Southern and Eastern Asia - Troup 6-12 Teacher Resources
Southern and Eastern Asia - Troup 6-12 Teacher Resources
Southern and Eastern Asia - Troup 6-12 Teacher Resources
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
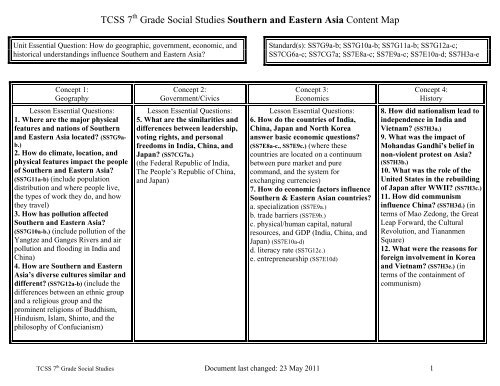
TCSS 7 th Grade Social Studies <strong>Southern</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong> Content Map<br />
Unit Essential Question: How do geographic, government, economic, <strong>and</strong><br />
historical underst<strong>and</strong>ings influence <strong>Southern</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong>?<br />
Concept 1:<br />
Geography<br />
Lesson Essential Questions:<br />
1. Where are the major physical<br />
features <strong>and</strong> nations of <strong>Southern</strong><br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong> located? (SS7G9ab.)<br />
2. How do climate, location, <strong>and</strong><br />
physical features impact the people<br />
of <strong>Southern</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong>?<br />
(SS7G11a-b) (include population<br />
distribution <strong>and</strong> where people live,<br />
the types of work they do, <strong>and</strong> how<br />
they travel)<br />
3. How has pollution affected<br />
<strong>Southern</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong>?<br />
(SS7G10a-b.) (include pollution of the<br />
Yangtze <strong>and</strong> Ganges Rivers <strong>and</strong> air<br />
pollution <strong>and</strong> flooding in India <strong>and</strong><br />
China)<br />
4. How are <strong>Southern</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong><br />
<strong>Asia</strong>’s diverse cultures similar <strong>and</strong><br />
different? (SS7G<strong>12</strong>a-b) (include the<br />
differences between an ethnic group<br />
<strong>and</strong> a religious group <strong>and</strong> the<br />
prominent religions of Buddhism,<br />
Hinduism, Islam, Shinto, <strong>and</strong> the<br />
philosophy of Confucianism)<br />
Concept 2:<br />
Government/Civics<br />
Lesson Essential Questions:<br />
5. What are the similarities <strong>and</strong><br />
differences between leadership,<br />
voting rights, <strong>and</strong> personal<br />
freedoms in India, China, <strong>and</strong><br />
Japan? (SS7CG7a.)<br />
(the Federal Republic of India,<br />
The People’s Republic of China,<br />
<strong>and</strong> Japan)<br />
St<strong>and</strong>ard(s): SS7G9a-b; SS7G10a-b; SS7G11a-b; SS7G<strong>12</strong>a-c;<br />
SS7CG6a-c; SS7CG7a; SS7E8a-c; SS7E9a-c; SS7E10a-d; SS7H3a-e<br />
Concept 3:<br />
Economics<br />
Lesson Essential Questions:<br />
6. How do the countries of India,<br />
China, Japan <strong>and</strong> North Korea<br />
answer basic economic questions?<br />
(SS7E8a-c., SS7E9c.) (where these<br />
countries are located on a continuum<br />
between pure market <strong>and</strong> pure<br />
comm<strong>and</strong>, <strong>and</strong> the system for<br />
exchanging currencies)<br />
7. How do economic factors influence<br />
<strong>Southern</strong> & <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong>n countries?<br />
a. specialization (SS7E9a.)<br />
b. trade barriers (SS7E9b.)<br />
c. physical/human capital, natural<br />
resources, <strong>and</strong> GDP (India, China, <strong>and</strong><br />
Japan) (SS7E10a-d)<br />
d. literacy rate (SS7G<strong>12</strong>c.)<br />
