Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
11-2<br />
1. Plan<br />
Objectives<br />
1 To find the surface area of a<br />
prism<br />
2 To find the surface area of a<br />
cylinder<br />
Examples<br />
1 Finding Surface Area of<br />
a Prism<br />
2 Using Formulas to Find<br />
Surface Area<br />
3 Finding Surface Area of<br />
a Cylinder<br />
4 Real-World Connection<br />
Math Background<br />
This lesson uses the area formulas<br />
from Chapter 10 and nets to<br />
develop formulas for the lateral<br />
and surface areas of prisms and<br />
cylinders. Nets especially simplify<br />
finding these areas for nonright<br />
prisms, such as parallelepipeds.<br />
The key idea is that the lateral<br />
faces of any prism are<br />
parallelograms.<br />
More Math Background: p. 596C<br />
Lesson Planning and<br />
Resources<br />
See p. 596E for a list of the<br />
resources that support this lesson.<br />
PowerPoint<br />
608<br />
Bell Ringer Practice<br />
Check Skills You’ll Need<br />
For intervention, direct students to:<br />
Finding Area<br />
Lesson 1-9: Examples 4–6<br />
Extra Skills, Word Problems, Proof<br />
Practice, Ch. 1<br />
Areas of Regular Polygons<br />
Lesson 10-3: Example 2<br />
Extra Skills, Word Problems, Proof<br />
Practice, Ch. 10<br />
11-2<br />
What You’ll Learn<br />
• To find the surface area of a<br />
prism<br />
• To find the surface area of a<br />
cylinder<br />
. . . And Why<br />
To find the area covered by a<br />
drum on a roller used in road<br />
construction, as in Example 4<br />
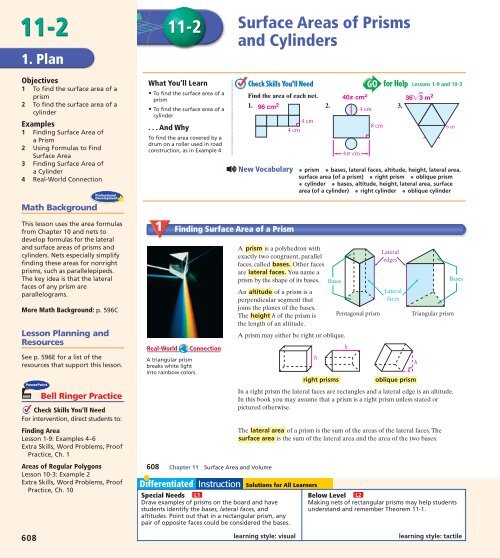
1 Finding Surface Area of a Prism<br />
Real-World Connection<br />
A triangular prism<br />
breaks white light<br />
into rainbow colors.<br />
608 Chapter 11 Surface Area and Volume<br />
Special Needs L1<br />
Draw examples of prisms on the board and have<br />
students identify the bases, lateral faces, and<br />
altitudes. Point out that in a rectangular prism, any<br />
pair of opposite faces could be considered the bases.<br />
Surface Areas of Prisms<br />
and Cylinders<br />
Check Skills You’ll Need GO for Help<br />
Find the area of each net.<br />
1. 96 cm 2.<br />
4 cm<br />
3.<br />
2<br />
40 cm2 π 36 m2 "3<br />
4 cm<br />
4 cm<br />
4 � cm<br />
8 cm<br />
Lessons 1-9 and 10-3<br />
New Vocabulary • prism • bases, lateral faces, altitude, height, lateral area,<br />
surface area (of a prism) • right prism • oblique prism<br />
• cylinder • bases, altitude, height, lateral area, surface<br />
area (of a cylinder) • right cylinder • oblique cylinder<br />
A prism is a polyhedron with<br />
exactly two congruent, parallel<br />
faces, called bases. Other faces<br />
are lateral faces. You name a<br />
Lateral<br />
edges<br />
prism by the shape of its bases. Bases<br />
Bases<br />
An altitude of a prism is a<br />
Lateral<br />
perpendicular segment that<br />
joins the planes of the bases.<br />
faces<br />
The height h of the prism is<br />
the length of an altitude.<br />
Pentagonal prism Triangular prism<br />
A prism may either be right or oblique.<br />
h<br />
right prisms<br />
oblique prism<br />
In a right prism the lateral faces are rectangles and a lateral edge is an altitude.<br />
In this book you may assume that a prism is a right prism unless stated or<br />
pictured otherwise.<br />
The lateral area of a prism is the sum of the areas of the lateral faces. The<br />
surface area is the sum of the lateral area and the area of the two bases.<br />
h<br />
h<br />
6 m<br />
Below Level L2<br />
