IWC Annual Report 2008 - Institut für Wasserchemie und chemische ...
IWC Annual Report 2008 - Institut für Wasserchemie und chemische ...
IWC Annual Report 2008 - Institut für Wasserchemie und chemische ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Dispersivity,µm<br />
8<br />
50 100 150 200 250<br />
HA<br />
No HA<br />
1.1.4 Stabilization of Colloids in Multiphase Systems<br />
F<strong>und</strong>ing: DFG<br />
Colloids and nanoparticles are not only enhancing the transport of contaminants<br />
which are otherwise immobile but also potential hazardous materials themselves. The<br />
mobility of colloids and nanoparticles in shallow aquifers is controlled by colloid-colloid,<br />
colloid-interface interactions and the stability of the colloids.<br />
Conventional transport investigations (spatial resolution<br />
0.01 to 100 m, temporal resolution minutes to days)<br />
give integrated results of the overall transport processes.<br />
There is little chance to quantify single processes unambiguously.<br />
In contrast, micromodel experiments offer a<br />
spatial resultion in the µm range and a temporal resolution<br />
down to milliseconds but limited heterogeneity.<br />
These experiments, therefore, are best for the quantification<br />
of single-particle/single-interface processes.<br />
Processes on the pore scale are relevant for the transport<br />
of nanoparticles in particular. While some industrial<br />
researchers argue that synthetic nanoparticles are only<br />
stable in their stabilizing solutions, thus the environmental<br />
impact will be negligible, experimental data shows that<br />
humic substances are stabilizing synthetic nanoparticles.<br />
When colloids and nanoparticles are passing through the<br />
soil, interactions with humic substances are likely. The<br />
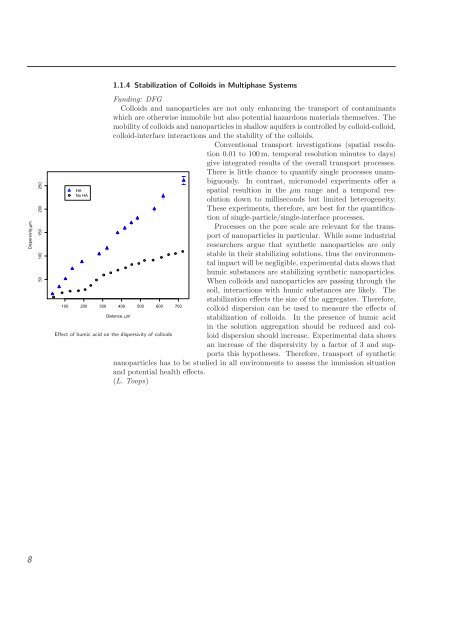
stabilization effects the size of the aggregates. Therefore,<br />
colloid dispersion can be used to measure the effects of<br />
stabilization of colloids. In the presence of humic acid<br />
in the solution aggregation should be reduced and colloid<br />
dispersion should increase. Experimental data shows<br />
an increase of the dispersivity by a factor of 3 and supports<br />
this hypotheses. Therefore, transport of synthetic<br />
nanoparticles has to be studied in all environments to assess the immission situation<br />
and potential health effects.<br />
(L. Toops)<br />
100 200 300 400 500 600 700<br />
Distance, µm<br />
Effect of humic acid on the dispersivity of colloids