addition law for this generalized form,shows equivalence with Weierstrass form, provesaddition law, gives theta parameterization . . .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 14
Elliptic geared for cryptoIntroduce further parameter d to cover more curves over kx 2 (+ y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ), c, d ≠ 0, dc 4 ≠ 1.)xP y Q + y P x QP + Q =c(1 + dx P x Q y P y Q ) , y P y Q − x P x Q.c(1 − dx P x Q y P y Q )Neutral element is (0, c), this is an affine point!−(x P , y P ) = (−x P , y P ).D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 15
Elliptic geared for cryptoIntroduce further parameter d to cover more curves over kx 2 (+ y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ), c, d ≠ 0, dc 4 ≠ 1.)xP y Q + y P x QP + Q =c(1 + dx P x Q y P y Q ) , y P y Q − x P x Q.c(1 − dx P x Q y P y Q )Neutral element is (0, c), this is an affine point!−(x P , y P ) = (−x P , y P ).[2]P =(xP y P + y P x Pc(1 + dx P x P y P y P ) , y P y P − x P x Pc(1 − dx P x P y P y P )).D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 15
Elliptic geared for cryptoIntroduce further parameter d to cover more curves over kx 2 (+ y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ), c, d ≠ 0, dc 4 ≠ 1.)xP y Q + y P x QP + Q =c(1 + dx P x Q y P y Q ) , y P y Q − x P x Q.c(1 − dx P x Q y P y Q )Neutral element is (0, c), this is an affine point!−(x P , y P ) = (−x P , y P ).[2]P =(xP y P + y P x Pc(1 + dx P x P y P y P ) , y P y P − x P x Pc(1 − dx P x P y P y P )Unified group operations!).D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 15
Elliptic geared for cryptoIntroduce further parameter d to cover more curves over kx 2 (+ y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ), c, d ≠ 0, dc 4 ≠ 1.)xP y Q + y P x QP + Q =c(1 + dx P x Q y P y Q ) , y P y Q − x P x Q.c(1 − dx P x Q y P y Q )A = Z P · Z Q ; B = A 2 ; C = X P · X Q ; D = Y P · Y Q ;E = d · C · D; F = B − E; G = B + E;X P +Q = A · F · ((X P + Y P ) · (X Q + Y Q ) − C − D);Y P +Q = A · G · (D − C); Z P +Q = c · F · G.D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 15
Elliptic geared for cryptoIntroduce further parameter d to cover more curves over kx 2 (+ y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ), c, d ≠ 0, dc 4 ≠ 1.)xP y Q + y P x QP + Q =c(1 + dx P x Q y P y Q ) , y P y Q − x P x Q.c(1 − dx P x Q y P y Q )A = Z P · Z Q ; B = A 2 ; C = X P · X Q ; D = Y P · Y Q ;E = d · C · D; F = B − E; G = B + E;X P +Q = A · F · ((X P + Y P ) · (X Q + Y Q ) − C − D);Y P +Q = A · G · (D − C); Z P +Q = c · F · G.Needs 10M + 1S + 1C + 1D + 7A.At least one of c, d small: x 2 + y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ) andx 2 + y 2 = ¯c 2 (1 + ¯dx 2 y 2 ) isomorphic if c 4 d = ¯c 4 ¯d.¯c 4 ¯d = (c 4 d) −1 gives quadratic twist.D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 15
Unified? Unified!No exceptional cases? What if a denominator is zero?If d is not a square then Edwards addition law iscomplete: For x 2 1 + y2 1 = 1 + dx2 1 y2 1 andx 2 2 + y2 2 = 1 + dx2 2 y2 2 always dx 1x 2 y 1 y 2 ≠ ±1.Outline of proof:If (dx 1 x 2 y 1 y 2 ) 2 = 1 then (x 1 + dx 1 x 2 y 1 y 2 y 1 ) 2 =dx 2 1 y2 1 (x 2 + y 2 ) 2 . Conclude that d is a square. But d is nota square!If d is not a square then there is exactly one point oforder 2 and two of order 4. Otherwise the full 2-torsiongroup is k-rational.Plane curve has 2 singular points at infinity; theirblow-ups are defined over k( √ d) and have order 2.D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 16
Fastest unified addition-or-doubling formulSystemCost of unified addition-or-doublingProjective 11M+6S+1D; see Brier/Joye ’03Projective if a 4 = −1 13M+3S; see Brier/Joye ’02Jacobi intersection 13M+2S+1D; see Liardet/Smart ’01Jacobi quartic 10M+3S+1D; see Billet/Joye ’01Hessian 12M; see Joye/Quisquater ’01Edwards (c = 1) 10M+1S+1DExactly the same formulae for doubling (nore-arrangement like in Hessian where2(X 1 : Y 1 : Z 1 ) = (Z 1 : X 1 : Y 1 ) + (Y 1 : Z 1 : X 1 );no if-else)No exceptional cases if d is not a square. Formulaecorrect for all affine inputs (incl. (0, c), P + (−P )).D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 17
Spotlight on the transformationCurve x 2 + y 2 = c 2 (1 + dx 2 y 2 ) in Edwards form is birationallyequivalent to curveE : (1/e)v 2 = u 3 + (4/e − 2)u 2 + uin Montgomery form, where e = 1 − dc 4 .Let (x 1 , y 1 ) + (x 2 , y 2 ) = (x 3 , y 3 ) on Edwards curve. PutP i = ∞ if (x i , y i ) = (0, c);P i = (0, 0) if (x i , y i ) = (0, −c);P i = (u i , v i ) if x i ≠ 0, where u i = (c + y i )/(c − y i ) andv i = 2c(c + y i )/(c − y i )x i .Then P i ∈ E(k) and P 1 + P 2 = P 3 .D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 18
D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 19
D. J. Bernstein & T. <strong>Lange</strong> http://hyperelliptic.org/tanja/newelliptic – p. 20