Chapter 5 Measurement of Atmospheric Pressure
Chapter 5 Measurement of Atmospheric Pressure
Chapter 5 Measurement of Atmospheric Pressure
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
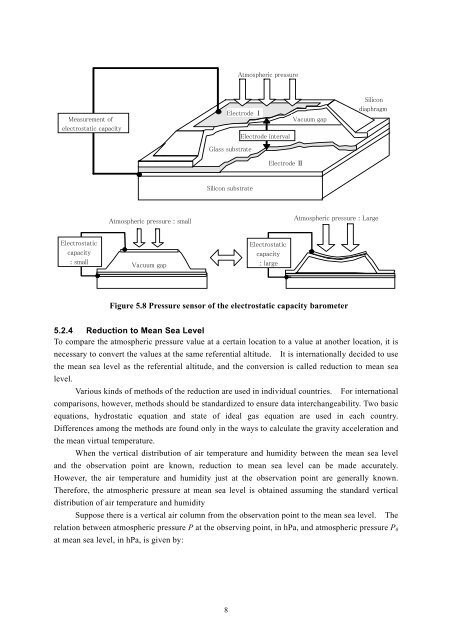
<strong>Atmospheric</strong> pressure<strong>Measurement</strong> <strong>of</strong>electrostatic capacityElectrode ⅠElectrode intervalVacuum gapSilicondiaphragmGlass substrateElectrode ⅡSilicon substrate<strong>Atmospheric</strong> pressure : small<strong>Atmospheric</strong> pressure : LargeElectrostaticcapacity: smallVacuum gapElectrostaticcapacity: largeFigure 5.8 <strong>Pressure</strong> sensor <strong>of</strong> the electrostatic capacity barometer5.2.4 Reduction to Mean Sea LevelTo compare the atmospheric pressure value at a certain location to a value at another location, it isnecessary to convert the values at the same referential altitude. It is internationally decided to usethe mean sea level as the referential altitude, and the conversion is called reduction to mean sealevel.Various kinds <strong>of</strong> methods <strong>of</strong> the reduction are used in individual countries. For internationalcomparisons, however, methods should be standardized to ensure data interchangeability. Two basicequations, hydrostatic equation and state <strong>of</strong> ideal gas equation are used in each country.Differences among the methods are found only in the ways to calculate the gravity acceleration andthe mean virtual temperature.When the vertical distribution <strong>of</strong> air temperature and humidity between the mean sea leveland the observation point are known, reduction to mean sea level can be made accurately.However, the air temperature and humidity just at the observation point are generally known.Therefore, the atmospheric pressure at mean sea level is obtained assuming the standard verticaldistribution <strong>of</strong> air temperature and humiditySuppose there is a vertical air column from the observation point to the mean sea level. Therelation between atmospheric pressure P at the observing point, in hPa, and atmospheric pressure P 0at mean sea level, in hPa, is given by:8




![関東地方の「紅葉の見ごろ予想」[PDF形式:250KB] - 気象庁](https://img.yumpu.com/47747063/1/184x260/pdf250kb-.jpg?quality=85)

![雨に関する各市町村の50年に一度の値一覧[PDF形式:417KB] - 気象庁](https://img.yumpu.com/47450161/1/190x134/50pdf417kb-.jpg?quality=85)
![1か月予報[九州北部地方]解説資料](https://img.yumpu.com/47153516/1/184x260/1.jpg?quality=85)
![職員募集案内パンフレット[PDF形式:約9MB] - 気象庁](https://img.yumpu.com/45714300/1/184x260/pdf9mb-.jpg?quality=85)


![ダウンロードファイル[PDF形式: 約15MB] - 気象庁](https://img.yumpu.com/43657928/1/190x135/pdf-15mb-.jpg?quality=85)