Making nets of rectangular prisms may help students<br />
understand and remember Theorem 11-1.<br />
learning style: visual learning style: tactile
5 cm<br />
1. 216 cm 2<br />
1 A B C D E<br />
2 A B C D E<br />
3 A B C D E<br />
4 A B C D E<br />
5 A B C D E<br />
B C D E<br />
6 cm<br />
4 cm<br />
Quick Check<br />
5 cm<br />
Test-Taking Tip<br />
3 cm<br />
A question could ask<br />
for either surface area<br />
or lateral area of a<br />
solid. Read the<br />
question carefully.<br />
12 cm<br />
Quick Check<br />
1<br />
2<br />
2<br />
EXAMPLE<br />
Finding Surface Area of a Prism<br />
Use a net to find the surface area of the prism at the left.<br />
Surface Area = Lateral Area + area of bases<br />
= sum of areas of lateral faces + area of bases<br />
= (5 ? 4 + 5 ? 3 + 5 ? 4 + 5 ? 3) + 2(3)(4)<br />
= 70 + 24<br />
= 94<br />
The surface area of the prism is 94 cm2 .<br />
1 Use a net to find the surface area<br />
of the triangular prism. See left.<br />
You can find formulas for lateral and surface areas by looking at a net for a prism.<br />
Perimeter of base<br />
a � b � c � d d<br />
c<br />
d<br />
c<br />
Base<br />
h<br />
a b c d a b<br />
h<br />
a b c d<br />
h<br />
Perimeter Height<br />
Lateral Area � ph<br />
You can use the formulas with any right prism.<br />
EXAMPLE<br />
Using Formulas to Find Surface Area<br />
Multiple Choice What is the surface area of the prism?<br />
72 cm 2 78 cm 2 84 cm 2 96 cm 2<br />
By the Pythagorean Theorem, the hypotenuse of the<br />
triangular base is 5 cm.<br />
L.A. = ph Use the formula for lateral area.<br />
= 12 ? 6 p ≠ 3 ± 4 ± 5 ≠ 12 cm<br />
= 72<br />
The lateral area of the prism is 72 cm2 .<br />
Now use the formula for surface area.<br />
S.A. = L.A. + 2B<br />
5 cm<br />
6 cm<br />
= 72 + 2(6) = 84 B ≠ (3 ? 4) ≠ 6 cm2 1<br />
2<br />
The surface area of the prism is 84 cm 2 . Choice C is the answer.<br />
Use formulas to find the lateral area and surface area<br />
of the prism.<br />
432 m 2 ; about 619 m 2<br />
Advanced Learners L4<br />
After Example 2, ask students to write a formula for<br />
the surface area of a rectangular prism with edges of<br />
length
Guided Instruction<br />
Tactile Learners<br />
Have students tape the sides of a<br />
sheet of paper together (without<br />
overlapping) to form a cylinder.<br />
Ask: What is the lateral area of<br />
the cylinder? the area of the<br />
paper<br />
Connection to Algebra<br />
The formula for the surface area<br />
of a cylinder is sometimes written<br />
as S.A. = 2pr(r + h). Have<br />
students show that this formula<br />
is equivalent to the formula<br />
S.A. = 2prh + 2pr 2 .<br />
4<br />
610<br />
EXAMPLE<br />
Diversity<br />
Some students may never<br />
have seen a steamroller. Have<br />
other students explain how<br />
steamrollers work.<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Additional Examples<br />
The radius of the base of a<br />
cylinder is 6 ft, and its height is<br />
9 ft. Find its surface area in terms<br />
of p. 180π ft2 3<br />
12 Finding Surface Area of a Cylinder<br />
Real-World<br />
Key Concepts Theorem 11-1 Lateral and Surface Areas of a Prism<br />
Connection<br />
A full turn of the roller inks a<br />
rectangle with area equal to<br />
the roller’s lateral area.<br />
Like a prism, a cylinder has two congruent parallel bases. However, the bases of<br />
a cylinder are circles. An altitude of a cylinder is a perpendicular segment that<br />
joins the planes of the bases. The height h of a cylinder is the length of an altitude.<br />
Bases<br />
h<br />
