J4
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
N<br />
A<br />
N<br />
A<br />
Q<br />
N<br />
45 0<br />
5cm<br />
P<br />
B<br />
4cm<br />
40 0 135 0<br />
R<br />
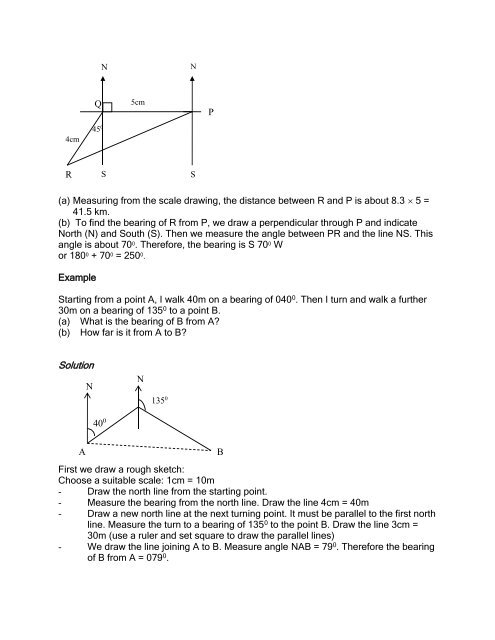
(a) Measuring from the scale drawing, the distance between R and P is about 8.3 5 =<br />
41.5 km.<br />
(b) To find the bearing of R from P, we draw a perpendicular through P and indicate<br />
North (N) and South (S). Then we measure the angle between PR and the line NS. This<br />
angle is about 70 0 . Therefore, the bearing is S 70 0 W<br />
or 180 0 + 70 0 = 250 0 .<br />
Example<br />
S<br />
A<br />
S<br />
Starting from a point A, I walk 40m on a bearing of 040 0 . Then I turn and walk a further<br />
30m on a bearing of 135 0 to a point B.<br />
(a) What is the bearing of B from A?<br />
(b) How far is it from A to B?<br />
Solution<br />
N<br />
N<br />
A<br />
B<br />
First we draw a rough sketch:<br />
Choose a suitable scale: 1cm = 10m<br />
- Draw the north line from the starting point.<br />
- Measure the bearing from the north line. Draw the line 4cm = 40m<br />
- Draw a new north line at the next turning point. It must be parallel to the first north<br />
line. Measure the turn to a bearing of 135 0 to the point B. Draw the line 3cm =<br />
30m (use a ruler and set square to draw the parallel lines)<br />
- We draw the line joining A to B. Measure angle NAB = 79 0 . Therefore the bearing<br />
of B from A = 079 0 .