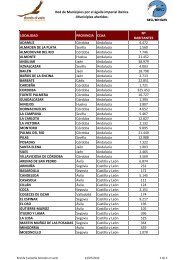
Medidas <strong>beneficiosas</strong> <strong>para</strong> <strong>las</strong> <strong>aves</strong>, financiables a través del nuevo reglamento de desarrollo ruralDistribución en <strong>las</strong> áreas consideradasEn la tabla que se presenta a continuación se indica en cuáles de estas áreas se constata la presencia regular de <strong>las</strong> especiestratadas.Nombre científico Nombre vernáculo DistribuciónArdea purpurea Garza Imperial D, BE, A, DEArdeola ralloides Garcilla Cangrejera D, BE, A, DEChlidonias hybrida Fumarel Cariblanco D, BE, A, DEChlidonias niger Fumarel Común D, BE, A, DECiconia ciconia Cigüeña Blanca D, BECiconia nigra Cigüeña Negra D, BEEgretta garzetta Garceta Común D, BE, A, DEIxobrychus minutus Avetorillo Común D, BE, A, DEHimantopus himantopus Cigüeñuela Común D, BE, A, DELarus audouinii Gaviota de Audouin A, DEMarmaronetta angustirostris Cerceta Pardilla D, BE, APhoenicopterus (ruber) roseus Flamenco Común D, BE, DEPlatalea leucorodia Espátula Común D, BE, DEPlegadis falcinellus Morito Común D, BE, A, DEPluvialis apricaria Chorlito Dorado Europeo D, BE, A, DEPorphyrio porphyrio Calamón Común D, BE, A, DEPorzana parva Polluela Bastarda D, BE, A, DEPorzana porzana Polluela Pintoja D, BE, A, DEPorzana pusilla Polluela Chica D, BE, A, DESterna (Gelochelidon) nilotica Pagaza Piconegra D, BE, AD: Doñana; BE: Brazo del Este; A: L’Albufera; DE: Delta de l’Ebre.Tendencia poblacional:De este grupo de especies, se apuntan tendenciasregresivas en <strong>las</strong> últimas décadas <strong>para</strong> Chlidonias hybrida,Chlidonias niger y Marmaronetta angustirostris.Ecología:Alimentación: Todas estas especies se alimentan en elarrozal cuando éste se encuentra inundado. Las épocas defangueo (primavera y otoño), cuando la cantidad de aguaen <strong>las</strong> tab<strong>las</strong> es reducida y emergen numerosos invertebrados,resultan especialmente importantes.Reproducción: Del listado de especies, tan sólo laCigüeñuela Común instala sus nidos de forma habitual enlos bordes del arrozal.Amenazas y factores limitantes:- El incremento en el uso de los fitosanitarios, reduce la cantidadde alimento disponible.- El uso de venenos específicos contra cangrejo rojo(Procambarus clarkii) y rata (Rattus norvergicus) provocaefectos de intoxicación acumulativa o directa.- La concentración parcelaria supone una reducción estructuraldel sistema, con la consiguiente limitación del espacio<strong>para</strong> la nidificación, la alimentación y el descanso dediferentes especies.- El cosechado nocturno supone la muerte directa denumerosas <strong>aves</strong> de diferentes especies.Medidas de gestión:• Promover la producción ecológica de arroz (sin herbicidas,fitosanitarios ni abonos químicos).• Uso de bacterias (Bacillus thuringiensis) en la siembracontra quironómidos.• Prohibir el cosechado nocturno.• Promover la puesta en práctica de técnicas diversas deacolchamiento, plantas autóctonas o cortado y quemade hierbas de los márgenes, <strong>para</strong> sustituir el uso de herbicidas,buscando márgenes vegetados con plantas queno invadan el arrozal.• Establecer márgenes anchos, con tubos de desagüeenterrados, <strong>para</strong> evitar los agujeros de cangrejo rojo(Procambarus clarkii) y rata (Rattus norvergicus).• Construir estructuras en los canales de riego que permitansalir a <strong>las</strong> crías de <strong>aves</strong> que caigan o salten a ellos.• Promover la inundación de los arrozales en otoño einvierno y el mantenimiento de algunos campos en esteestado durante todo el año. Esta medida proporciona alimentoy áreas de reposo a <strong>las</strong> <strong>aves</strong>.• Para alejar a determinadas especies de <strong>aves</strong> durante lanoche (flamencos, por el pisoteo de la siembra), utilizarsólo señales luminosas, no cañones de gas.Bibliografía:- Acosta, M.; Mugica, L.; Mancina, C. & Ruiz, X. 1996.Resource partitioning between glossy and white ibises in190
APÉNDICE II: Fichas de <strong>aves</strong>a rice field system in south central Cuba. ColonialWaterbirds, 19: 65-72.- Bambaradeniya, C.N.B.; Edirisinghe, J.P.; De Silva, D.N.;Gunatilleke, C.V.S.; Ranawana, K.B. & Wijekoon, S.2004. Biodiversity associated with an irrigated rice agroecosystemin Sri Lanka. Biodiversity and Conservation, 13:1715-1753.- Burfield, I. & Van Bommel, F. (Comps.) 2004. Birds inEurope: Population Estimates, Trends and ConservationStatus. Conservation Series nº 12, <strong>BirdLife</strong> International,Cambridge.- Campos, F. & Lekuona, J.M. 2001. Are Rice Fields aSuitable Foraging Habitat for Purple Herons During theBreeding Season? Waterbirds, 24: 450-452.