right cylinders<br />
oblique cylinder<br />
In this book you may assume that a cylinder is a right cylinder unless<br />
stated or pictured otherwise.<br />
To find the area of the curved surface of a cylinder, visualize “unrolling” it. The<br />
area of the resulting rectangle is the lateral area of the cylinder. The surface area<br />
of a cylinder is the sum of the lateral area and the areas of the two circular bases.<br />
You can find formulas for these areas by looking at a net for a cylinder.<br />
Key Concepts Theorem 11-2 Lateral and Surface Areas of a Cylinder<br />
610 Chapter 11 Surface Area and Volume<br />
h<br />
The lateral area of a right prism is the product of<br />
the perimeter of the base and the height.<br />
L.A. = ph<br />
The surface area of a right prism is the sum of<br />
the lateral area and the areas of the two bases.<br />
S.A. = L.A. + 2B<br />
2pr<br />
Lateral<br />
Area<br />
The lateral area of a right cylinder is the product of the<br />
circumference of the base and the height of the cylinder.<br />
L.A. = 2prh, or L.A. = pdh<br />
The surface area of a right cylinder is the sum of the lateral<br />
area and the areas of the two bases.<br />
S.A. = L.A. + 2B, or S.A. = 2prh + 2pr2 h<br />
r<br />
h<br />
Surface<br />
Area<br />
h<br />
μ<br />
r<br />
r<br />
h<br />
p is the<br />
perimeter<br />
of a base.<br />
B is the area of a base.<br />
h<br />
Area of a base<br />
B � pr 2<br />
B is the area<br />
of a base. r
Quick Check<br />
Quick Check<br />
Example 1<br />
(page 609)<br />
3<br />
4<br />
EXAMPLE<br />
Finding Surface Area of a Cylinder<br />
The radius of the base of a cylinder is 4 in. and its height is 6 in. Find the surface<br />
area of the cylinder in terms of p.<br />
S.A. = L.A. + 2B Use the formula for surface area of a cylinder.<br />
= 2prh + 2(pr 2 ) Substitute the formulas for lateral area and area of a circle.<br />
= 2p(4)(6) + 2p(4 2 ) Substitute 4 for r and 6 for h.<br />
= 48p + 32p Simplify.<br />
= 80p<br />
The surface area of the cylinder is 80p in. 2 .<br />
3 Find the surface area of a cylinder with height 10 cm and radius 10 cm in terms of p.<br />
400 cm2 π<br />
EXAMPLE Real-World Connection<br />
Machinery The drums of the roller at the left are cylinders of length 3.5 ft. The<br />
diameter of the large drum is 4.2 ft. What area does the large drum cover in one<br />
full turn? Round your answer to the nearest square foot.<br />
The area covered is the lateral area of a cylinder that has a diameter of 4.2 ft and a<br />
height of 3.5 ft.<br />
L.A. = pdh Use the formula for lateral area of a cylinder.<br />
= p(4.2)(3.5) Substitute.<br />
= 46.181412 Use a calculator.<br />
In one full turn, the large drum covers about 46 ft 2 .<br />
The small drum has diameter 3 ft.<br />
a. To the nearest square foot, what area does the small drum cover in one turn?<br />
b. Critical Thinking What area does the small drum cover in one turn of the<br />
large drum? same as large drum (about 46 ft2 4<br />
33 ft<br />
)<br />
2<br />
EXERCISES<br />
For more exercises, see Extra Skill, Word Problem, and Proof Practice.<br />
Practice and Problem Solving<br />
A<br />
Practice by Example<br />
GO for<br />
Help<br />
Use a net to find the surface area of each prism.<br />
1. 2. 3.<br />
4. a. Classify the prism.<br />
b. Find the lateral area of the prism.<br />
c. The bases are regular hexagons. Find<br />
the sum of their areas. 48 cm2 6 ft<br />
29 cm<br />
6 ft<br />
6 ft<br />
4 in.<br />
8 in.<br />
6.5 cm<br />
19 cm<br />
1726 cm<br />
