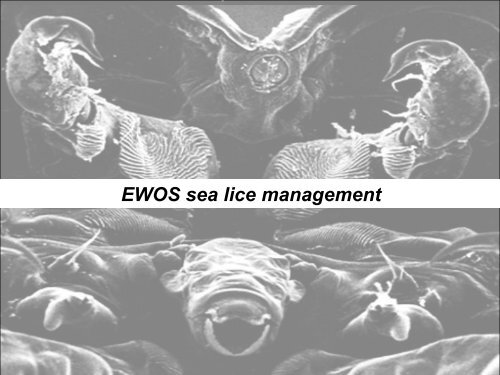
EWOS sea lice management
Surviving lice - Lusedata
Surviving lice - Lusedata
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>EWOS</strong> <strong>sea</strong> <strong>lice</strong> <strong>management</strong><br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
Diflubenzuron Releeze ®<br />
• Mode of action is to inhibit deposition of chitin<br />
• Effective against all moulting stages<br />
• MRL and withdrawal period established<br />
• Commercial use Chile and Norway<br />
• Assessing requirements in UK and Canada<br />
• Resistance monitoring and <strong>management</strong> a key focus<br />
• <strong>EWOS</strong> Norway – product manager Hege Hovland (tomorrow)<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
Lice levels<br />
<strong>EWOS</strong> Releeze ®<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
Control<br />
B<br />
C<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
2 27 32<br />
Days post challenge<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
<strong>EWOS</strong> Releeze ®<br />
• Resistance monitoring – LD 50 test (VESO)<br />
• Cold temperature efficacy<br />
• Egg string / viability of infective stages<br />
• Rotation of compounds (remove adults)<br />
• Development of integrated pest <strong>management</strong><br />
• Additional tools to remove <strong>lice</strong> surviving treatments<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
www.ewosinnovation.com<br />
Wadsworth (1998)
Fast M., Ross N., Craft C., Locke S., MacKinnon S., Johnson S. (2004)<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com<br />
Wadsworth (1998)
Immune suppressants released<br />
• Prostaglandin PGE 2<br />
• Range of proteases<br />
• Phosphatases<br />
• Macrophage inhibitors<br />
Effect on a range of factors<br />
• Reduced respiratory burst<br />
• Lower macrophage activity<br />
• Increased cell death<br />
• Decreased numbers of mucosal cells<br />
• Down-regulation of immune genes (interleukin IL-1ß and MHC-1)<br />
• Local and systemic immune suppression<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
Growing understanding of suppression<br />
• Firth K.J., Johnson S.C., Ross N.W. (2000). Characterization of proteases in the skin mucus of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)<br />
infected with the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) and in the whole-body louse homogenate. Journal of Parasitology. 86.<br />
1199–1205.<br />
• Nolan D., Raune N., Van Der Heijden M., Quabis E.S, Costelloe J., Wendellar S.E. (2000). Juvenile Lepeophtheirus<br />
salmonis (Kroyer) affect the skin and gills of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum) and the host response to a handling<br />
procedure. Aquaculture Re<strong>sea</strong>rch. 31. 823–833.<br />
• Kvamme, B.O., Kongshaug, H. & Nilsen, F. (2005). Organisation of trypsin genes in the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus<br />
salmonis, Crustacea, Copepoda) genome. Gene 352, 63-74.<br />
• Fast M.D., Ross N.W., Muise D.M., Johnson S.C. (2006). Differential gene expression in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, infected<br />
with Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae). Journal of Aquatic Health. 18. 116–127.<br />
• Fast M.D., Johnson S., Eddy T., Pinto D., Ross N. (2007). Lepeophtheirus salmonis secretory / excretory products and their<br />
effects on Atlantic salmon immune gene regulation. Parasite Immunology. 29. 179–189<br />
• Fast, M.D., Johnson S., Eddy T., Pinto D., Ross N. (2008). Cortisol response and immune-related effects of Atlantic salmon<br />
(Salmo salar Linnaeus) subjected to short- and long term stress. Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 24. 194–204<br />
• Wagner G., Fast M., Johnson S.C. (2008). Physiology and immunology of Lepeophtheirus salmonis infections of salmonids.<br />
Trends in Parasitology. 24. 176-183.<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
Boost Control<br />
• Can reduce <strong>sea</strong> <strong>lice</strong> attachment (38%)<br />
• Improved when combined with medicines<br />
Allow increased immunity against <strong>lice</strong><br />
Burrells et al., 2000<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
Lice levels<br />
20<br />
18<br />
16<br />
14<br />
12<br />
10<br />
8<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
0<br />
Surviving <strong>lice</strong> – slow development<br />
0ppb 1ppb 5ppb<br />
Ch 4 PAM1 PAF1 PAM2 PAF2 AM Total<br />
Lice developmental stages<br />
5<br />
1<br />
0<br />
www.ewosinnovation.com
Other Control Mechanisms<br />
Some <strong>lice</strong> survive treatment<br />
Less robust against immune response<br />
Boosted fish remove >50%<br />
Removing resistant population<br />
Reduce effectiveness from<br />
the treated <strong>lice</strong><br />
Allow increased immunity against <strong>lice</strong><br />
www.ewosinnovation.com<br />
Wadsworth (1998)
www.ewosinnovation.com