- Comín, F. A.; Romero, J.A.; Hernández, O. & Menéndez,M. 2001. Restoration of Wetlands from Abandoned RiceFields for Nutrient Removal, and Biological Communityand Landscape Diversity. Restoration Ecology, 9: 201-208.- Cramp, S. & Simmons, K.E.L. (Eds.) 1998. The CompleteBirds of the Western Palearctic. Oxford University Press,Oxford.- Delord, K.; Kayser, Y.; Cohez, D.; Befeld, S. & Hafner, H.2004. Fluctuations in chick diet of the Squacco HeronArdeola ralloides in southern France: changes over the <strong>las</strong>t30 years: The composition varied between colony site,month and year. Bird Study, 51: 69-75.- Díaz, M.; Asensio, B. & Tellería, J.L. 1996. Aves Ibéricas I.No Paseriformes. J.M. Reyero, Madrid.- Elphick, C.S. & Oring, L.W. 1998. Winter Management ofCalifornian Rice Fields for Waterbirds. Journal of AppliedEcology, 35: 95-108.- Fasola, M. 1986. Resource use of foraging herons in agriculturaland nonagricultural habitats in Italy. ColonialWaterbirds, 9: 139-148.- Fasola, M. 1994. Opportunistic use of foraging resourcesby heron communities in southern Europe. Ecography,17: 113-123.- Heath, M.; Borggreve, C. & Peet, N. 2001. European birdpopulations: estimates and trends. Conservation Series nº10, <strong>BirdLife</strong> International, Cambridge.- Lee, R.C., Jr. 1984. Nesting biology of the Black Tern(Chlidonias niger) in rice fields of the Central Valley,California. Master’s thesis, Calif. State Univ., Sacramento.- Madroño, A.; González, C. & Atienza, J.C. (Eds.) LibroRojo de <strong>las</strong> Aves de España. Dirección General <strong>para</strong> laBiodiversidad – <strong>SEO</strong>/<strong>BirdLife</strong>, Madrid.- Mañosa, S.; Mateo, R. & Guitart, R. 2001. A Review of theEffects of Agricultural and Industrial Contamination on theEbro Delta Biota and Wildlife. Environmental Monitoringand Assessment, 71: 187-205.- Marques, P.A.M. & Vicente, L. 1999. Seasonal variation ofwaterbird prey abundance in the Sado estuary rice fields.Ardeola, 46: 231-234.- Martí, R. & Del Moral, J.C. (Eds.) At<strong>las</strong> de <strong>las</strong> AvesReproductoras de España. Dirección General <strong>para</strong> laBiodiversidad – <strong>SEO</strong>/<strong>BirdLife</strong>, Madrid.- Mateo, R.; Belliure, J.; Dolz, J.C.; Aguilar Serrano, J.M. &Guitart, R. 2004. High Prevalences of Lead Poisoning inWintering Waterfowl in Spain. Archives of EnvironmentalContamination and Toxicology, 35: 342-347.- Shimada, T.; Bowman, A. & Ishida, M. 2000. Effects of floodingon a wetland bird community. Ecological Research,15: 229-235.- Tourenq, C.; Benhamou, S. ; Sadoul, N. ; Sandoz, A.;Mesléard, F.; Martin, J.L. & Hafner, H. 2004. Spatial relationshipsbetween tree-nesting heron colonies and rice fieldsin the Camargue, France. The Auk, 121: 192-202.191
- Page 1:
MEDIDAS BENEFICIOSAS PARA LAS AVESL
- Page 5 and 6:
ANTECEDENTESÍNDICEPágina1. Justif
- Page 8 and 9:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 10 and 11:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 12 and 13:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 14 and 15:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 16 and 17:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 18 and 19:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 20 and 21:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 22 and 23:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 24 and 25:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 26 and 27:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 28 and 29:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 30 and 31:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 32 and 33:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 34 and 35:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 36 and 37:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 38 and 39:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 40 and 41:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 42 and 43:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 44:
Medidas beneficiosas para las aves,
- Page 47 and 48:
RESULTADOSCASTILLA Y LEÓNCódigo N
- Page 49 and 50:
RESULTADOSCASTILLA Y LEÓNCódigo N
- Page 51 and 52:
RESULTADOSCASTILLA-LA MANCHACódigo
- Page 53 and 54:
RESULTADOSFigura 9. Mapa de distrib
- Page 55 and 56:
RESULTADOSCATALUNYACódigo Nombre Z
- Page 57 and 58:
RESULTADOSCATALUNYACódigo Nombre Z
- Page 59 and 60:
RESULTADOSCOMUNIDAD VALENCIANACódi
- Page 61 and 62:
RESULTADOSEXTREMADURACódigo Nombre
- Page 63 and 64:
RESULTADOSEXTREMADURACódigo Nombre
- Page 65 and 66:
RESULTADOSGALICIACódigo Nombre ZEP
- Page 67 and 68:
RESULTADOSILLES BALEARSCódigo Nomb
- Page 69 and 70:
RESULTADOSLA RIOJACódigo Nombre ZE
- Page 71 and 72:
RESULTADOSNAVARRACódigo Nombre ZEP
- Page 73 and 74:
RESULTADOSPAÍS VASCOCódigo Nombre
- Page 75 and 76:
RESULTADOSARROZALES COSTEROSCódigo
