population ecology ii - Biology
population ecology ii - Biology
population ecology ii - Biology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Estimating Population Density<br />
Quadrat methods<br />
Quadrat: a sampling area<br />
of any shape<br />
Quadrats can be contiguous<br />
or random<br />
Capture-recapture methods
Quadrat Methods<br />
Mean density =<br />
Total individuals<br />
Total area of quadrats
Quadrat No. Individuals (y)<br />
1 9<br />
2 15<br />
3 7<br />
4 4<br />
5 8<br />
6 6<br />
7 11<br />
8 5<br />
9 11<br />
10 8<br />
N = number of<br />
quadrats<br />
= 100<br />
n = number of<br />
quadrats<br />
sampled<br />
= 10
Sample Mean<br />
Sample Variance<br />
Sample Standard Deviation
Mean Density<br />
Estimate Total Population<br />
Estimate Variance of T
Capture-recapture methods<br />
Key assumptions of the capturerecapture<br />
method:<br />
<strong>population</strong> closure<br />
mark integrity<br />
equal catchability
Marked animals in Marked animals in<br />
second sample first sample<br />
------------------------ = ----------------------------<br />
Total caught in Total <strong>population</strong> size<br />
second sample<br />
5 / 20 = 16 / T<br />
T = 64<br />
Density = T / total area
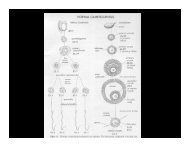
Dispersion: the spatial arrangement of<br />
individuals within <strong>population</strong>s<br />
Three patterns:<br />
Uniform<br />
Random<br />
Aggregated<br />
or clumped
Estimating Population Dispersion<br />
Quadrat methods<br />
Poisson Probability Distribution<br />
Are individuals randomly distributed among<br />
quadrats?<br />
Distance methods
Poisson Probability Distribution<br />
Let X = number of individuals in a quadrat<br />
µ = <strong>population</strong> density<br />
Expected value of X<br />
Variance of X
Are moss shoots randomly distributed?
=[P(Y=0)]N<br />
N
Poisson distribution and natural sampling<br />
units<br />
Are corn-borer larvae<br />
randomly distributed among<br />
corn stems?
Test Statistic
Variance-to-Mean Ratio is a measure of<br />
dispersion<br />
E(X) = µ Var(X) = µ<br />
V/M = 1 Random dispersion<br />
V/M < 1 Uniform dispersion<br />
V/M > 1 Aggregated dispersion
The pattern of dispersion exhibited by a group of<br />
organisms depends on the spatial scale on which the<br />
organisms are studied
This association is clearly demonstrated by<br />
the relationship between the V/M and<br />
quadrat size<br />
Caveat: If the true<br />
pattern is random,<br />
then the V/M is<br />
unaffected by<br />
quadrat size<br />
Quadrat size V/M Ratio<br />
10 0.939<br />
15 1.057<br />
20 0.996<br />
25 1.134<br />
30 1.393<br />
35 1.567<br />
40 1.634
Distance methods<br />
F(r) = Pr(distance to nearest neighbor < r)<br />
= probability that a circle of radius r is not empty<br />
A= area of study region<br />
N= number of points<br />
r
Test for randomness<br />
Refer Z to the Standard<br />
Normal Probability<br />
Distribution<br />
Sample mean of nearest<br />
neighbor distances