Cp physics Web Review ch 17 Electric Force
Cp physics Web Review ch 17 Electric Force - Planet Holloway
Cp physics Web Review ch 17 Electric Force - Planet Holloway
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Name: ______________________ Class: _________________ Date: _________<br />
ID: A<br />
<strong>Cp</strong> <strong>physics</strong> <strong>Web</strong> <strong>Review</strong> <strong>ch</strong> <strong>17</strong> <strong>Electric</strong> <strong>Force</strong><br />
Multiple Choice<br />
Identify the <strong>ch</strong>oice that best completes the statement or answers the question.<br />
____<br />
____<br />
1. An attracting force occurs between two <strong>ch</strong>arged objects when the <strong>ch</strong>arges are of<br />
a. unlike signs. c. equal magnitude.<br />
b. like signs. d. unequal magnitude.<br />
2. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk and becomes positively <strong>ch</strong>arged,<br />
a. electrons are removed from the rod. c. protons are added to the silk.<br />
b. protons are removed from the silk. d. the silk remains neutral.<br />
____<br />
____<br />
____<br />
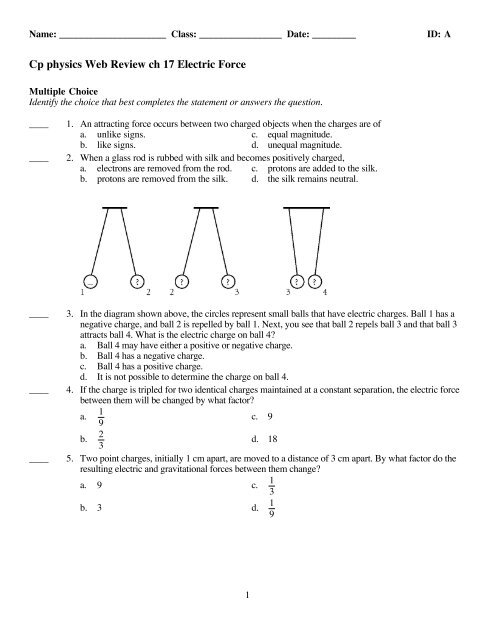
3. In the diagram shown above, the circles represent small balls that have electric <strong>ch</strong>arges. Ball 1 has a<br />
negative <strong>ch</strong>arge, and ball 2 is repelled by ball 1. Next, you see that ball 2 repels ball 3 and that ball 3<br />
attracts ball 4. What is the electric <strong>ch</strong>arge on ball 4?<br />
a. Ball 4 may have either a positive or negative <strong>ch</strong>arge.<br />
b. Ball 4 has a negative <strong>ch</strong>arge.<br />
c. Ball 4 has a positive <strong>ch</strong>arge.<br />
d. It is not possible to determine the <strong>ch</strong>arge on ball 4.<br />
4. If the <strong>ch</strong>arge is tripled for two identical <strong>ch</strong>arges maintained at a constant separation, the electric force<br />
between them will be <strong>ch</strong>anged by what factor?<br />
a.<br />
1<br />
9<br />
c. 9<br />
b.<br />
2<br />
3<br />
d. 18<br />
5. Two point <strong>ch</strong>arges, initially 1 cm apart, are moved to a distance of 3 cm apart. By what factor do the<br />
resulting electric and gravitational forces between them <strong>ch</strong>ange?<br />
a. 9 c.<br />
1<br />
3<br />
b. 3 d.<br />
1<br />
9<br />
1
Name: ______________________<br />
ID: A<br />
Problem<br />
6. What is the electric force between a proton and an alpha particle (<strong>ch</strong>arge 2e) that are separated by a<br />
distance of 3.0 × 10 −6 m? (e = 1.60 × 10 −19 C, k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9 N•m 2 /C 2 )<br />
7. An alpha particle (<strong>ch</strong>arge 2e) is sent at high speed toward a gold nucleus. The electric force acting on<br />
the alpha particle is 91.0 N when it is 2.00 × 10 −14 m away from the gold nucleus. What is the <strong>ch</strong>arge<br />
on the gold nucleus, as a whole number multiple of e? (e = 1.60 × 10 −19 C, k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9<br />
N•m 2 /C 2 )<br />
8. Charge A and <strong>ch</strong>arge B are 2.2 m apart. Charge A is 1.0 C, and <strong>ch</strong>arge B is 2.0 C. Charge C, whi<strong>ch</strong> is<br />
2.0 C, is located between them and is in electrostatic equilibrium. How far from <strong>ch</strong>arge A is <strong>ch</strong>arge C?<br />
