FINAL\Page158_EALYear11_Vocabulary_for_writing_annotations
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Bonus<br />
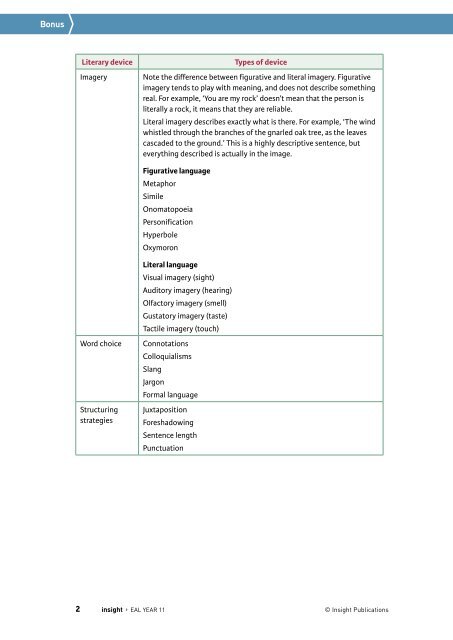
Literary device<br />
Imagery<br />
Types of device<br />
Note the difference between figurative and literal imagery. Figurative<br />
imagery tends to play with meaning, and does not describe something<br />
real. For example, ‘You are my rock’ doesn’t mean that the person is<br />
literally a rock, it means that they are reliable.<br />
Literal imagery describes exactly what is there. For example, ‘The wind<br />
whistled through the branches of the gnarled oak tree, as the leaves<br />
cascaded to the ground.’ This is a highly descriptive sentence, but<br />
everything described is actually in the image.<br />
Figurative language<br />
Metaphor<br />
Simile<br />
Onomatopoeia<br />
Personification<br />
Hyperbole<br />
Oxymoron<br />
Word choice<br />
Structuring<br />
strategies<br />
Literal language<br />
Visual imagery (sight)<br />
Auditory imagery (hearing)<br />
Olfactory imagery (smell)<br />
Gustatory imagery (taste)<br />
Tactile imagery (touch)<br />
Connotations<br />
Colloquialisms<br />
Slang<br />
Jargon<br />
Formal language<br />
Juxtaposition<br />
Foreshadowing<br />
Sentence length<br />
Punctuation<br />
2 insight EAL YEAR 11<br />
© Insight Publications