Fragile States: Defining Difficult Environments for Poverty ... - INEE
Fragile States: Defining Difficult Environments for Poverty ... - INEE
Fragile States: Defining Difficult Environments for Poverty ... - INEE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
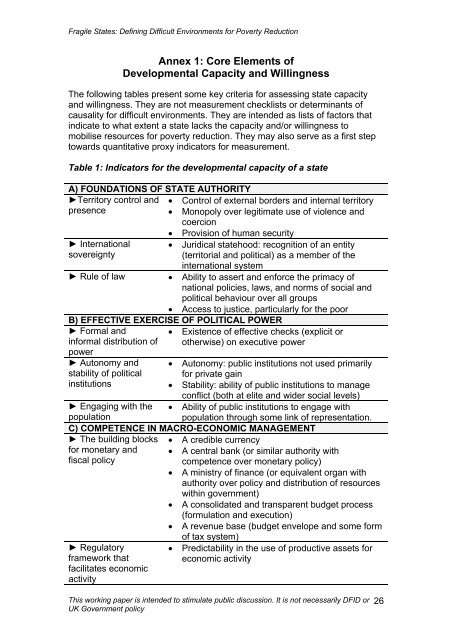
<strong>Fragile</strong> <strong>States</strong>: <strong>Defining</strong> <strong>Difficult</strong> <strong>Environments</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Poverty</strong> ReductionAnnex 1: Core Elements ofDevelopmental Capacity and WillingnessThe following tables present some key criteria <strong>for</strong> assessing state capacityand willingness. They are not measurement checklists or determinants ofcausality <strong>for</strong> difficult environments. They are intended as lists of factors thatindicate to what extent a state lacks the capacity and/or willingness tomobilise resources <strong>for</strong> poverty reduction. They may also serve as a first steptowards quantitative proxy indicators <strong>for</strong> measurement.Table 1: Indicators <strong>for</strong> the developmental capacity of a stateA) FOUNDATIONS OF STATE AUTHORITY►Territory control and • Control of external borders and internal territorypresence• Monopoly over legitimate use of violence andcoercion► Internationalsovereignty• Provision of human security• Juridical statehood: recognition of an entity(territorial and political) as a member of theinternational system► Rule of law • Ability to assert and en<strong>for</strong>ce the primacy ofnational policies, laws, and norms of social andpolitical behaviour over all groups• Access to justice, particularly <strong>for</strong> the poorB) EFFECTIVE EXERCISE OF POLITICAL POWER► Formal andin<strong>for</strong>mal distribution ofpower► Autonomy andstability of politicalinstitutions• Existence of effective checks (explicit orotherwise) on executive power• Autonomy: public institutions not used primarily<strong>for</strong> private gain• Stability: ability of public institutions to manageconflict (both at elite and wider social levels)• Ability of public institutions to engage withpopulation through some link of representation.► Engaging with thepopulationC) COMPETENCE IN MACRO-ECONOMIC MANAGEMENT► The building blocks<strong>for</strong> monetary andfiscal policy► Regulatoryframework thatfacilitates economicactivity• A credible currency• A central bank (or similar authority withcompetence over monetary policy)• A ministry of finance (or equivalent organ withauthority over policy and distribution of resourceswithin government)• A consolidated and transparent budget process(<strong>for</strong>mulation and execution)• A revenue base (budget envelope and some <strong>for</strong>mof tax system)• Predictability in the use of productive assets <strong>for</strong>economic activityThis working paper is intended to stimulate public discussion. It is not necessarily DFID orUK Government policy26