Spring 06, Physics 262:801 Final Exam Name:SOLUTIONS Section B
Spring 06, Physics 262:801 Final Exam Name:SOLUTIONS Section B
Spring 06, Physics 262:801 Final Exam Name:SOLUTIONS Section B
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
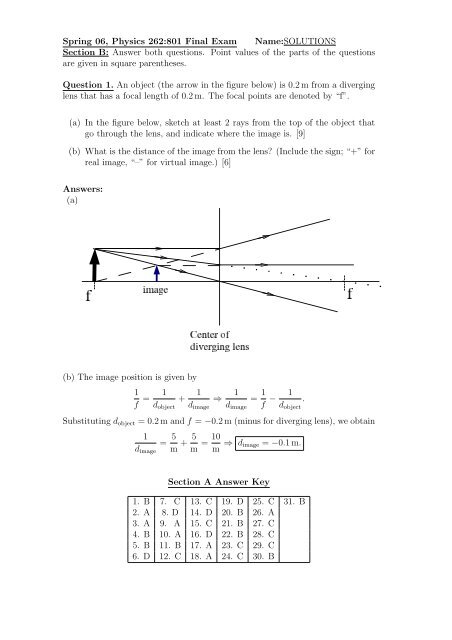
<strong>Spring</strong> <strong>06</strong>, <strong>Physics</strong> <strong>262</strong>:<strong>801</strong> <strong>Final</strong> <strong>Exam</strong> <strong>Name</strong>:<strong>SOLUTIONS</strong><strong>Section</strong> B: Answer both questions. Point values of the parts of the questionsare given in square parentheses.Question 1. An object (the arrow in the figure below) is 0.2 m from a diverginglens that has a focal length of 0.2 m. The focal points are denoted by “f”.(a) In the figure below, sketch at least 2 rays from the top of the object thatgo through the lens, and indicate where the image is. [9](b) What is the distance of the image from the lens? (Include the sign; “+” forreal image, “–” for virtual image.) [6]Answers:(a)(b) The image position is given by1f = 1d object+ 1d image⇒ 1d image= 1 f − 1d object.Substituting d object = 0.2 m and f = −0.2 m (minus for diverging lens), we obtain1= 5 d image m + 5 m = 10m ⇒ d image = −0.1 m.<strong>Section</strong> A Answer Key1. B 7. C 13. C 19. D 25. C 31. B2. A 8. D 14. D 20. B 26. A3. A 9. A 15. C 21. B 27. C4. B 10. A 16. D 22. B 28. C5. B 11. B 17. A 23. C 29. C6. D 12. C 18. A 24. C 30. B
Question 2. A 8-kg +1.0 C charge is projected directly at a fixed +4.0 C charge.When the 8-kg +1.0 C charge is very far away from the fixed +4.0 C charge, itsspeed is 3.0 × 10 3 m/s. (In this problem, use k = 9.0 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 .)(a) What is the kinetic energy of the 8-kg +1.0 C object when it is very faraway from the +4.0 C charge? [5](b) How close does the +1.0 C charge get to the +4.0 C charge before it isrepelled backwards? [10]Answers:(a) K = 1 2 mv2 = 1 2 · (8 kg) · (3.0 × 103 m/s) 2 = 3.6 × 10 7 J.(b) At the closest point of approach, the +1.0 C charge is instantaneously atrest. Therefore, all its energy has been converted into electric potentialenergy. The electric potential energy between two point charges is U =kQ 1 Q 2 /r, where Q are the charges involved and r is the distance betweenthem. By conservation of energy, the the kinetic energy at the beginning(when the +1.0 C charge is far away from the +4.0 C charge and hence theelectric potential energy is negligible) equals the potential energy at thepoint the +1.0 C is closest to the +4.0 C (since the kinetic energy is zero).Equating the two givesK = kQ 1Q 2r min⇒ r min = kQ 1Q 2K .Substituting k = 9.0 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 , Q 1 = +1.0 C, Q 2 = +4.0 C and K =36 × 10 6 J givesr min = (9.0 × 109 Nm 2 /C 2 ) · (+1.0 C) · (+4.0 C)36 × 10 6 Nm= 1.0 × 10 3 m.