EUCAST posters at ECCMID 2012
EUCAST posters at ECCMID 2012
EUCAST posters at ECCMID 2012
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
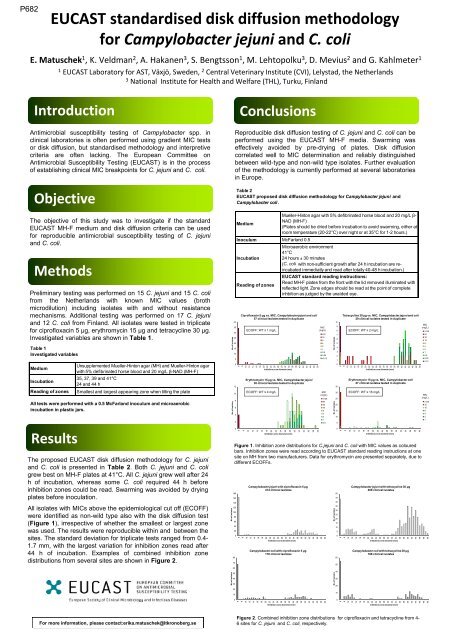
66668888066668888P682<strong>EUCAST</strong> standardised disk diffusion methodologyfor Campylobacter jejuni and C. coliE. M<strong>at</strong>uschek 1 , K. Veldman 2 , A. Hakanen 3 , S. Bengtsson 1 , M. Lehtopolku 3 , D. Mevius 2 and G. Kahlmeter 11<strong>EUCAST</strong> Labor<strong>at</strong>ory for AST, Växjö, Sweden, 2 Central Veterinary Institute (CVI), Lelystad, the Netherlands3N<strong>at</strong>ional Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), Turku, FinlandIntroductionAntimicrobial susceptibility testing of Campylobacter spp. inclinical labor<strong>at</strong>ories is often performed using gradient MIC testsor disk diffusion, but standardised methodology and interpretivecriteria are often lacking. The European Committee onAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (<strong>EUCAST</strong>) is in the processof establishing clinical MIC breakpoints for C. jejuni and C. coli.ObjectiveThe objective of this study was to investig<strong>at</strong>e if the standard<strong>EUCAST</strong> MH-F medium and disk diffusion criteria can be usedfor reproducible antimicrobial susceptibility testing of C. jejuniand C. coli.MethodsPreliminary testing was performed on 15 C. jejuni and 15 C. colifrom the Netherlands with known MIC values (brothmicrodilution) including isol<strong>at</strong>es with and without resistancemechanisms. Additional testing was performed on 17 C. jejuniand 12 C. coli from Finland. All isol<strong>at</strong>es were tested in triplic<strong>at</strong>efor ciprofloxacin 5 µg, erythromycin 15 µg and tetracycline 30 µg.Investig<strong>at</strong>ed variables are shown in Table 1.Table 1Investig<strong>at</strong>ed variablesMediumIncub<strong>at</strong>ionReading of zonesResultsUnsupplemented Mueller-Hinton agar (MH) and Mueller-Hinton agarwith 5% defibrin<strong>at</strong>ed horse blood and 20 mg/L β-NAD (MH-F)35, 37, 39 and 41°C24 and 44 hSmallest and largest appearing zone when tilting the pl<strong>at</strong>eAll tests were performed with a 0.5 McFarland inoculum and microaerobicincub<strong>at</strong>ion in plastic jars.The proposed <strong>EUCAST</strong> disk diffusion methodology for C. jejuniand C. coli is presented in Table 2. BothC. jejuni and C. coligrew best on MH-F pl<strong>at</strong>es <strong>at</strong> 41°C. All C. jejuni grew well after 24h of incub<strong>at</strong>ion, whereas some C. coli required 44 h beforeinhibition zones could be read. Swarming was avoided by dryingpl<strong>at</strong>es before inocul<strong>at</strong>ion.All isol<strong>at</strong>es with MICs above the epidemiological cut off (ECOFF)were identified as non-wild type also with the disk diffusion test(Figure 1), irrespective of whether the smallest or largest zonewas used. The results were reproducible within and between thesites. The standard devi<strong>at</strong>ion for triplic<strong>at</strong>e tests ranged from 0.4-1.7 mm, with the largest vari<strong>at</strong>ion for inhibition zones read after44 h of incub<strong>at</strong>ion. Examples of combined inhibition zonedistributions from several sites are shown in Figure 2.No of isol<strong>at</strong>esNo of isol<strong>at</strong>esNo of isol<strong>at</strong>esNo of isol<strong>at</strong>esReproducible disk diffusion testing of C. jejuni and C. coli can beperformed using the <strong>EUCAST</strong> MH-F media. Swarming waseffectively avoided by pre-drying of pl<strong>at</strong>es. Disk diffusioncorrel<strong>at</strong>ed well to MIC determin<strong>at</strong>ion and reliably distinguishedbetween wild-type and