MEASURING IMPACT Making Use of the Portfolio Organizational Learning at USAID
28Mzh2D
28Mzh2D
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
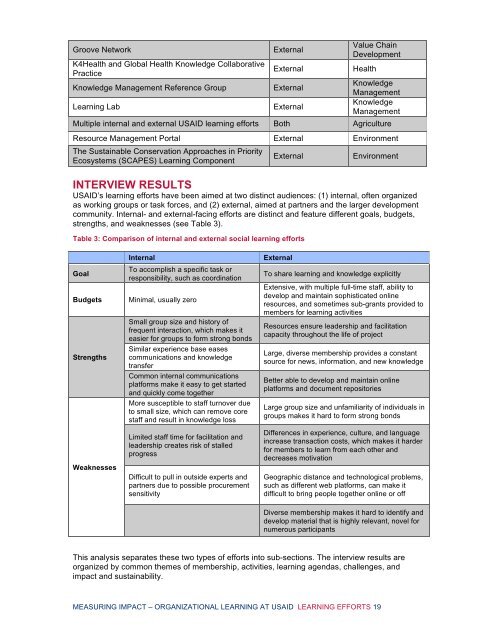
Groove Network<br />
K4Health<br />
Practice<br />
and Global Health Knowledge Collabor<strong>at</strong>ive<br />
Knowledge Management Reference Group<br />
<strong>Learning</strong> Lab<br />
External<br />
External<br />
External<br />
External<br />
Value Chain<br />
Development<br />
Health<br />
Knowledge<br />
Management<br />
Knowledge<br />
Management<br />
Multiple internal and external <strong>USAID</strong> learning efforts Both Agriculture<br />
Resource Management Portal External Environment<br />
The Sustainable Conserv<strong>at</strong>ion Approaches in Priority<br />
Ecosystems (SCAPES) <strong>Learning</strong> Component<br />
External<br />
Environment<br />
INTERVIEW RESULTS<br />
<strong>USAID</strong>’s learning efforts have been aimed <strong>at</strong> two distinct audiences: (1) internal, <strong>of</strong>ten organized<br />
as working groups or task forces, and (2) external, aimed <strong>at</strong> partners and <strong>the</strong> larger development<br />
community. Internal- and external-facing efforts are distinct and fe<strong>at</strong>ure different goals, budgets,<br />
strengths, and weaknesses (see Table 3).<br />
Table 3: Comparison <strong>of</strong> internal and external social learning efforts<br />
Goal<br />
Budgets<br />
Strengths<br />
Weaknesses<br />
Internal<br />
To accomplish a specific task or<br />
responsibility, such as coordin<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
Minimal, usually zero<br />
Small group size and history <strong>of</strong><br />
frequent interaction, which makes it<br />
easier for groups to form strong bonds<br />
Similar experience base eases<br />
communic<strong>at</strong>ions and knowledge<br />
transfer<br />
Common internal communic<strong>at</strong>ions<br />
pl<strong>at</strong>forms make it easy to get started<br />
and quickly come toge<strong>the</strong>r<br />
More susceptible to staff turnover due<br />
to small size, which can remove core<br />
staff and result in knowledge loss<br />
Limited staff time for facilit<strong>at</strong>ion and<br />
leadership cre<strong>at</strong>es risk <strong>of</strong> stalled<br />
progress<br />
Difficult to pull in outside experts and<br />
partners due to possible procurement<br />
sensitivity<br />
External<br />
To share learning and knowledge explicitly<br />
Extensive, with multiple full-time staff, ability to<br />
develop and maintain sophistic<strong>at</strong>ed online<br />
resources, and sometimes sub-grants provided to<br />
members for learning activities<br />
Resources ensure leadership and facilit<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
capacity throughout <strong>the</strong> life <strong>of</strong> project<br />
Large, diverse membership provides a constant<br />
source for news, inform<strong>at</strong>ion, and new knowledge<br />
Better able to develop and maintain online<br />
pl<strong>at</strong>forms and document repositories<br />
Large group size and unfamiliarity <strong>of</strong> individuals in<br />
groups makes it hard to form strong bonds<br />
Differences in experience, culture, and language<br />
increase transaction costs, which makes it harder<br />
for members to learn from each o<strong>the</strong>r and<br />
decreases motiv<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
Geographic distance and technological problems,<br />
such as different web pl<strong>at</strong>forms, can make it<br />
difficult to bring people toge<strong>the</strong>r online or <strong>of</strong>f<br />
Diverse membership makes it hard to identify and<br />
develop m<strong>at</strong>erial th<strong>at</strong> is highly relevant, novel for<br />
numerous participants<br />
This analysis separ<strong>at</strong>es <strong>the</strong>se two types <strong>of</strong> efforts into sub-sections. The interview results are<br />
organized by common <strong>the</strong>mes <strong>of</strong> membership, activities, learning agendas, challenges, and<br />
impact and sustainability.<br />
<strong>MEASURING</strong> <strong>IMPACT</strong> – ORGANIZATIONAL LEARNING AT <strong>USAID</strong> LEARNING EFFORTS 19