4 in.<br />
"3<br />
d. Find the surface area of the prism.<br />
4 cm<br />
10 cm<br />
2<br />
216 ft2 1–3. See margin for drawings.<br />
right hexagonal prism<br />
80 ± 32 in. 2 or<br />
about 125.3 in. 2<br />
240 cm<br />
"2<br />
2<br />
(240 ± 48 ) cm2 "3<br />
Lesson 11-2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 611<br />
1. 6.5 cm<br />
2. 3.<br />
6 ft<br />
6 ft<br />
29 cm<br />
6.5 cm<br />
19 cm<br />
6 ft<br />
4 in.<br />
8 in.<br />
4 in.<br />
4 "2<br />
in.<br />
4 "2 in.<br />
4 A company sells cornmeal and<br />
barley in cylindrical containers.<br />
The diameter of the base of the<br />
6-in. high cornmeal container is<br />
4 in. The diameter of the base of<br />
the 4-in. high barley container<br />
is 6 in. Which container has the<br />
greater surface area? barley<br />
container<br />
Resources<br />
• Daily Notetaking Guide 11-2<br />
L3<br />
• Daily Notetaking Guide 11-2—<br />
Adapted Instruction L1<br />
Closure<br />
Explain why the factor 2 appears<br />
in both terms of the formula for<br />
the surface area of a cylinder<br />
S.A. = 2prh + 2pr 2 . 2πrh is the<br />
lateral area, which is the area of<br />
a rectangle with one side equal<br />
to 2πr, the circumference of the<br />
base of the cylinder. The term<br />
2πr 2 is the sum of the areas of<br />
the two circular bases of the<br />
cylinder.<br />
611
3. Practice<br />
Assignment Guide<br />
1<br />
612<br />
A B 1-7, 16, 17, 19-21, 23,<br />
24, 26<br />
2 A B 8-15, 18, 22, 25,<br />
27-32<br />
C Challenge 33-37<br />
Test Prep 38-41<br />
Mixed Review 42-46<br />
Homework Quick Check<br />
To check students’ understanding<br />
of key skills and concepts, go over<br />
Exercises 4, 12, 18, 24, 26.<br />
Connection to Algebra<br />
Exercise 2 After students finish<br />
the exercise, ask: What formula<br />
gives the surface area of a cube<br />
with sides of length s? S.A. ≠ 6s 2<br />
Exercise 22 Point out that the<br />
surface area available for the<br />
label is in fact the lateral area of<br />
the can.<br />
Connection to<br />
Coordinate Geometry<br />
Exercise 26 Point out that the<br />
coordinates are listed in the<br />
order (x, y, z).<br />
GPS<br />
Enrichment<br />
Guided Problem Solving<br />
Reteaching<br />
Adapted Practice<br />
Practice<br />
© Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.<br />
Name Class Date<br />
Practice 11-2<br />
0<br />
Find the radius and m AB .<br />
1. 2. 3.<br />
A<br />
24 ft<br />
5 ft<br />
C<br />
Find the value of x to the nearest tenth.<br />
7. 8. 9.<br />
C<br />
12<br />
x<br />
120�<br />
B<br />
4. 5. x<br />
6.<br />
C<br />
x<br />
5<br />
8<br />
2<br />
C<br />
3<br />
C<br />
7 7<br />
3<br />
x<br />
3 x<br />
List what you can conclude from each diagram.<br />
10. �Q � �T, PR � SU<br />
11. �A � �J, BC � KL<br />
B<br />
K<br />
Q<br />
T<br />
P<br />
S<br />
A<br />
J<br />
R<br />
U<br />
C<br />
L<br />
Write a two-column proof, a paragraph proof, or a flow proof.<br />
12. Prove Theorem 11-5, part (2).<br />
Given: �O, OE # AB,<br />
OF # CD,AB=<br />
CD<br />
Prove: OE = OF<br />
0 0 0<br />
13. Given: �O with m AB = m BC = mCA<br />
Prove: m�ABC = m�BCA = m�CAB<br />
20<br />
C<br />
6 in.<br />
A B<br />
6 in.<br />
x<br />
C<br />
86�<br />
2 cm<br />
C<br />
x<br />
6<br />
C<br />
A<br />
B<br />
A<br />
E<br />
O<br />
B<br />
C<br />
F<br />
D<br />
C<br />
A<br />
O<br />
B<br />
5 cm<br />
L4<br />
L1<br />
L3<br />
L2<br />
L3<br />
Chords and Arcs<br />
B<br />
Example 2<br />
(page 609)<br />
Example 3<br />
