Ticks of Domestic Animals in Africa - Alan R Walker - Science Writer
Ticks of Domestic Animals in Africa - Alan R Walker - Science Writer
Ticks of Domestic Animals in Africa - Alan R Walker - Science Writer
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
14<br />
Festoons to Genital<br />
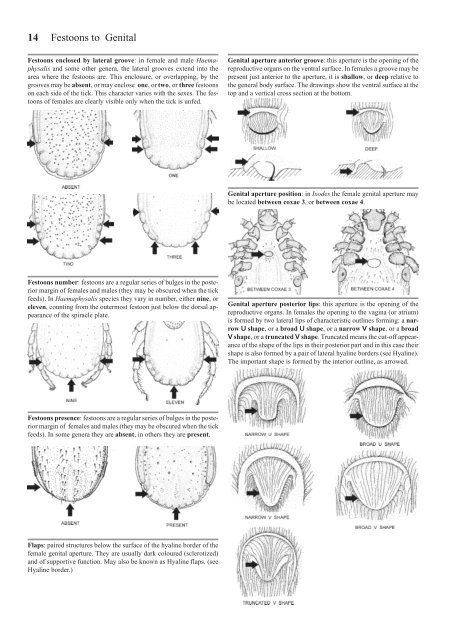
Festoons enclosed by lateral groove: <strong>in</strong> female and male Haemaphysalis<br />
and some other genera, the lateral grooves extend <strong>in</strong>to the<br />
area where the festoons are. This enclosure, or overlapp<strong>in</strong>g, by the<br />
grooves may be absent, or may enclose one, or two, or three festoons<br />
on each side <strong>of</strong> the tick. This character varies with the sexes. The festoons<br />
<strong>of</strong> females are clearly visible only when the tick is unfed.<br />
Festoons number: festoons are a regular series <strong>of</strong> bulges <strong>in</strong> the posterior<br />
marg<strong>in</strong> <strong>of</strong> females and males (they may be obscured when the tick<br />
feeds). In Haemaphysalis species they vary <strong>in</strong> number, either n<strong>in</strong>e, or<br />
eleven, count<strong>in</strong>g from the outermost festoon just below the dorsal appearance<br />
<strong>of</strong> the spiracle plate.<br />
Festoons presence: festoons are a regular series <strong>of</strong> bulges <strong>in</strong> the posterior<br />
marg<strong>in</strong> <strong>of</strong> females and males (they may be obscured when the tick<br />
feeds). In some genera they are absent, <strong>in</strong> others they are present.<br />
Flaps: paired structures below the surface <strong>of</strong> the hyal<strong>in</strong>e border <strong>of</strong> the<br />
female genital aperture. They are usually dark coloured (sclerotized)<br />
and <strong>of</strong> supportive function. May also be known as Hyal<strong>in</strong>e flaps. (see<br />
Hyal<strong>in</strong>e border.)<br />
Genital aperture anterior groove: this aperture is the open<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the<br />
reproductive organs on the ventral surface. In females a groove may be<br />
present just anterior to the aperture, it is shallow, or deep relative to<br />
the general body surface. The draw<strong>in</strong>gs show the ventral surface at the<br />
top and a vertical cross section at the bottom.<br />
Genital aperture position: <strong>in</strong> Ixodes the female genital aperture may<br />
be located between coxae 3, or between coxae 4.<br />
Genital aperture posterior lips: this aperture is the open<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the<br />
reproductive organs. In females the open<strong>in</strong>g to the vag<strong>in</strong>a (or atrium)<br />
is formed by two lateral lips <strong>of</strong> characteristic outl<strong>in</strong>es form<strong>in</strong>g: a narrow<br />
U shape, or a broad U shape, or a narrow V shape, or a broad<br />
V shape, or a truncated V shape. Truncated means the cut-<strong>of</strong>f appearance<br />
<strong>of</strong> the shape <strong>of</strong> the lips <strong>in</strong> their posterior part and <strong>in</strong> this case their<br />
shape is also formed by a pair <strong>of</strong> lateral hyal<strong>in</strong>e borders (see Hyal<strong>in</strong>e).<br />
The important shape is formed by the <strong>in</strong>terior outl<strong>in</strong>e, as arrowed.