9. Two equal positive <strong>ch</strong>arges, both q = 2.0 × 10 −6 C, interact with a third <strong>ch</strong>arge, Q = 4.0 × 10 −6 C, as<br />
shown in the figure above. What is the magnitude of the electric force on Q? (k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9<br />
N•m 2 /C 2 )<br />
10. Two point <strong>ch</strong>arges are 4.0 cm apart and have values of 30.0 µC and –30.0 µC, respectively. What is<br />
the electric field at the midpoint between the two <strong>ch</strong>arges? (k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9 N•m 2 /C 2 )<br />
2
ID: A<br />
<strong>Cp</strong> <strong>physics</strong> <strong>Web</strong> <strong>Review</strong> <strong>ch</strong> <strong>17</strong> <strong>Electric</strong> <strong>Force</strong><br />
Answer Section<br />
MULTIPLE CHOICE<br />
1. A<br />
2. A<br />
3. C<br />
4. C<br />
5. D<br />
PROBLEM<br />
6. 5.1 × 10 −<strong>17</strong> N<br />
Given<br />
q p<br />
= +e = +1.60 × 10 −19 C<br />
q α<br />
= +2e = +3.20 × 10 −19 C<br />
r = 3.0 × 10 −6 m<br />
k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9 N•m 2 /C 2<br />
Solution<br />
Ê<br />
q p<br />
q α Ê<br />
F electric<br />
= k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 ˆ<br />
r 2 Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
F electric<br />
= 5.1 × 10 −<strong>17</strong> N<br />
Ê<br />
+1.60 × 10 −19 ˆ<br />
C<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜ Ê +3.20 × 10 −19 Ë<br />
Á<br />
C ˆ ˆ<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
Ê<br />
3.0 × 10 −6 2<br />
ˆ<br />
m<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
1
ID: A<br />
7. 79e<br />
Given<br />
e = 1.60 ×10 −19 C<br />
q α<br />
= 2e = 3.20 × 10 −19 C<br />
F electric<br />
= 91.0 N<br />
r = 2.00 × 10 −14 m<br />
k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9 N•m 2 /C 2<br />
Solution<br />
F electric<br />
= k C<br />
q α<br />
q Gold<br />
r 2<br />
Rearrange to solve for q Gold<br />
.<br />
Ê Felectric<br />
Ë<br />
Á ˆ¯˜r 2<br />
(91.0 N)(2.00 × 10 −14 m) 2<br />
q Gold<br />
=<br />
=<br />
(k C<br />
)q α (8.99 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 )(3.20 × 10 −19 C) = 1.27 × 10 −<strong>17</strong> C<br />
q Gold<br />
= 1.27 × 10 −<strong>17</strong> C<br />
q e 1.60 × 10 −19 C = 79.4<br />
The <strong>ch</strong>arge on the gold nucleus must be an integer multiple of e.<br />
Integer (79.4)e = 79e<br />
2
ID: A<br />
8. 0.91 m<br />
Given<br />
r A, B<br />
= 2.2 m<br />
r C, A<br />
= d<br />
r C, B<br />
= 2.2 m – d<br />
q A<br />
= 1.0 C<br />
q B<br />
= 2.0 C<br />
q C<br />
= 2.0 C<br />
F C, A<br />
= F C, B<br />
= 0 N<br />
Solution<br />
F C, A<br />
= F C, B<br />
Ê<br />
q C<br />
q<br />
ˆ Ê<br />
A<br />
q C<br />
q<br />
ˆ<br />
B<br />
k C<br />
= k<br />
(r C, A<br />
) 2 C<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜ (r C, B<br />
) 2<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
q A<br />
d = q B<br />
2<br />
( 2.2 m − d) 2<br />
Ê d 2 ˆ Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜ Ë<br />
Á q ˆ¯˜ = ( 2.2 m − d) 2 Êq B<br />
Ë<br />
Á A<br />
ˆ¯˜<br />
d q B<br />
= ( 2.2 m − d) q A<br />
Ê<br />
ˆ<br />
d q B<br />
+ q<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
A<br />
¯<br />
˜ = q (2.2 m)<br />
A<br />
d =<br />
d = 0.91 m<br />
q A<br />
(2.2 m)<br />
q B<br />
+ q A<br />
