Quality Standards in Heritage Interpretation - Bildungswerk ...
Quality Standards in Heritage Interpretation - Bildungswerk ...
Quality Standards in Heritage Interpretation - Bildungswerk ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
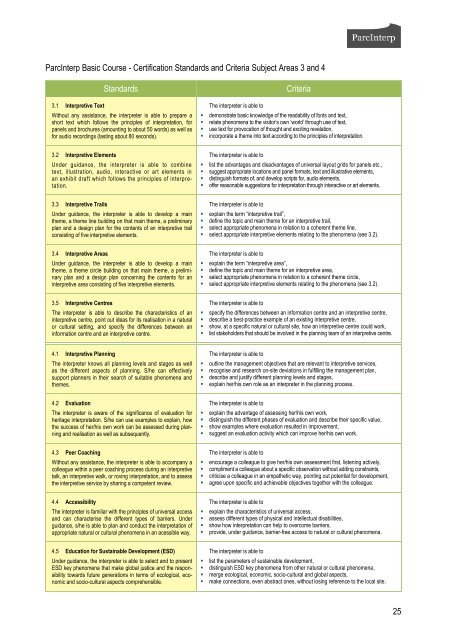
ParcInterp Basic Course - Certification <strong>Standards</strong> and Criteria Subject Areas 3 and 4<br />
3.1 Interpretive Text<br />
<strong>Standards</strong> Criteria<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to prepare a<br />
short text which follows the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of <strong>in</strong>terpretation, for<br />
panels and brochures (amount<strong>in</strong>g to about 50 words) as well as<br />
for audio record<strong>in</strong>gs (last<strong>in</strong>g about 80 seconds).<br />
3.2 Interpretive Elements<br />
Under guidance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to comb<strong>in</strong>e<br />
text, illustration, audio, <strong>in</strong>teractive or art elements <strong>in</strong><br />
an exhibit draft which follows the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of <strong>in</strong>terpretation.<br />
3.3 Interpretive Trails<br />
Under guidance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to develop a ma<strong>in</strong><br />
theme, a theme l<strong>in</strong>e build<strong>in</strong>g on that ma<strong>in</strong> theme, a prelim<strong>in</strong>ary<br />
plan and a design plan for the contents of an <strong>in</strong>terpretive trail<br />
consist<strong>in</strong>g of five <strong>in</strong>terpretive elements.<br />
3.4 Interpretive Areas<br />
Under guidance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to develop a ma<strong>in</strong><br />
theme, a theme circle build<strong>in</strong>g on that ma<strong>in</strong> theme, a prelim<strong>in</strong>ary<br />
plan and a design plan concern<strong>in</strong>g the contents for an<br />
<strong>in</strong>terpretive area consist<strong>in</strong>g of five <strong>in</strong>terpretive elements.<br />
3.5 Interpretive Centres<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to describe the characteristics of an<br />
<strong>in</strong>terpretive centre, po<strong>in</strong>t out ideas for its realisation <strong>in</strong> a natural<br />
or cultural sett<strong>in</strong>g, and specify the differences between an<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation centre and an <strong>in</strong>terpretive centre.<br />
4.1 Interpretive Plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter knows all plann<strong>in</strong>g levels and stages as well<br />
as the different aspects of plann<strong>in</strong>g. S/he can effectively<br />
support planners <strong>in</strong> their search of suitable phenomena and<br />
themes.<br />
4.2 Evaluation<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is aware of the significance of evaluation for<br />
heritage <strong>in</strong>terpretation. S/he can use examples to expla<strong>in</strong>, how<br />
the success of her/his own work can be assessed dur<strong>in</strong>g plann<strong>in</strong>g<br />
and realisation as well as subsequently.<br />
4.3 Peer Coach<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Without any assistance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to accompany a<br />
colleague with<strong>in</strong> a peer coach<strong>in</strong>g process dur<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>terpretive<br />
talk, an <strong>in</strong>terpretive walk, or rov<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>terpretation, and to assess<br />
the <strong>in</strong>terpretive service by shar<strong>in</strong>g a competent review.<br />
4.4 Accessibility<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is familiar with the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of universal access<br />
and can characterise the different types of barriers. Under<br />
guidance, s/he is able to plan and conduct the <strong>in</strong>terpretation of<br />
appropriate natural or cultural phenomena <strong>in</strong> an acessible way.<br />
4.5 Education for Susta<strong>in</strong>able Development (ESD)<br />
Under guidance, the <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to select and to present<br />
ESD key phenomena that make global justice and the responsibility<br />
towards future generations <strong>in</strong> terms of ecological, economic<br />
