Agronomic Crops
mJyPrJ
mJyPrJ
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Corn<br />
Earworms/<br />
Armyworms<br />
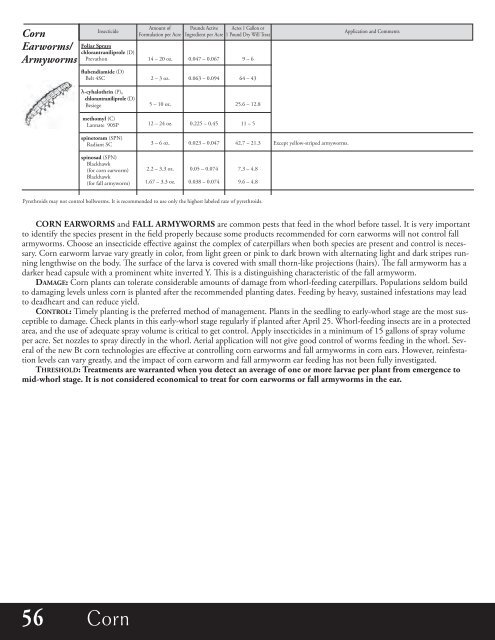
Insecticide<br />
Foliar sprays<br />
chlorantraniliprole (D)<br />
Prevathon<br />
flubendiamide (D)<br />
Belt 4SC<br />
Amount of<br />
Formulation per Acre<br />
14 – 20 oz.<br />
2 – 3 oz.<br />
Pounds Active<br />
Ingredient per Acre<br />
0.047 – 0.067<br />
0.063 – 0.094<br />
Acres 1 Gallon or<br />
1 Pound Dry Will Treat<br />
9 – 6<br />
64 – 43<br />
Application and Comments<br />
λ-cyhalothrin (P),<br />
chlorantraniliprole (D)<br />
Besiege<br />
5 – 10 oz.<br />
25.6 – 12.8<br />
methomyl (C)<br />
Lannate 90SP<br />
12 – 24 oz.<br />
0.225 – 0.45<br />
11 – 5<br />
spinetoram (SPN)<br />
Radiant SC<br />
3 – 6 oz.<br />
0.023 – 0.047<br />
42.7 – 21.3<br />
Except yellow-striped armyworms.<br />
spinosad (SPN)<br />
Blackhawk<br />
(for corn earworm)<br />
Blackhawk<br />
(for fall armyworm)<br />
2.2 – 3.3 oz.<br />
1.67 – 3.3 oz.<br />
0.05 – 0.074<br />
0.038 – 0.074<br />
7.3 – 4.8<br />
9.6 – 4.8<br />
Pyrethroids may not control bollworms. It is recommended to use only the highest labeled rate of pyrethroids.<br />
CoRn eARWoRMs and FALL ARMyWoRMs are common pests that feed in the whorl before tassel. It is very important<br />
to identify the species present in the field properly because some products recommended for corn earworms will not control fall<br />
armyworms. Choose an insecticide effective against the complex of caterpillars when both species are present and control is necessary.<br />
Corn earworm larvae vary greatly in color, from light green or pink to dark brown with alternating light and dark stripes running<br />
lengthwise on the body. e surface of the larva is covered with small thorn-like projections (hairs). e fall armyworm has a<br />
darker head capsule with a prominent white inverted Y. is is a distinguishing characteristic of the fall armyworm.<br />
DAMAGe: Corn plants can tolerate considerable amounts of damage from whorl-feeding caterpillars. Populations seldom build<br />
to damaging levels unless corn is planted after the recommended planting dates. Feeding by heavy, sustained infestations may lead<br />
to deadheart and can reduce yield.<br />
ContRoL: Timely planting is the preferred method of management. Plants in the seedling to early-whorl stage are the most susceptible<br />
to damage. Check plants in this early-whorl stage regularly if planted after April 25. Whorl-feeding insects are in a protected<br />
area, and the use of adequate spray volume is critical to get control. Apply insecticides in a minimum of 15 gallons of spray volume<br />
per acre. Set nozzles to spray directly in the whorl. Aerial application will not give good control of worms feeding in the whorl. Several<br />
of the new Bt corn technologies are effective at controlling corn earworms and fall armyworms in corn ears. However, reinfestation<br />
levels can vary greatly, and the impact of corn earworm and fall armyworm ear feeding has not been fully investigated.<br />
tHResHoLD: treatments are warranted when you detect an average of one or more larvae per plant from emergence to<br />
mid-whorl stage. It is not considered economical to treat for corn earworms or fall armyworms in the ear.<br />
56 Crop Corn Name