(page 611)<br />
Example 4<br />
(page 611)<br />
Apply Your Skills<br />
18. A cylinder and a<br />
prism both have two<br />
Onbases and lateral<br />
faces that are<br />
rectangular. The<br />
bases of a cylinder<br />
are circles and the<br />
bases of a prism are<br />
polygons.<br />
21d. 438 units2 ;<br />
1752 units2 ; 4 : 1<br />
GO<br />
nline<br />
Homework Help<br />
Visit: PHSchool.com<br />
Web Code: aue-1102<br />
612 Chapter 11 Surface Area and Volume<br />
20. Answers may vary.<br />
Sample:<br />
Use formulas to find the lateral area and surface area of each prism. Show your<br />
answer to the nearest whole number.<br />
880 cm<br />
5. 4 ft 6. 3 in. 7.<br />
2 ; 1121 cm2 4 in.<br />
8 in.<br />
10 ft<br />
5 ft<br />
5 in.<br />
120 ft2 ; 220 ft2 96 in. 2 ; 108 in. 2<br />
Find the surface area of each cylinder in terms of π.<br />
8. 2 cm<br />
9. 3 cm<br />
10.<br />
11. A standard drinking straw is 19.5 cm long and has a diameter of 0.6 cm. How<br />
many square centimeters of plastic are used in one straw? Round your answer<br />
to the nearest tenth. 36.8 cm 2<br />
12. Packaging A cylindrical carton of oatmeal with radius 3.5 in. is 9 in. tall. If all<br />
surfaces except the top are made of cardboard, how much cardboard is used to<br />
make the oatmeal carton? Round your answer to the nearest square inch.<br />
236.4 in.<br />
Find the surface area of each cylinder to the nearest whole number.<br />
13. 4 in.<br />
14. 15.<br />
8 cm<br />
2<br />
Orange<br />
Juice<br />
8 cm<br />
40π cm 2<br />
107 in. 2<br />
1<br />
6<br />
2<br />
in.<br />
4 cm<br />
6 m 9 m<br />
226 m 2<br />
16.5π cm 2<br />
22 cm<br />
5 cm Regular<br />
octagon<br />
20 cm<br />
16. A triangular prism has base edges 4 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm long. Its lateral area<br />
is 300 cm2 . What is the height of the prism? 20 cm<br />
17. Estimation Estimate the surface area of a cube with edges 4.95 cm long.<br />
18. Writing Explain how a cylinder and a prism are alike and how they<br />
are different. See left.<br />
19. A hexagonal pencil is a hexagonal prism. A base<br />
edge of the pencil has length 4 mm. The pencil<br />
(without eraser) has height 170 mm. How much<br />
surface area of a hexagonal pencil gets painted?<br />
20. Open-Ended Draw a net for a rectangular<br />
prism with a surface area of 220 cm2 . See margin.<br />
21. Consider a box with dimensions 3, 4, and 5.<br />
a. Find its surface area. 94 units2 b. Double each dimension and then find the new surface area. 376 units2 150 cm<br />
c. Find the ratio of the new surface area to the original surface area. 4:1<br />
d. Repeat parts (a)–(c) for a box with dimensions 6, 9, and 11.<br />
e. Make a Conjecture How does doubling the dimensions of a rectangular<br />
prism affect the surface area?<br />
2<br />
4080 mm2 See left.<br />
The surface area becomes 4 times as large.<br />
4 cm<br />
3 cm<br />
4 cm<br />
14 cm<br />
7 in.<br />
11 in.<br />
101.5π in. 2<br />
1407 cm 2
1 in.<br />
7 1 2 in.<br />
4 in.<br />
Exercise 24<br />
27. cylinder of radius 4<br />
and height 2;<br />
48π units 2<br />
28. cylinder of radius 2<br />
and height 4;<br />
24π units 2<br />
29. cylinder of radius 2<br />
and height 4;<br />
24π units 2<br />
30. cylinder of radius 4<br />
and height 2;<br />
48π units 2<br />
GO<br />
for Help<br />
For a guide to solving<br />
Exercise 32, see p. 615.<br />
31b. Surface area is<br />
more than doubled.<br />
C<br />
Challenge<br />
22. Multiple Choice A cylindrical can of cocoa has the<br />
