spec
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
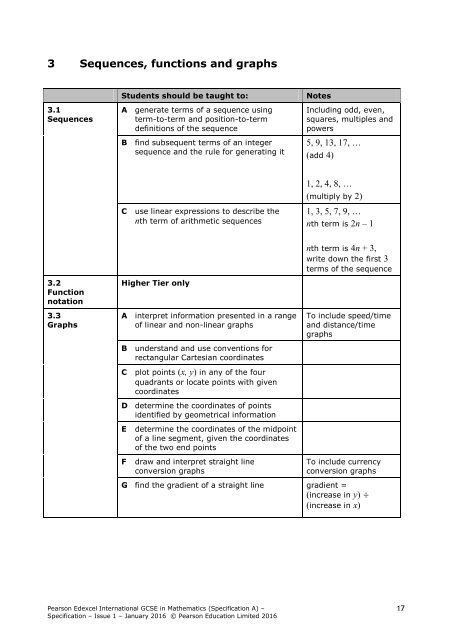
3 Sequences, functions and graphs<br />
3.1<br />
Sequences<br />
Students should be taught to:<br />
A generate terms of a sequence using<br />
term-to-term and position-to-term<br />
definitions of the sequence<br />
B find subsequent terms of an integer<br />
sequence and the rule for generating it<br />
Notes<br />
Including odd, even,<br />
squares, multiples and<br />
powers<br />
5, 9, 13, 17, …<br />
(add 4)<br />
C use linear expressions to describe the<br />
nth term of arithmetic sequences<br />
1, 2, 4, 8, …<br />
(multiply by 2)<br />
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, …<br />
nth term is 2n – 1<br />
3.2<br />
Function<br />
notation<br />
Higher Tier only<br />
nth term is 4n + 3,<br />
write down the first 3<br />
terms of the sequence<br />
3.3<br />
Graphs<br />
A interpret information presented in a range<br />
of linear and non-linear graphs<br />
B understand and use conventions for<br />
rectangular Cartesian coordinates<br />
C plot points (x, y) in any of the four<br />
quadrants or locate points with given<br />
coordinates<br />
D determine the coordinates of points<br />
identified by geometrical information<br />
E<br />
F<br />
determine the coordinates of the midpoint<br />
of a line segment, given the coordinates<br />
of the two end points<br />
draw and interpret straight line<br />
conversion graphs<br />
To include speed/time<br />
and distance/time<br />
graphs<br />
To include currency<br />
conversion graphs<br />
G find the gradient of a straight line gradient =<br />
(increase in y) ÷<br />
(increase in x)<br />
Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Mathematics (Specification A) –<br />
Specification – Issue 1 – January 2016 © Pearson Education Limited 2016<br />
17