Leveraging the Internet of Things and Analytics for Smart Energy Management
1UbH4b2
1UbH4b2
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Exploring <strong>the</strong> Possibilities: <strong>Internet</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Things</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>Analytics</strong><br />
In <strong>the</strong> age <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>Internet</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Things</strong> (IoT), each device can be connected to <strong>the</strong> internet or intranet, or to<br />
o<strong>the</strong>r devices on <strong>the</strong> network. This enables <strong>the</strong> collection <strong>of</strong> a variety <strong>of</strong> in<strong>for</strong>mation from <strong>the</strong> devices,<br />
including data on operations, configuration, energy consumption, <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> power factor. The IoT enables<br />
devices to make smart decisions based upon analytical rules that serve <strong>the</strong> purpose <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> devices best.<br />
The devices can send, receive, store, <strong>and</strong> leverage in<strong>for</strong>mation, sending <strong>the</strong> in<strong>for</strong>mation individually to<br />
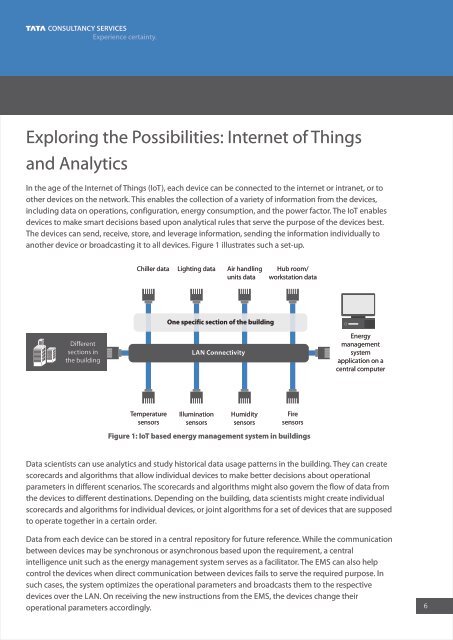
ano<strong>the</strong>r device or broadcasting it to all devices. Figure 1 illustrates such a set-up.<br />
Chiller data Lighting data Air h<strong>and</strong>ling<br />
units data<br />
Hub room/<br />
workstation data<br />
Different<br />
sections in<br />
<strong>the</strong> building<br />
One specific section <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> building<br />
LAN Connectivity<br />
<strong>Energy</strong><br />
management<br />
system<br />
application on a<br />
central computer<br />
Temperature<br />
sensors<br />
Illumination<br />
sensors<br />
Humidity<br />
sensors<br />
Fire<br />
sensors<br />
Figure 1: IoT based energy management system in buildings<br />
Data scientists can use analytics <strong>and</strong> study historical data usage patterns in <strong>the</strong> building. They can create<br />
scorecards <strong>and</strong> algorithms that allow individual devices to make better decisions about operational<br />
parameters in different scenarios. The scorecards <strong>and</strong> algorithms might also govern <strong>the</strong> flow <strong>of</strong> data from<br />
<strong>the</strong> devices to different destinations. Depending on <strong>the</strong> building, data scientists might create individual<br />
scorecards <strong>and</strong> algorithms <strong>for</strong> individual devices, or joint algorithms <strong>for</strong> a set <strong>of</strong> devices that are supposed<br />
to operate toge<strong>the</strong>r in a certain order.<br />
Data from each device can be stored in a central repository <strong>for</strong> future reference. While <strong>the</strong> communication<br />
between devices may be synchronous or asynchronous based upon <strong>the</strong> requirement, a central<br />
intelligence unit such as <strong>the</strong> energy management system serves as a facilitator. The EMS can also help<br />
control <strong>the</strong> devices when direct communication between devices fails to serve <strong>the</strong> required purpose. In<br />
such cases, <strong>the</strong> system optimizes <strong>the</strong> operational parameters <strong>and</strong> broadcasts <strong>the</strong>m to <strong>the</strong> respective<br />
devices over <strong>the</strong> LAN. On receiving <strong>the</strong> new instructions from <strong>the</strong> EMS, <strong>the</strong> devices change <strong>the</strong>ir<br />
operational parameters accordingly. 6