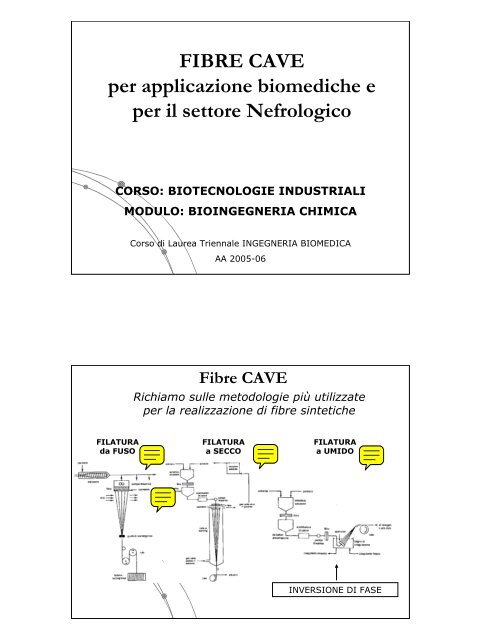
FIBRE CAVE per applicazione biomediche e per il settore Nefrologico
FIBRE CAVE per applicazione biomediche e per il settore Nefrologico
FIBRE CAVE per applicazione biomediche e per il settore Nefrologico
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
<strong>per</strong> <strong>applicazione</strong> <strong>biomediche</strong> e<br />
<strong>per</strong> <strong>il</strong> <strong>settore</strong> <strong>Nefrologico</strong><br />
CORSO: BIOTECNOLOGIE INDUSTRIALI<br />
FILATURA<br />
da FUSO<br />
MODULO: BIOINGEGNERIA CHIMICA<br />
Corso di Laurea Triennale INGEGNERIA BIOMEDICA<br />
AA 2005-06<br />
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Richiamo sulle metodologie più ut<strong>il</strong>izzate<br />
<strong>per</strong> la realizzazione di fibre sintetiche<br />
FILATURA<br />
a SECCO<br />
FILATURA<br />
a UMIDO<br />
INVERSIONE DI FASE
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Moderne tecnologie di f<strong>il</strong>atura hanno <strong>per</strong>messo di realizzare strutture<br />
<strong>per</strong> impiego in campo medico<br />
IMPIEGHI<br />
• processi di dialisi<br />
• rico<strong>per</strong>tura di stent coronarici<br />
• sistemi a r<strong>il</strong>ascio controllato di<br />
principi attivi<br />
• tissue engineering<br />
Ut<strong>il</strong>izzo di <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
BIODEGRADABILI <strong>per</strong> f<strong>il</strong>i da sutura<br />
riassorbib<strong>il</strong>i<br />
<strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Preparazione di fibre cave <strong>per</strong> Inversione<br />
Schema dell’apparato di preparazione di fibre<br />
cave <strong>per</strong> inversione in bagno di coagulo.<br />
(wet-spinning)
Fibra cava in POLISULFONE<br />
Alcuni esempi<br />
Alcuni esempi<br />
Fibra cava in POLIACRILONITRILE<br />
microporosa
Schema rappresentativo realizzazione fibre cave ad umido:<br />
laboratorio<br />
pump<br />
polymer solution<br />
nanoparticles<br />
suspension<br />
needles<br />
fiber<br />
fiber<br />
glass tank spinneret water<br />
rotating bobbin<br />
Scheme of hollow fibers production by wet spinning<br />
Realizzazione fibre cave ad umido: laboratorio
Schema rappresentativo realizzazione fibre cave ad umido<br />
<strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
LAVORI SVOLTI NEI NOSTRI<br />
LABORATORI<br />
Fibre <strong>per</strong> WET spinning<br />
PLA fiber DX/PLA fiber CH/PLA fiber<br />
(microporosa)<br />
Ut<strong>il</strong>izzazione di <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong> in ambito BIOMEDICO
Schema rappresentativo realizzazione fibre cave con<br />
procedimento intermedio tra secco e umido<br />
pump<br />
Polymer solution<br />
spinneret<br />
rotating<br />
bobbin<br />
non-solvent<br />
fiber<br />
needles<br />
Scheme of hollow fibers production<br />
by dry-wet spinning<br />
Fibre cave con procedimento intermedio tra secco e umido<br />
Interno di<br />
fibra cava in<br />
PLA con<br />
depositate<br />
nanosfere in<br />
PLGA <strong>per</strong> <strong>il</strong><br />
r<strong>il</strong>ascio<br />
controllato
Fibre cave: esempi di spinneret<br />
Spinneret <strong>per</strong> Melt-Spinning<br />
Spinneret <strong>per</strong> Dry o Wet-Spinning<br />
Fibre cave: esempi di spinneret
<strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Schema impianto f<strong>il</strong>atura <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong>.<br />
(wet-spinning)<br />
Melt spinning – hollow fibers
Melt spinning – hollow fibers<br />
EXTRUDER φ 12/20D VSF - MAC.GI s.r.l<br />
T1<br />
(°C)<br />
70<br />
T2<br />
(°C)<br />
80<br />
T3<br />
(°C)<br />
85<br />
Tem<strong>per</strong>ature parameters<br />
in the different section of<br />
the head for Poly-ε-<br />
Caprolactone/starch (TP)<br />
90/10<br />
Tj<br />
(°C)<br />
95<br />
Coaxial head for<br />
single-layer tube<br />
Th<br />
(°C)<br />
105<br />
Ts<br />
(°C)<br />
105
EXTRUDER φ 12/20D VSF - MAC.GI s.r.l<br />
SEM ANALYSIS<br />
Tubes of different dimensions<br />
Horizontal<br />
Vertical<br />
EXTRUDER φ 12/20D VSF - MAC.GI s.r.l
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
IMPIEGHI<br />
• processi di dialisi<br />