e. entrepreneurship (SS7E10d)<br />
Concept 4:<br />
History<br />
8. How did nationalism lead to<br />
independence in India <strong>and</strong><br />
Vietnam? (SS7H3a.)<br />
9. What was the impact of<br />
Moh<strong>and</strong>as G<strong>and</strong>hi’s belief in<br />
non-violent protest on <strong>Asia</strong>?<br />
(SS7H3b.)<br />
10. What was the role of the<br />
United States in the rebuilding<br />
of Japan after WWII? (SS7H3c.)<br />
11. How did communism<br />
influence China? (SS7H3d.) (in<br />
terms of Mao Zedong, the Great<br />
Leap Forward, the Cultural<br />
Revolution, <strong>and</strong> Tiananmen<br />
Square)<br />
<strong>12</strong>. What were the reasons for<br />
foreign involvement in Korea<br />
<strong>and</strong> Vietnam? (SS7H3e.) (in<br />
terms of the containment of<br />
communism)<br />
TCSS 7 th Grade Social Studies Document last changed: 23 May 2011 1
Vocabulary 1:<br />
Huang He (Yellow River) Ganges River<br />
Indus River Mekong River<br />
Bay of Bengal Indian Ocean<br />
Sea of Japan China<br />
Yellow Sea Gobi Desert<br />
South China Sea India<br />
Indonesia Japan<br />
North Korea South Korea<br />
Taklimakan Desert Vietnam<br />
Himalayan Mountains<br />
Korean Peninsula<br />
Yangtze (Chang Jiang) River<br />
ethnic group<br />
Buddhism<br />
Hinduism<br />
Islam<br />
Shinto<br />
polytheism<br />
Confucianism<br />
monotheism<br />
Human capital (education/training)<br />
Natural Resource (oil)<br />
Population distribution<br />
St<strong>and</strong>ard of living<br />
Literacy Rate<br />
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)<br />
TCSS 7 th Grade Social Studies <strong>Southern</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Eastern</strong> <strong>Asia</strong> Content Map<br />
Vocabulary 2:<br />
Parliamentary democracy<br />
Monarchy<br />
Theocracy<br />
Republic<br />
Communist state<br />
Constitutional Monarchy<br />
Federal Republic<br />
Federal Republic of India<br />
The People’s Republic of China<br />
Japan<br />
Voting rights<br />
Personal freedoms<br />
Unitary**<br />
Confederation**<br />
Federal**<br />
Autocratic**<br />
Oligarchic**<br />
Democratic – parliamentary,<br />
presidential**<br />
monarch**<br />
President**<br />
Prime minister**<br />
** Taught throughout each unit<br />
<strong>Teacher</strong> information to include during lesson<br />
Vocabulary 3:<br />
China<br />
India<br />
Japan<br />
North Korea<br />
Pure market**<br />
Pure comm<strong>and</strong>**<br />
Mixed economy**<br />
Continuum**<br />
Specialization**<br />
Trade barriers**<br />
Tariffs**<br />
Quotas**<br />
Embargos**<br />
Exchange rates**<br />
Currency**<br />
Human capital (education/training)**<br />
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)**<br />
Investment**<br />
Capital (factories, machinery, <strong>and</strong> technology)**<br />
Entrepreneurship**<br />
Vocabulary 4:<br />
India<br />
Nationalism<br />
colonization<br />
Vietnam<br />
Moh<strong>and</strong>as G<strong>and</strong>hi<br />
Passive resistance (“non-violent<br />
protest”)<br />
Japan<br />
China<br />
Mao Zedong<br />
Great Leap Forward<br />
Cultural Revolution<br />
Tiananmen Square<br />
Korea<br />
Vietnam<br />
Containment<br />
Communism<br />
Domino Theory<br />
Ho Chi Minh<br />
TCSS 7 th Grade Social Studies Document last changed: 23 May 2011 2