Quality Standards in Heritage Interpretation - Bildungswerk ...
Quality Standards in Heritage Interpretation - Bildungswerk ...
Quality Standards in Heritage Interpretation - Bildungswerk ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
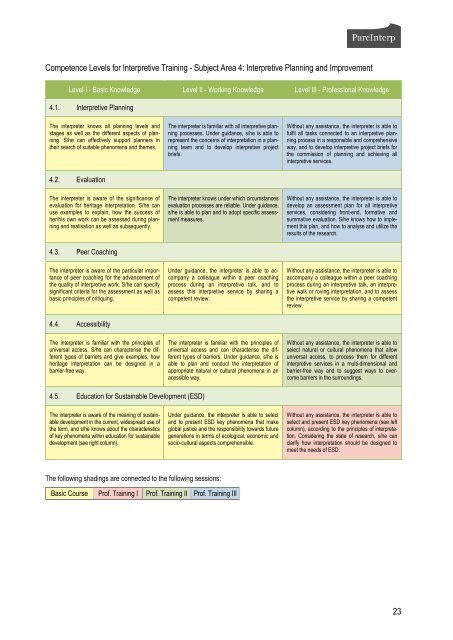
Competence Levels for Interpretive Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g - Subject Area 4: Interpretive Plann<strong>in</strong>g and Improvement<br />
Level I - Basic Knowledge Level II - Work<strong>in</strong>g Knowledge Level III - Professional Knowledge<br />
4.1. Interpretive Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter knows all plann<strong>in</strong>g levels and<br />
stages as well as the different aspects of plann<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
S/he can effectively support planners <strong>in</strong><br />
their search of suitable phenomena and themes.<br />
4.2. Evaluation<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is aware of the significance of<br />
evaluation for heritage <strong>in</strong>terpretation. S/he can<br />
use examples to expla<strong>in</strong>, how the success of<br />
her/his own work can be assessed dur<strong>in</strong>g plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and realisation as well as subsequently.<br />
4.3. Peer Coach<strong>in</strong>g<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is aware of the particular importance<br />
of peer coach<strong>in</strong>g for the advancement of<br />
the quality of <strong>in</strong>terpretive work. S/he can specify<br />
significant criteria for the assessment as well as<br />
basic pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of critiqu<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
4.4. Accessibility<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is familiar with the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of<br />
universal access. S/he can characterise the different<br />
types of barriers and give examples, how<br />
heritage <strong>in</strong>terpretation can be designed <strong>in</strong> a<br />
barrier-free way.<br />
4.5. Education for Susta<strong>in</strong>able Development (ESD)<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is aware of the mean<strong>in</strong>g of susta<strong>in</strong>able<br />
development <strong>in</strong> the current, widespread use of<br />
the term, and s/he knows about the characteristics<br />
of key phenomena with<strong>in</strong> education for susta<strong>in</strong>able<br />
development (see right column).<br />
The follow<strong>in</strong>g shad<strong>in</strong>gs are connected to the follow<strong>in</strong>g sessions:<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is familiar with all <strong>in</strong>terpretive plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
processes. Under guidance, s/he is able to<br />
represent the concerns of <strong>in</strong>terpretation <strong>in</strong> a plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
team and to develop <strong>in</strong>terpretive project<br />
briefs.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter knows under which circumstances<br />
evaluation processes are reliable. Under guidance,<br />
s/he is able to plan and to adopt specific assessment<br />
measures.<br />
Under guidance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to accompany<br />
a colleague with<strong>in</strong> a peer coach<strong>in</strong>g<br />
process dur<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>terpretive talk, and to<br />
assess this <strong>in</strong>terpretive service by shar<strong>in</strong>g a<br />
competent review.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is familiar with the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of<br />
universal access and can characterise the different<br />
types of barriers. Under guidance, s/he is<br />
able to plan and conduct the <strong>in</strong>terpretation of<br />
appropriate natural or cultural phenomena <strong>in</strong> an<br />
acessible way.<br />
Under guidance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to select<br />
and to present ESD key phenomena that make<br />
global justice and the responsibility towards future<br />
generations <strong>in</strong> terms of ecological, economic and<br />
socio-cultural aspects comprehensible.<br />
Basic Course Prof. Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g I Prof. Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g II Prof. Tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g III<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
fulfil all tasks connected to an <strong>in</strong>terpretive plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
process <strong>in</strong> a responsible and comprehensive<br />
way, and to develop <strong>in</strong>terpretive project briefs for<br />
the commission of plann<strong>in</strong>g and achiev<strong>in</strong>g all<br />
<strong>in</strong>terpretive services.<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
develop an assessment plan for all <strong>in</strong>terpretive<br />
services, consider<strong>in</strong>g front-end, formative and<br />
summative evaluation. S/he knows how to implement<br />
this plan, and how to analyse and utilize the<br />
results of the research.<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
accompany a colleague with<strong>in</strong> a peer coach<strong>in</strong>g<br />
process dur<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>terpretive talk, an <strong>in</strong>terpretive<br />
walk or rov<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>terpretation, and to assess<br />
the <strong>in</strong>terpretive service by shar<strong>in</strong>g a competent<br />
review.<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
select natural or cultural phenomena that allow<br />
universal access, to process them for different<br />
<strong>in</strong>terpretive services <strong>in</strong> a multi-dimensional and<br />
barrier-free way and to suggest ways to overcome<br />
barriers <strong>in</strong> the surround<strong>in</strong>gs.<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
select and present ESD key phenomena (see left<br />
column), accord<strong>in</strong>g to the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of <strong>in</strong>terpretation.<br />
Consider<strong>in</strong>g the state of research, s/he can<br />
clarify how <strong>in</strong>terpretation should be designed to<br />
meet the needs of ESD.<br />
23