• rico<strong>per</strong>tura di stent coronarici<br />
• sistemi a r<strong>il</strong>ascio controllato di principi attivi<br />
Bioreattore a <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
• tissue engineering<br />
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong>
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong>: Applicazioni “emo<strong>per</strong>fusione”<br />
Ut<strong>il</strong>izzazione di <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong> in ambito BIOMEDICO<br />
Dializzatore a <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Dializzatore costituito da un fascio di fibre cave (circa<br />
10.000) con diametro intorno ai 200 µm<br />
VANTAGGIO: elevato rapporto su<strong>per</strong>ficie di scambio/volume<br />
Rico<strong>per</strong>tura<br />
di stent<br />
coronarici<br />
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Ut<strong>il</strong>izzazione di <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong> in ambito BIOMEDICO<br />
LAVORI SVOLTI NEI NOSTRI LABORATORI<br />
MATERIALI:<br />
PDLLA<br />
PLLA<br />
PCL
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
LAVORI SVOLTI NEI NOSTRI LABORATORI<br />
Prof<strong>il</strong>i di f<strong>il</strong>atura<br />
Ut<strong>il</strong>izzazione di <strong>FIBRE</strong> <strong>CAVE</strong> in ambito BIOMEDICO<br />
LAVORI SVOLTI NEI NOSTRI LABORATORI<br />
Sistemi a<br />
RILASCIO<br />
CONTROLLATO di<br />
principi attivi<br />
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Realizzazione di <strong>FIBRE</strong><br />
<strong>CAVE</strong> <strong>per</strong> <strong>il</strong> r<strong>il</strong>ascio<br />
controllato di farmaci e<br />
farmaci modello in 1 o 2<br />
steps (con nanoparticelle)
Metodologie innovative<br />
Fibre<br />
Electrospinning: sfrutta la forza elettrostatica generata da una sorgente di<br />
potenziale ad alto voltaggio. Si forma una “goccia” emisferica sulla<br />
su<strong>per</strong>ficie di una soluzione polimerica da cui nasce un getto carico<br />
elettricamente che viene eiettato da un cap<strong>il</strong>lare e da origine alla FIBRA.<br />
SCHEMA DEL<br />
PROCESSO<br />
Nuove tecnologie tess<strong>il</strong>i <strong>per</strong> <strong>il</strong> medicale:<br />
ELECTROSPINNING<br />
ELECTROSPINNING<br />
Metodo <strong>per</strong> la preparazione di fibre polimeriche in genere con diametri<br />
dell’ordine della nanoscala e di matrici fibrose “non-tessute” composte<br />
da queste<br />
“Nanoscale fibrous scaffolds can provide an optimal template for cells<br />
to seed, migrate and grow, mimicking the structure and biological<br />
functions of the natural extracellular matrix (ECM)” [1]<br />
[1] Zheng-Ming Huang, Y. -Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki and S. Ramakrishna<br />
“A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites”<br />
Composites Science and Technology, Vol 63, 15, Nov2003
MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS<br />
Electrospinning of gelatin<br />
IN PROGRESS…<br />
Da evitare<br />
MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS<br />
Electrospinning of PCL (10% in CH2Cl2 )<br />
IN PROGRESS…<br />
Da evitare
MORPHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS<br />
Electrospinning of PCL (15% in CH 2 Cl 2 )<br />
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Electrospinning<br />
Grande varietà di applicazioni:<br />
• membrane semi<strong>per</strong>meab<strong>il</strong>i, f<strong>il</strong>tri<br />
• fibre di rinforzo in materiali compositi<br />
• tissue engineering<br />
• microsuture interne<br />
• drug delivery (sup/vol)<br />
<strong>FIBRE</strong> POROSE<br />
Ing. Franca Bertoni……work in progress<br />
A differenza dei metodi classici, quali melt, dry o wet<br />
spinning (5-500 µm), l’electrospinning <strong>per</strong>mette di ottenere<br />
nanofibre con dimensioni dell’ordine dei 50-500 nm
Fibre <strong>CAVE</strong><br />
Electrospinning<br />
Materiali testati con questa tecnologia<br />
ALCUNI ESEMPI<br />
SETA Bombyx mori e Samia<br />
cynthia ricini<br />
copolimero PMMA-r-TAN<br />
PEO<br />
PCL, PLA, PGA<br />
(BIODEGRADABILI)<br />
MONOCRYL<br />
monof<strong>il</strong>amento <strong>per</strong> sutura<br />
in copolimero a blocchi<br />
PCL-PGA