Lecture Notes Dermatology - Graham-Brown, Robin, Burns, Tony
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
58 Acne, acneiform eruptions and rosacea<br />
notably systemic steroids, phenytoin, isoniazid<br />
and lithium.<br />
Oil - induced acne occurs when mineral oils<br />
come into close contact with the skin. This is often<br />
at unusual sites, such as the lower abdomen and<br />
thighs.<br />
Chloracne is a specific change in which comedones<br />
appear after exposure to chlorinated chemical<br />
compounds. Famous examples are the release<br />
of dioxin from an explosion at Seveso in Italy and<br />
the poisoning of a prominent Ukrainian politician.<br />
Systemic upsets also occur.<br />
(a)<br />
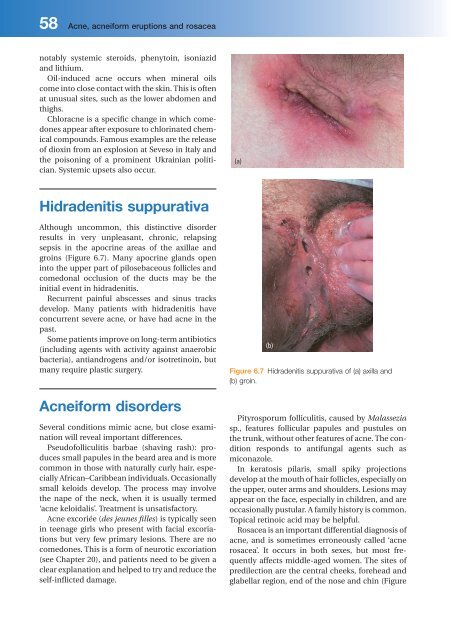
Hidradenitis s uppurativa<br />
Although uncommon, this distinctive disorder<br />
results in very unpleasant, chronic, relapsing<br />
sepsis in the apocrine areas of the axillae and<br />
groins (Figure 6.7 ). Many apocrine glands open<br />
into the upper part of pilosebaceous follicles and<br />
comedonal occlusion of the ducts may be the<br />
initial event in hidradenitis.<br />
Recurrent painful abscesses and sinus tracks<br />
develop. Many patients with hidradenitis have<br />
concurrent severe acne, or have had acne in the<br />
past.<br />
Some patients improve on long - term antibiotics<br />
(including agents with activity against anaerobic<br />
bacteria), antiandrogens and/or isotretinoin, but<br />
many require plastic surgery.<br />
Acneiform d isorders<br />
Several conditions mimic acne, but close examination<br />
will reveal important differences.<br />
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (shaving rash): produces<br />
small papules in the beard area and is more<br />
common in those with naturally curly hair, especially<br />
African – Caribbean individuals. Occasionally<br />
small keloids develop. The process may involve<br />
the nape of the neck, when it is usually termed<br />
‘ acne keloidalis ’ . Treatment is unsatisfactory.<br />
Acne excori é e ( des jeunes filles ) is typically seen<br />
in teenage girls who present with facial excoriations<br />
but very few primary lesions. There are no<br />
comedones. This is a form of neurotic excoriation<br />
(see Chapter 20 ), and patients need to be given a<br />
clear explanation and helped to try and reduce the<br />
self - inflicted damage.<br />
(b)<br />
Figure 6.7 Hidradenitis suppurativa of (a) axilla and<br />
(b) groin.<br />
Pityrosporum folliculitis, caused by Malassezia<br />
sp., features follicular papules and pustules on<br />
the trunk, without other features of acne. The condition<br />
responds to antifungal agents such as<br />
miconazole.<br />
In keratosis pilaris, small spiky projections<br />
develop at the mouth of hair follicles, especially on<br />
the upper, outer arms and shoulders. Lesions may<br />
appear on the face, especially in children, and are<br />
occasionally pustular. A family history is common.<br />
Topical retinoic acid may be helpful.<br />
Rosacea is an important differential diagnosis of<br />
acne, and is sometimes erroneously called ‘ acne<br />
rosacea ’ . It occurs in both sexes, but most frequently<br />
affects middle - aged women. The sites of<br />
predilection are the central cheeks, forehead and<br />
glabellar region, end of the nose and chin (Figure