non-wild type isol<strong>at</strong>es. Further evalu<strong>at</strong>ionof the methodology is currently performed <strong>at</strong> several labor<strong>at</strong>oriesin Europe.40353025201510180160140120100807060504030201050121086420806040200ConclusionsTable 2<strong>EUCAST</strong> proposed disk diffusion methodology for Campylobacter jejuni andCampylobacter coli .Mueller-Hinton agar with 5% defibrin<strong>at</strong>ed horse blood and 20 mg/L β-NAD (MH-F)Medium(Pl<strong>at</strong>es should be dried before incub<strong>at</strong>ion to avoid swarming, either <strong>at</strong>room temper<strong>at</strong>ure (20-22°C) over night or <strong>at</strong> 35°C for 1-2 hours.)Inoculum McFarland 0.5Incub<strong>at</strong>ionReading of zonesCiprofloxacin 5 µg vs. MIC, Campylobacter jejuni and coli57 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es tested in duplic<strong>at</strong>e1010ECOFF: WT ≤ 1 mg/L1012Campylobacter jejuni with ciprofloxacin 5 µg414 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es121412141614161816182022182024202226Erythromycin 15 µg vs. MIC, Campylobacter jejuni30 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es tested in duplic<strong>at</strong>eECOFF: WT ≤ 4 mg/L2422282628303234Inhibition zone diameter (mm)Campylobacter coli with ciprofloxacin 5 µg170 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es3024322634Inhibition zone diameter (mm)28Inhibition zone diameter (mm)Microaerobic environment41°C24 hours ± 30 minutes(C. coli with non-sufficient growth after 24 h incub<strong>at</strong>ion are reincub<strong>at</strong>edimmedi<strong>at</strong>ly and read after totally 40-48 h incub<strong>at</strong>ion.)<strong>EUCAST</strong> standard reading instructions:Read MH-F pl<strong>at</strong>es from the front with the lid removed illumin<strong>at</strong>ed withreflected light. Zone edges should be read <strong>at</strong> the point of completeinhbition as judged by the unaided eye.3630383640323842344044364642483844504046MIC(mg/L)≥32481684210.50.25≤0.12MIC(mg/L)≥12864321684210.550No of isol<strong>at</strong>esNo of isol<strong>at</strong>esNo of isol<strong>at</strong>esNo of isol<strong>at</strong>es1098765432103530252015105050454035302520151050605040302010Tetracycline 30 µg vs. MIC, Campylobacter jejuni and coli29 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es tested in duplic<strong>at</strong>e1010ECOFF: WT ≤ 2 mg/LErythromycin 15 µg vs. MIC, Campylobacter coli27 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es tested in duplic<strong>at</strong>e1012Campylobacter jejuni with tetracycline 30 µg409 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es12141214161416101214161820222426283032343638404244184616481850202218202420222624222826Campylobacter coli with tetracycline 30 µg168 clinical isol<strong>at</strong>es24302832263034Inhibition zone diameter (mm)ECOFF: WT ≤ 16 mg/L28Inhibition zone diameter (mm)Figure 1. Inhibition zone distributions for C.jejuni and C. coli with MIC values as colouredbars. Inhibition zones were read according to <strong>EUCAST</strong> standard reading instructions <strong>at</strong> onesite on MH from two manufacturers. D<strong>at</strong>a for erythromycin are presented separ<strong>at</strong>ely, due todifferent ECOFFs.3236303438Inhibition zone diameter (mm)364038404244464850010121416182022242628303234363840424446485032423444364638485040MIC(mg/L)≥12864321684210.50.250.12MIC(mg/L)≥12832168421Inhibition zone diameter (mm)Inhibition zone diameter (mm)For more inform<strong>at</strong>ion, please contact:erika.m<strong>at</strong>uschek@ltkronoberg.seFigure 2. Combined inhibition zone distributions for ciprofloxacin and tetracycline from 4-6 sites for C. jejuni and C. coli, respectively.