and socio-cultural aspects comprehensible.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� demonstrate basic knowledge of the readability of fonts and text,<br />
� relate phenomena to the visitor’s own ‘world’ through use of text,<br />
� use text for provocation of thought and excit<strong>in</strong>g revelation,<br />
� <strong>in</strong>corporate a theme <strong>in</strong>to text accord<strong>in</strong>g to the pr<strong>in</strong>ciples of <strong>in</strong>terpretation.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� list the advantages and disadvantages of universal layout grids for panels etc.,<br />
� suggest appropriate locations and panel formats, text and illustrative elements,<br />
� dist<strong>in</strong>guish formats of, and develop scripts for, audio elements,<br />
� offer reasonable suggestions for <strong>in</strong>terpretation through <strong>in</strong>teractive or art elements.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� expla<strong>in</strong> the term “<strong>in</strong>terpretive trail”,<br />
� def<strong>in</strong>e the topic and ma<strong>in</strong> theme for an <strong>in</strong>terpretive trail,<br />
� select appropriate phenomena <strong>in</strong> relation to a coherent theme l<strong>in</strong>e,<br />
� select appropriate <strong>in</strong>terpretive elements relat<strong>in</strong>g to the phenomena (see 3.2).<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� expla<strong>in</strong> the term “<strong>in</strong>terpretive area”,<br />
� def<strong>in</strong>e the topic and ma<strong>in</strong> theme for an <strong>in</strong>terpretive area,<br />
� select appropriate phenomena <strong>in</strong> relation to a coherent theme circle,<br />
� select appropriate <strong>in</strong>terpretive elements relat<strong>in</strong>g to the phenomena (see 3.2).<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� specify the differences between an <strong>in</strong>formation centre and an <strong>in</strong>terpretive centre,<br />
� describe a best-practice example of an exist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>terpretive centre,<br />
� show, at a specific natural or cultural site, how an <strong>in</strong>terpretive centre could work,<br />
� list stakeholders that should be <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> the plann<strong>in</strong>g team of an <strong>in</strong>terpretive centre.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� outl<strong>in</strong>e the management objectives that are relevant to <strong>in</strong>terpretive services,<br />
� recognise and research on-site deviations <strong>in</strong> fulfill<strong>in</strong>g the management plan,<br />
� describe and justify different plann<strong>in</strong>g levels and stages,<br />
� expla<strong>in</strong> her/his own role as an <strong>in</strong>terpreter <strong>in</strong> the plann<strong>in</strong>g process.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� expla<strong>in</strong> the advantage of assess<strong>in</strong>g her/his own work,<br />
� dist<strong>in</strong>guish the different phases of evaluation and describe their specific value,<br />
� show examples where evaluation resulted <strong>in</strong> improvement,<br />
� suggest an evaluation activity which can improve her/his own work.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� encourage a colleague to give her/his own assessment first, listen<strong>in</strong>g actively,<br />
� compliment a colleague about a specific observation without add<strong>in</strong>g constra<strong>in</strong>ts,<br />
� criticise a colleague <strong>in</strong> an empathetic way, po<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g out potential for development,<br />
� agree upon specific and achievable objectives together with the colleague.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� expla<strong>in</strong> the characteristics of universal access,<br />
� assess different types of physical and <strong>in</strong>tellectual disabilities,<br />
� show how <strong>in</strong>terpretation can help to overcome barriers,<br />
� provide, under guidance, barrier-free access to natural or cultural phenomena.<br />
The <strong>in</strong>terpreter is able to<br />
� list the parameters of susta<strong>in</strong>able development,<br />
� dist<strong>in</strong>guish ESD key phenomena from other natural or cultural phenomena,<br />
� merge ecological, economic, socio-cultural and global aspects,<br />
� make connections, even abstract ones, without los<strong>in</strong>g reference to the local site.<br />
25