=<br />
1.0 C (2.2 m)<br />
2.0 C + 1.0 C = 0.91 m<br />
3
ID: A<br />
9. 0.46 N<br />
Given<br />
q 1<br />
= 2.0 × 10 −6 C<br />
q 2<br />
= 2.0 × 10 −6 C<br />
Q = 4.0 × 10 −6 C<br />
r q 1 ,Q = r q 2 ,Q = 0.50 m<br />
θ = tan −1 (0.30 m/0.40 m) = 37°<br />
k C<br />
= 8.99 ×10 9 Nm 2 /C 2<br />
Solution<br />
Ê Ê<br />
F = F = k qQ<br />
2.0 × 10 −6 ˆ<br />
C<br />
q 1 ,Q q 2 ,Q C<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Ár ˆ<br />
= Ê<br />
8.99 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 ˆ Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜ Ê 4.0 × 10 −6 C ˆ ˆ<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
q,Q ¯<br />
˜ 2 Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
= 0.29 N<br />
( 0.50 m) 2<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
For F : F = (F q 1 , Q x,q 1 ,Q q 1<br />
)(cos 37°) = (0.29 N)(cos 37°) = 0.23 N<br />
,Q<br />
F = (F y,q 1 ,Q q 1<br />
)(sin 37°) = (0.29 N)(sin 37°) = 0.<strong>17</strong> N<br />
,Q<br />
For F : F = (F q 2 , Q x,q 1 ,Q q 2<br />
)(cos 37°) = (0.29 N)(cos 37°) = 0.23 N<br />
,Q<br />
F = –(F y,q 2 ,Q q 2<br />
)(sin 37°) = –(0.29 N)(sin 37°) = –0.<strong>17</strong> N<br />
,Q<br />
F x,tot<br />
= F + F x,q 1 ,Q x,q 2<br />
= 0.23 N + 0.23 N = 0.46 N<br />
,Q<br />
F y,tot<br />
= F + F y,q 1 ,Q y,q 2<br />
= 0.<strong>17</strong> N +(–0.<strong>17</strong> N) = 0 N<br />
,Q<br />
F Q,tot<br />
=<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
F Q,tot<br />
= 0.46 N<br />
ˆ<br />
¯<br />
F x,tot<br />
˜ 2<br />
+<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
ÁF ˆ<br />
y,tot ¯<br />
˜ 2<br />
= ( 0.46 N) 2 + 0 = 0.46 N<br />
4
ID: A<br />
10. 1.3 × 10 9 N/C<br />
Given<br />
r 1<br />
= r 2<br />
= 2.0 cm = 2.0 × 10 −2 m<br />
θ 1<br />
= 0°<br />
θ 2<br />
= 180°<br />
q 1<br />
= 30 µC = 3.0 × 10 −5 C<br />
q 2<br />
= −30 µC = −3.0 × 10 −5 C<br />
k C<br />
= 8.99 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2<br />
Solution<br />
q 1<br />
E 1<br />
= k C<br />
r = Ê<br />
8.99 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 ˆ<br />
2<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
1<br />
q 2<br />
E 2<br />
= k C<br />
r = Ê<br />
8.99 × 10 9 Nm 2 /C 2 ˆ<br />
2<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
2<br />
Ê<br />
3.0 × 10 −5 C<br />
Ê<br />
2.0 × 10 −2 ˆ<br />
m<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
−3.0 × 10 −5 C<br />
Ê<br />
2.0 × 10 −2 ˆ<br />
m<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
2<br />
2<br />
ˆ<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
ˆ<br />
¯<br />
˜<br />
= 6.7 × 10 8 N/C<br />
= −6.7 × 10 8 N/C<br />
For E 1<br />
: E x,1<br />
= (E 1<br />
)(cos 0°) = (6.7 × 10 8 N/C)(cos 0°) = 6.7 × 10 8 N/C<br />
E y,1<br />
= 0 N/C<br />
For E 2<br />
: E x,2<br />
= (E 2<br />
)(cos 180°) = (−6.7 × 10 8 N/C)(cos 180°) = 6.7 × 10 8 N/C<br />
E y,2<br />
= 0 N/C<br />
E x,tot<br />
= E x,1<br />
+ E x,2<br />
= 6.7 × 10 8 N/C + 6.7 × 10 8 N/C = 1.3 × 10 9 N/C<br />
E y,tot<br />
= E y,1<br />
+ E y,2<br />
= 0 N/C + 0 N/C = 0 N/C<br />
E tot<br />
=<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
ˆ<br />
¯<br />
E x,tot<br />
˜ 2<br />
E tot<br />
= 1.3 × 10 9 N/C<br />
+<br />
Ê<br />
Ë<br />
ÁE ˆ<br />
y,tot ¯<br />
˜ 2<br />
= 1.3 × 10 9 2<br />
Ê<br />
ˆ<br />
N/C<br />
Ë<br />
Á<br />
¯<br />
˜ + 0 = 1.3 × 10 9 N/C<br />
5