A Simplified Multivariant SMA Model Based on Invariant Plane ...
A Simplified Multivariant SMA Model Based on Invariant Plane ...
A Simplified Multivariant SMA Model Based on Invariant Plane ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
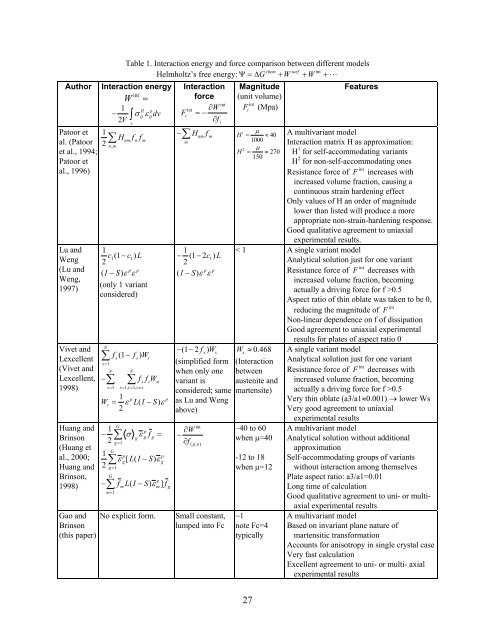
Table 1. Interacti<strong>on</strong> energy and force comparis<strong>on</strong> between different models<br />
chem surf int<br />
Helmholtz’s free energy: Ψ = ∆G<br />
+ W + W + �<br />
Author Interacti<strong>on</strong> energy<br />
W int Interacti<strong>on</strong><br />
=<br />
1 II p<br />
−<br />
2V z σ ij ε ijdv<br />
v<br />
force<br />
int<br />
int W<br />
Fi<br />
=−<br />
f i<br />
∂<br />
Magnitude<br />
Features<br />
∂<br />
(unit volume)<br />
int<br />
Fi (Mpa)<br />
Patoor et 1<br />
al. (Patoor ∑ Hnm fnfm 2 nm ,<br />
et al., 1994;<br />
Patoor et<br />
al., 1996)<br />
−∑ Hnm fm<br />
m<br />
H 1 µ<br />
= ≈40<br />
1000<br />
H 2 µ<br />
= ≈270<br />
150<br />
Lu and<br />
Weng<br />
(Lu and<br />
Weng,<br />
1997)<br />
Vivet and<br />
Lexcellent<br />
(Vivet and<br />
Lexcellent,<br />
1998)<br />
Huang and<br />
Brins<strong>on</strong><br />
(Huang et<br />
al., 2000;<br />
Huang and<br />
Brins<strong>on</strong>,<br />
1998)<br />
1<br />
c1( 1−<br />
c1) L<br />
2<br />
p p<br />
( I − S)<br />
ε ε<br />
(<strong>on</strong>ly 1 variant<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sidered)<br />
N<br />
∑<br />
s=<br />
1<br />
−<br />
N<br />
f ( 1−<br />
f ) W<br />
s s s<br />
N<br />
∑ ∑<br />
f f W<br />
s t st<br />
s=<br />
1 s= 1, t= 1,<br />
t≠s 1 p p<br />
Ws= ε L( I −S)<br />
ε<br />
2<br />
G<br />
1<br />
p<br />
− σ ε f =<br />
1<br />
∑<br />
2 g=<br />
1<br />
G<br />
∑<br />
2 g=<br />
1<br />
G<br />
∑<br />
m=<br />
1<br />
g g<br />
p<br />
p<br />
ε [ LI ( − S)<br />
ε<br />
g<br />
p<br />
− f L( I −S)<br />
ε ] f<br />
g<br />
m m<br />
g<br />
g<br />
1<br />
− −<br />
2<br />
−<br />
1 2 ( c1) L<br />
p p<br />
( I S)<br />
ε ε<br />
−( 1−2f ) W<br />
s s<br />
(simplified form<br />
when <strong>on</strong>ly <strong>on</strong>e<br />
variant is<br />
c<strong>on</strong>sidered; same<br />
as Lu and Weng<br />
above)<br />
− ∂W<br />
∂<br />
f ( gn , )<br />
Gao and No explicit form. Small c<strong>on</strong>stant,<br />
Brins<strong>on</strong><br />
(this paper)<br />
lumped into Fc<br />
int<br />
< 1<br />
W s ≈ 0.468<br />
(Interacti<strong>on</strong><br />
between<br />
austenite and<br />
martensite)<br />
–40 to 60<br />
when µ=40<br />
-12 to 18<br />
when µ=12<br />
~1<br />
note Fc=4<br />
typically<br />
27<br />
A multivariant model<br />
Interacti<strong>on</strong> matrix H as approximati<strong>on</strong>:<br />
H 1 for self-accommodating variants<br />
H 2 for n<strong>on</strong>-self-accommodating <strong>on</strong>es<br />
Resistance force of F int increases with<br />
increased volume fracti<strong>on</strong>, causing a<br />
c<strong>on</strong>tinuous strain hardening effect<br />
Only values of H an order of magnitude<br />
lower than listed will produce a more<br />
appropriate n<strong>on</strong>-strain-hardening resp<strong>on</strong>se.<br />
Good qualitative agreement to uniaxial<br />
experimental results.<br />
A single variant model<br />
Analytical soluti<strong>on</strong> just for <strong>on</strong>e variant<br />
Resistance force of F int decreases with<br />
increased volume fracti<strong>on</strong>, becoming<br />
actually a driving force for f >0.5<br />
Aspect ratio of thin oblate was taken to be 0,<br />
reducing the magnitude of F int<br />
N<strong>on</strong>-linear dependence <strong>on</strong> f of dissipati<strong>on</strong><br />
Good agreement to uniaxial experimental<br />
results for plates of aspect ratio 0<br />
A single variant model<br />
Analytical soluti<strong>on</strong> just for <strong>on</strong>e variant<br />
Resistance force of F int decreases with<br />
increased volume fracti<strong>on</strong>, becoming<br />
actually a driving force for f >0.5<br />
Very thin oblate (a3/a1≈0.001) → lower Ws<br />
Very good agreement to uniaxial<br />
experimental results<br />
A multivariant model<br />
Analytical soluti<strong>on</strong> without additi<strong>on</strong>al<br />
approximati<strong>on</strong><br />
Self-accommodating groups of variants<br />
without interacti<strong>on</strong> am<strong>on</strong>g themselves<br />
Plate aspect ratio: a3/a1=0.01<br />
L<strong>on</strong>g time of calculati<strong>on</strong><br />
Good qualitative agreement to uni- or multiaxial<br />
experimental results<br />
A multivariant model<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>Based</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong> invariant plane nature of<br />
martensitic transformati<strong>on</strong><br />
Accounts for anisotropy in single crystal case<br />
Very fast calculati<strong>on</strong><br />
Excellent agreement to uni- or multi- axial<br />
experimental results