IJRI-ME-02-030 FATIGUE FAILURE ANALYSIS OF STEAM TURBINE SHAFT USING FEM TECHNIQUE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
International Journal of Research and Innovation on Science, Engineering and Technology (<strong>IJRI</strong>SET)<br />
Materials AISI 4130<br />
Steel<br />
Temperature<br />
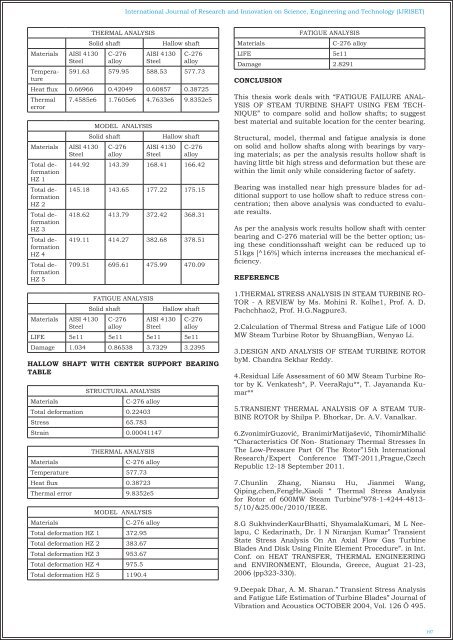
THERMAL <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
Solid shaft<br />
C-276<br />
alloy<br />
AISI 4130<br />
Steel<br />
Hallow shaft<br />
C-276<br />
alloy<br />
591.63 579.95 588.53 577.73<br />
Heat flux 0.66966 0.42049 0.60857 0.38725<br />
Thermal<br />
error<br />
Materials AISI 4130<br />
Steel<br />
Total deformation<br />
HZ 1<br />
Total deformation<br />
HZ 2<br />
Total deformation<br />
HZ 3<br />
Total deformation<br />
HZ 4<br />
Total deformation<br />
HZ 5<br />
Materials AISI 4130<br />
Steel<br />
7.4585e6 1.7605e6 4.7633e6 9.8352e5<br />
MODEL <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
Solid shaft<br />
C-276<br />
alloy<br />
AISI 4130<br />
Steel<br />
Hallow shaft<br />
C-276<br />
alloy<br />
144.92 143.39 168.41 166.42<br />
145.18 143.65 177.22 175.15<br />
418.62 413.79 372.42 368.31<br />
419.11 414.27 382.68 378.51<br />
709.51 695.61 475.99 470.09<br />
<strong>FATIGUE</strong> <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
Solid shaft<br />
C-276<br />
alloy<br />
AISI 4130<br />
Steel<br />
Hallow shaft<br />
C-276<br />
alloy<br />
LIFE 5e11 5e11 5e11 5e11<br />
Damage 1.034 0.86538 3.7329 3.2395<br />
HALLOW <strong>SHAFT</strong> WITH CENTER SUPPORT BEARING<br />
TABLE<br />
Materials<br />
STRUCTURAL <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
C-276 alloy<br />
Total deformation 0.22403<br />
Stress 65.783<br />
Strain 0.00041147<br />
Materials<br />
THERMAL <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
C-276 alloy<br />
Temperature 577.73<br />
Heat flux 0.38723<br />
Thermal error 9.8352e5<br />
Materials<br />
MODEL <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
C-276 alloy<br />
Total deformation HZ 1 372.95<br />
Total deformation HZ 2 383.67<br />
Total deformation HZ 3 953.67<br />
Total deformation HZ 4 975.5<br />
Total deformation HZ 5 1190.4<br />
Materials<br />
LIFE<br />
<strong>FATIGUE</strong> <strong>ANALYSIS</strong><br />
C-276 alloy<br />
5e11<br />
Damage 2.8291<br />
CONCLUSION<br />
This thesis work deals with “<strong>FATIGUE</strong> <strong>FAILURE</strong> ANAL-<br />
YSIS <strong>OF</strong> <strong>STEAM</strong> <strong>TURBINE</strong> <strong>SHAFT</strong> <strong>USING</strong> <strong>FEM</strong> TECH-<br />
NIQUE” to compare solid and hollow shafts; to suggest<br />
best material and suitable location for the center bearing.<br />
Structural, model, thermal and fatigue analysis is done<br />
on solid and hollow shafts along with bearings by varying<br />
materials; as per the analysis results hollow shaft is<br />
having little bit high stress and deformation but these are<br />
within the limit only while considering factor of safety.<br />
Bearing was installed near high pressure blades for additional<br />
support to use hollow shaft to reduce stress concentration;<br />
then above analysis was conducted to evaluate<br />
results.<br />
As per the analysis work results hollow shaft with center<br />
bearing and C-276 material will be the better option; using<br />
these conditionsshaft weight can be reduced up to<br />
51kgs [^16%] which interns increases the mechanical efficiency.<br />
REFERENCE<br />
1.THERMAL STRESS <strong>ANALYSIS</strong> IN <strong>STEAM</strong> <strong>TURBINE</strong> RO-<br />
TOR - A REVIEW by Ms. Mohini R. Kolhe1, Prof. A. D.<br />
Pachchhao2, Prof. H.G.Nagpure3.<br />
2.Calculation of Thermal Stress and Fatigue Life of 1000<br />
MW Steam Turbine Rotor by ShuangBian, Wenyao Li.<br />
3.DESIGN AND <strong>ANALYSIS</strong> <strong>OF</strong> <strong>STEAM</strong> <strong>TURBINE</strong> ROTOR<br />
byM. Chandra Sekhar Reddy.<br />
4.Residual Life Assessment of 60 MW Steam Turbine Rotor<br />
by K. Venkatesh*, P. VeeraRaju**, T. Jayananda Kumar**<br />
5.TRANSIENT THERMAL <strong>ANALYSIS</strong> <strong>OF</strong> A <strong>STEAM</strong> TUR-<br />
BINE ROTOR by Shilpa P. Bhorkar, Dr. A.V. Vanalkar.<br />
6.ZvonimirGuzović, BranimirMatijašević, TihomirMihalić<br />
“Characteristics Of Non- Stationary Thermal Stresses In<br />
The Low-Pressure Part Of The Rotor”15th International<br />
Research/Expert Conference TMT-2011,Prague,Czech<br />
Republic 12-18 September 2011.<br />
7.Chunlin Zhang, Niansu Hu, Jianmei Wang,<br />
Qiping,chen,FengHe,Xiaoli “ Thermal Stress Analysis<br />
for Rotor of 600MW Steam Turbine”978-1-4244-4813-<br />
5/10/&25.00c/2010/IEEE.<br />
8.G SukhvinderKaurBhatti, ShyamalaKumari, M L Neelapu,<br />
C Kedarinath, Dr. I N Niranjan Kumar” Transient<br />
State Stress Analysis On An Axial Flow Gas Turbine<br />
Blades And Disk Using Finite Element Procedure”. in Int.<br />
Conf. on HEAT TRANSFER, THERMAL ENGINEERING<br />
and ENVIRON<strong>ME</strong>NT, Elounda, Greece, August 21-23,<br />
2006 (pp323-330).<br />
9.Deepak Dhar, A. M. Sharan.” Transient Stress Analysis<br />
and Fatigue Life Estimation of Turbine Blades” Journal of<br />
Vibration and Acoustics OCTOBER 2004, Vol. 126 Õ 495.<br />
197