Global Chemicals Outlook - UNEP
Global Chemicals Outlook - UNEP
Global Chemicals Outlook - UNEP
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
16<br />
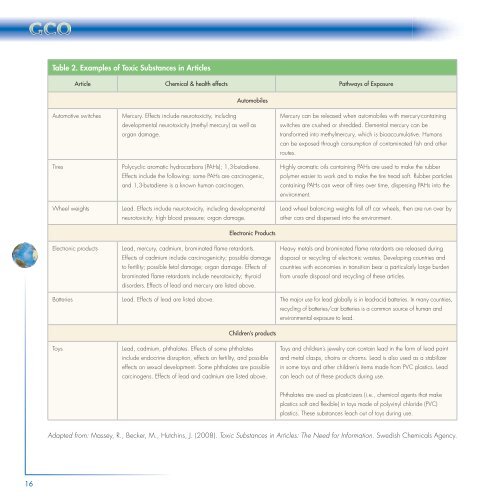
Table 2. Examples of Toxic Substances in Articles<br />
Article Chemical & health effects Pathways of Exposure<br />
Automotive switches Mercury. Effects include neurotoxicity, including<br />
Automobiles<br />
developmental neurotoxicity (methyl mercury) as well as<br />
organ damage.<br />
Tires Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs); 1,3-butadiene.<br />
Effects include the following: some PAHs are carcinogenic,<br />
and 1,3-butadiene is a known human carcinogen.<br />
Wheel weights Lead. Effects include neurotoxicity, including developmental<br />
neurotoxicity; high blood pressure; organ damage.<br />
Electronic Products<br />
Electronic products Lead, mercury, cadmium, brominated fl ame retardants.<br />
Effects of cadmium include carcinogenicity; possible damage<br />
to fertility; possible fetal damage; organ damage. Effects of<br />
brominated fl ame retardants include neurotoxicity; thyroid<br />
disorders. Effects of lead and mercury are listed above.<br />
Mercury can be released when automobiles with mercury-containing<br />
switches are crushed or shredded. Elemental mercury can be<br />
transformed into methylmercury, which is bioaccumulative. Humans<br />
can be exposed through consumption of contaminated fi sh and other<br />
routes.<br />
Highly aromatic oils containing PAHs are used to make the rubber<br />
polymer easier to work and to make the tire tread soft. Rubber particles<br />
containing PAHs can wear off tires over time, dispersing PAHs into the<br />
environment.<br />
Lead wheel balancing weights fall off car wheels, then are run over by<br />
other cars and dispersed into the environment.<br />
Heavy metals and brominated fl ame retardants are released during<br />
disposal or recycling of electronic wastes. Developing countries and<br />
countries with economies in transition bear a particularly large burden<br />
from unsafe disposal and recycling of these articles.<br />
Batteries Lead. Effects of lead are listed above. The major use for lead globally is in lead-acid batteries. In many countries,<br />
recycling of batteries/car batteries is a common source of human and<br />
environmental exposure to lead.<br />
Children’s products<br />
Toys Lead, cadmium, phthalates. Effects of some phthalates<br />
include endocrine disruption, effects on fertility, and possible<br />
effects on sexual development. Some phthalates are possible<br />
carcinogens. Effects of lead and cadmium are listed above.<br />
Toys and children’s jewelry can contain lead in the form of lead paint<br />
and metal clasps, chains or charms. Lead is also used as a stabilizer<br />
in some toys and other children’s items made from PVC plastics. Lead<br />
can leach out of these products during use.<br />
Phthalates are used as plasticizers (i.e., chemical agents that make<br />
plastics soft and fl exible) in toys made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC)<br />
plastics. These substances leach out of toys during use.<br />
Adapted from: Massey, R., Becker, M., Hutchins, J. (2008). Toxic Substances in Articles: The Need for Information. Swedish <strong>Chemicals</strong> Agency.