You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The periodic table<br />
Practical<br />
Reactions of the halogens<br />
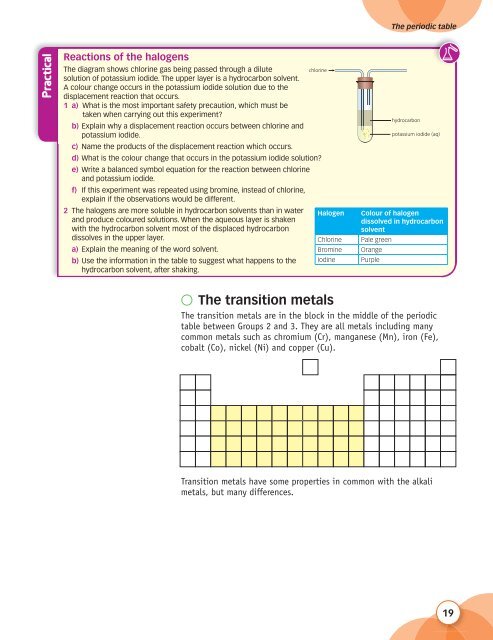
The diagram shows chlorine gas being passed through a dilute<br />
chlorine<br />
solution of potassium iodide. The upper layer is a hydrocarbon solvent.<br />
A colour change occurs in the potassium iodide solution due to the<br />
displacement reaction that occurs.<br />
1 a) What is the most important safety precaution, which must be<br />
taken when carrying out this experiment?<br />
b) Explain why a displacement reaction occurs between chlorine and<br />
potassium iodide.<br />
c) Name the products of the displacement reaction which occurs.<br />
d) What is the colour change that occurs in the potassium iodide solution?<br />
e) Write a balanced symbol equation for the reaction between chlorine<br />
and potassium iodide.<br />
f) If this experiment was repeated using bromine, instead of chlorine,<br />
explain if the observations would be different.<br />
2 The halogens are more soluble in hydrocarbon solvents than in water Halogen<br />
and produce coloured solutions. When the aqueous layer is shaken<br />
with the hydrocarbon solvent most of the displaced hydrocarbon<br />
dissolves in the upper layer.<br />
Chlorine<br />
a) Explain the meaning of the word solvent.<br />
Bromine<br />
b) Use the information in the table to suggest what happens to the Iodine<br />
hydrocarbon solvent, after shaking.<br />
hydrocarbon<br />
potassium iodide (aq)<br />
Colour of halogen<br />
dissolved in hydrocarbon<br />
solvent<br />
Pale green<br />
Orange<br />
Purple<br />
● The transition metals<br />
The transition metals are in the block in the middle of the periodic<br />
table between Groups 2 and 3. They are all metals including many<br />
common metals such as chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe),<br />
cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu).<br />
Transition metals have some properties in common with the alkali<br />
metals, but many differences.<br />
19