dimensions shown at the right. What is the<br />
approximate surface area available for the label? A<br />
110 in. 2 148 in. 2<br />
179 in. 2 219 in. 2<br />
23. Pest Control A flour moth trap has the shape of<br />
a triangular prism that is open on both ends. An<br />
environmentally safe chemical draws the moth<br />
inside the prism, which is lined with an adhesive.<br />
Find the surface area of the trap. 47.5 in. 2<br />
24. Packaging A typical box for a videocassette tape is open on one side as<br />
pictured at the left. How many square inches of cardboard are in a typical box<br />
for a videocassette tape? about 75.5 in. 2<br />
GPS<br />
25. Suppose that a cylinder has a radius of r units, and that the height of the<br />
x2 x 2<br />
cylinder is also r units. The lateral area of the cylinder is 98p square units.<br />
a. Algebra Find the value of r. 7 units<br />
b. Find the surface area of the cylinder. 196π units 2<br />
26. a. Geometry in 3 Dimensions Find the three<br />
coordinates of each vertex A, B, C, and D<br />
of the rectangular prism.<br />
b. Find AB. 5<br />
c. Find BC. 3<br />
d. Find CD. 4<br />
e. Find the surface area of the prism. 94 units2 A(3, 0, 0); B(3, 5, 0);<br />
C(0, 5, 0); D(0, 5, 4)<br />
Visualization The plane region is revolved<br />
completely about the given line to sweep out<br />
a solid of revolution. Describe the solid and<br />
find its surface area in terms of π. 27–30. See left.<br />
27. the y-axis 28. the x-axis<br />
29. the line y = 2 30. the line x = 4<br />
31. a. Critical Thinking Suppose you double the radius of a right cylinder. How<br />
does that affect the lateral area? Lateral area is doubled.<br />
b. How does that affect the surface area? b-c. See left below.<br />
c. Use the formula for surface area of a right cylinder to explain why the<br />
surface area in part (b) was not doubled.<br />
32. a. Packaging Some cylinders have wrappers<br />
with a spiral seam. Peeled off, the wrapper<br />
has the shape of a parallelogram. The<br />
6 in.<br />
wrapper for a biscuit container has base<br />
7.5 in. and height 6 in. Find the radius and<br />
height of the container. r < 1.2 in.; h ≠ 6 in.<br />
7.5 in.<br />
b. Find the surface area of the container. about 54 in. 2<br />
Judging by appearances, what is the surface area of each solid?<br />
31c. S.A. ≠ 2πr 33. 34. 4 m<br />
35.<br />
8 in.<br />
4 cm<br />
8 cm<br />
3 in.<br />
6 m 3 m<br />
10 in.<br />
Lesson 11-2 Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 613<br />
2 ± 2πrh;<br />
if r doubles:<br />
S.A. ≠ 2(4πr2 ±<br />
2πrh). Since r is<br />
squared, surface<br />
area is more than<br />
doubled.<br />
(148 ± 66.5π) cm2 (84 ± 20π) m2 (220 – 8π) in. 2<br />
lesson quiz, PHSchool.com, Web Code: aua-1102<br />
7 cm<br />
x<br />
2 in.<br />
z<br />
1<br />
1 O<br />
3<br />
A<br />
C O C O A<br />
3<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
O<br />
4 in.<br />
3.5 in.<br />
y<br />
1<br />
5 in.<br />
C<br />
2 4 y<br />
B<br />
2 3 4<br />
5 in.<br />
7 in.<br />
D<br />
x<br />
4. Assess & Reteach<br />
PowerPoint<br />
Lesson Quiz<br />
Use the prism below for Exercises<br />
1 and 2.<br />
1. Use a net to find the surface<br />
area.<br />
8 ft<br />
8 ft<br />
10 ft<br />
6 ft<br />
7 ft 7 ft<br />
6 ft<br />
8 ft<br />
8 ft<br />
6 ft<br />
S.A. ≠ 216 ft 2<br />
7 ft<br />
2. Use a formula to find<br />
the surface area.<br />
S.A. ≠ L.A. ± 2B ≠<br />
168 ± 48 ≠ 216; 216 ft 2<br />
3. The height of a prism is<br />
5 cm. Its rectangular bases<br />