- Page 77 and 78:
BIBLIOGRAFÍABIBLIOGRAFÍAESPECIESA
- Page 79 and 80:
BIBLIOGRAFÍABarros, C.; De Borbón
- Page 81 and 82:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAClaro, J.C. 2002. Pers
- Page 83 and 84:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAFajardo, I. & Babiloni
- Page 85 and 86:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAHeredia, R. & Razin, M
- Page 87 and 88:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAMañosa, S. & Real, J.
- Page 89 and 90:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAPalacios, F.; Garzón,
- Page 91 and 92:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAStoate, C.; Borralho,
- Page 93 and 94:
BIBLIOGRAFÍAGENERALAebischer, N.J.
- Page 95 and 96:
APÉNDICE I:Fichas de medidas
- Page 97 and 98:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasÍNDI
- Page 99 and 100:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasMODER
- Page 101 and 102:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidas- Gan
- Page 103 and 104:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasAves
- Page 105 and 106:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidas- Ter
- Page 107 and 108:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidas- Fom
- Page 109 and 110:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasneces
- Page 111 and 112:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasORDEN
- Page 113 and 114:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidaspisot
- Page 115 and 116:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidas21; u
- Page 117 and 118:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasAves
- Page 119 and 120:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasde ba
- Page 121 and 122:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidas- Gan
- Page 123 and 124:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasPosib
- Page 125 and 126:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidasINCEN
- Page 127 and 128:
APÉNDICE I: Fichas de medidas• L
- Page 129 and 130:
APÉNDICE II:Fichas de aves
- Page 131 and 132:
APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesÍNDICE
- Page 133 and 134:
APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesAlauda
- Page 135 and 136:
APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- Lucio
- Page 137 and 138:
APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesIbéric
- Page 139 and 140:
APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- Limit
- Page 141 and 142: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesras, cu
- Page 143 and 144: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves• Man
- Page 145 and 146: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesAbundan
- Page 147 and 148: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves• Exc
- Page 149 and 150: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avescens, a
- Page 151 and 152: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesBibliog
- Page 153 and 154: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesOtis ta
- Page 155 and 156: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesPterocl
- Page 157 and 158: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves• Fom
- Page 159 and 160: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesdas de
- Page 161 and 162: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesAegypiu
- Page 163 and 164: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesBibliog
- Page 165 and 166: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avespor otr
- Page 167 and 168: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- La co
- Page 169 and 170: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesAliment
- Page 171 and 172: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesEmberiz
- Page 173 and 174: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesEcolog
- Page 175 and 176: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesFrench
- Page 177 and 178: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesteras,
- Page 179 and 180: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesLanius
- Page 181 and 182: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- Garc
- Page 183 and 184: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- Cramp
- Page 185 and 186: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- El ci
- Page 187 and 188: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesPyrrhoc
- Page 189 and 190: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de aves- Piers
- Page 191: APÉNDICE II: Fichas de avesEspecie
- Page 195 and 196: ANEXO IIICategorías de amenaza y d
- Page 197 and 198: ANEXO IIINombre científico Nombre
- Page 199 and 200: ANEXO IIIun taxón en esta categor
- Page 202: SEO/BirdLife, fundada en 1954, es l