have 3-cm and 9-cm sides. Find<br />
its surface area. 174 cm 2<br />
4. The radius of the base<br />
of a cylinder is 16 in., and its<br />
height is 4 in. Find its surface<br />
area in terms of p. 640π in. 2<br />
5. A contractor paints all but the<br />
bases of a 28-ft high cylindrical<br />
water tank. The diameter of<br />
the base is 22 ft. How many<br />
square feet are painted?<br />
Round to the nearest hundred.<br />
1900 ft 2<br />
Alternative Assessment<br />
Have partners design and label<br />
two different prisms, each having<br />
a surface area of 200 cm 2 .<br />
613
Test Prep<br />
Resources<br />
For additional practice with a<br />
variety of test item formats:<br />
• Standardized Test Prep, p. 657<br />
• Test-Taking Strategies, p. 652<br />
• Test-Taking Strategies with<br />
Transparencies<br />
614<br />
Test Prep<br />
Multiple Choice<br />
41. [2] a. Lateral area is<br />
the perimeter<br />
times height.<br />
Since the lateral<br />
area is 48 in. 2 and<br />
the perimeter of<br />
the k is 24 in.,<br />
h ≠ 2 in.<br />
b. S.A. ≠ 96 in. 2<br />
[1] correct explanation<br />
correct surface area<br />
Short Response<br />
Mixed Review<br />
GO for<br />
Help<br />
Lesson 11-1<br />
Lesson 10-7<br />
Lesson 6-7<br />
x2 x 2<br />
614 Chapter 11 Surface Area and Volume<br />
36. Algebra The sum of the height and radius of a cylinder is 9 m. The surface area<br />
of the cylinder is 54p m2 . Find the height and the radius. h ≠ 6 m; r ≠ 3 m<br />
37. Each edge of the large cube at the right is<br />
12 inches long. The cube is painted on the<br />
outside, and then cut into 27 smaller cubes.<br />
Answer these questions about the 27 cubes.<br />
a. How many are painted on 4, 3, 2, 1, and 0 faces?<br />
b. What is the total surface area that is unpainted?<br />
a. 0, 8, 12, 6, 1 b. 1728 in. 2<br />
38. What is the surface area of the figure<br />
to the nearest tenth? C<br />
A. 335.7 m 2 B. 411.6 m 2<br />
C. 671.5 m 2 D. 721.2 m 2<br />
20.1 m<br />
39. If the radius and height of a cylinder are<br />
both doubled, then the surface area is 9. J<br />
F. the same G. doubled H. tripled J. quadrupled<br />
40. A cylinder of radius r sits snugly inside a cube. Which expression represents<br />
the difference of their lateral areas? D<br />
A. 2r 2 (8 - p) B. 2r(p - 2) C. 2r(4 - p) D. 4r 2 (4 - p)<br />
41. The sides of a base of a right triangular prism are 6 in., 8 in., and 10 in. The<br />
lateral area of the prism is 48 in. 2 . a–b. See left.<br />
a. Find the height of the prism. Explain your reasoning.<br />
b. What is the surface area of the prism?<br />
Sketch each space figure and then draw a net for it. Label the net with<br />
its dimensions.<br />
42. a rectangular box with height 5 cm and a base 3 cm by 4 cm<br />
42–43. See back of book.<br />
43. a cube with 2-in. sides<br />
Find the area of each part of the circle to the nearest tenth.<br />
44. sector QOP 37.7 cm2 0<br />
45. the segment of the circle bounded by QP and QP<br />
22.1 cm<br />
46. In the kite at the right AB = AD and CB = CD.<br />
P 120�<br />
O<br />
Q<br />
Points P, Q, R, and S are midpoints.<br />
a. Determine the coordinates of the<br />
midpoints.<br />
b. RQ = ■; SP = ■;<br />
C(2c, 0)<br />
R<br />
B (0, 2b)<br />
Q<br />
O A (2a, 0)<br />
PQ = ■; SR = ■ a – c; a – c; 2b; 2b<br />
c. Use your answers to part (b) to explain<br />
why PQRS must be a parallelogram.<br />
S<br />
P<br />
D (0, -2b)<br />
2<br />
R(c, b), S(c, –b),<br />
P(a, –b), Q(a, b)<br />
Opposite sides are O.<br />
6 cm<br />
7.4 m<br />
6.8 m